The risk of infection increases with the depth and duration of neutropenia
Neutropenia
A condition characterized by abnormally low levels of white blood cells called neutrophils.
Full Answer
Are the guidelines for febrile neutropenia specific to leukemia?
Open in a separate window Guidelines used for febrile neutropenia are based on best available data, and a challenge is that studies for febrile neutropenia are usually not specific for leukemia. In Table 4we have indicated the main population in the studies supporting the current guidelines.
Should neutropenic patients with fever be managed inpatient or outpatient?
The management of neutropenic patients who present with fever can be divided into inpatient versus outpatient management. It is also important to identify patients presenting to the outpatient setting who will require inpatient referral [1] (Tables (Tables66and and77). Table 6 Talcott’s rules
How is fever defined in children with chemotherapy-induced neutropenia?
(See "Fever in children with chemotherapy-induced neutropenia" .) Fever in neutropenic patients is defined as a single oral temperature of ≥38.3°C (101°F) or a temperature of ≥38.0°C (100.4°F) sustained over a one-hour period [ 2 ].
Which antibiotics are used to treat fever in neutropenic patients with cancer?
Kern WV, Marchetti O, Drgona L, et al: Oral antibiotics for fever in low-risk neutropenic patients with cancer: A double-blind, randomized, multicenter trial comparing single daily moxifloxacin with twice daily ciprofloxacin plus amoxicillin/clavulanic acid combination therapy--EORTC infectious diseases group trial XV.

Are leukemia patients neutropenic?
Half of people with cancer who are receiving chemotherapy have some level of neutropenia. It is a common side effect in people with leukemia. People who have neutropenia have a higher risk of getting serious infections. This is because they do not have enough neutrophils to kill organisms that cause infection.
What is neutropenic fever in cancer patients?
A neutropenic fever is an emergency in a cancer patient. Patients with neutropenia are unable to fight infection. This is due to a low number of neutrophils. An infection can quickly turn into sepsis and become life threatening.
What causes fever in neutropenic patients?
What causes neutropenic fever? Neutropenic fever is caused by conditions that decrease neutrophil production or increase neutrophil destruction.
How is neutropenic fever treated?
Regimens include the following: Amoxicillin-clavulanate 500 mg/125 mg PO q8h plus ciprofloxacin 500 mg PO q12h. Moxifloxacin 400 mg PO daily. If penicillin allergic, substitute clindamycin 300 mg PO q6h for amoxicillin-clavulanate.
How is neutropenia treated in cancer patients?
If you are neutropenic, your doctor may temporarily halt your cancer treatment to give your body time to increase its white blood cell levels. How do doctors manage neutropenia? Your doctor may prescribe medicine, such as Neupogen, to maintain or boost your white blood cell levels.
How does leukemia cause neutropenia?
In acute leukemia, normal bone marrow function is to more or less extent, replaced by abnormal maturation and dysregulated proliferative immature cells, resulting in neutropenia and impaired granulocyte function.
Is neutropenic fever an emergency?
Neutropenic fever is an oncologic emergency, with over 100,000 cases per year. It is defined by a single oral temperature > 38.3o C or temperature > 38.0o C for 1 hour with neutropenia.
How do you reduce a fever from chemo?
Over-the-Counter (OTC) and Home Remedies Once your medical team has determined that your fever is being caused by chemotherapy and not an underlying infection, they may recommend over-the-counter medication, such as Tylenol (acetaminophen), to treat the fever and relieve any other symptoms.
What is a neutropenic complication?
The main complication of neutropenia is an increased risk of infection. Neutrophils are made in the bone marrow. They are short-lived cells that travel extensively throughout the body and can enter tissues other cells cannot. Most commonly, cancer patients develop neutropenia due to chemotherapy.
What are neutropenic precautions?
Neutropenic precautions are common-sense protocols that help avoid infections at home and in clinical settings, like hospitals. Neutropenia is earmarked by low levels of white blood cells called neutrophils . Neutrophils are abundant in people with healthy immune systems.
How quickly should treatment be initiated for suspected neutropenic sepsis?
Failure to treat promptly can be fatal. Intravenous antibiotics must be given within one hour of arrival to hospital or within one hour of the signs and symptoms developing if the patient is already an inpatient.
When is vancomycin used in neutropenic fever?
(†) Indications to add vancomycin include hemodynamic instability, skin or catheter site infection, concern for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia, and blood cultures with gram-positive bacteria before final identification and susceptibilities.
What is the temperature of a neutropenic patient?
Fever — Fever in neutropenic patients is defined as a single oral temperature of ≥38.3°C (101°F) or a temperature of ≥38.0°C (100.4°F) sustained over a one-hour period [ 2 ]. The definition of fever and appropriate methods for measuring body temperature are discussed in greater detail separately. (See "Overview of neutropenic fever syndromes", section on 'Fever' and "Overview of neutropenic fever syndromes", section on 'Temperature measurement' .)
Can cytotoxic antineoplastic therapy cause invasive infection?
Cancer patients receiving cytotoxic antineoplastic therapy sufficient to adversely affect myelopoiesis and the developmental integrity of the gastrointestinal mucosa are at risk for invasive infection due to colonizing bacteria or fungi that translocate across intestinal mucosal surfaces.
Is UpToDate a substitute for medical advice?
The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your own physician or other qualified health care professional regarding any medical questions or conditions. The use of UpToDate content is governed by the UpToDate Terms of Use. ©2021 UpToDate, Inc. All rights reserved.
Can elevated body temperature be a sign of infection?
Since the magnitude of the neutrophil-mediated component of the inflammatory response may be muted in neutropenic patients [ 1 ], an elevated body temperature may be the earliest and only sign of infection.
Is there an ESKAPE for febrile neutropenic cancer?
Bow EJ. There should be no ESKAPE for febrile neutropenic cancer patients: the dearth of effective antibacterial drugs threatens anticancer efficacy. J Antimicrob Chemother 2013; 68:492.
How to manage neutropenic fever?
Management for neutropenic fever first starts with a discussion of appropriate prophylaxis which has been risk stratified on the basis of the anticipated duration of neutropenia [1]. The optimal time to choose a patient’s regimen for a future neutropenic fever is during the initial consult by an infectious diseases consultant after discussing all of the risk stratifying past medical issues for a particular patient including but not limited to previous infections especially while neutropenic. In addition, prophylaxis against Pseudomonasand other Enterobacteriaceae are of outmost importance in this population. Unfortunately, Pseudomonascontinues to be a significant cause for neutropenic fever. Other enteric gram-negative rods (GNRs) are important sources of bacteremia after chemotherapy induced mucosal damage resulting in mucositis/enteritis and bacterial translocation [2].
What is neutropenia in chemo?
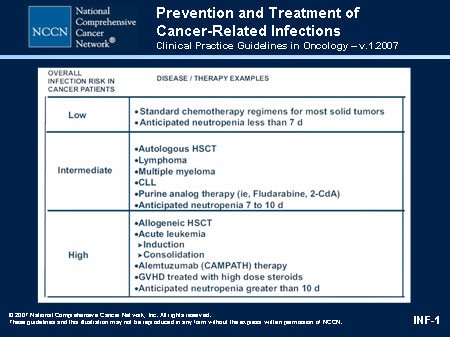
Neutropenia is defined as an abnormally low absolute neutrophil count (ANC) and can be further delineated as severe or profound (see below). Recipients of chemotherapy will often have a decreased ANC leading to an increased risk of infections specifically from bacterial sources. Neutropenia traditionally is risk stratified based on duration and depth of neutropenia. Recipients of chemotherapy for acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) and stem cell transplants (SCTs) often are deemed as having high risk neutropenia due to significant depth and duration of neutropenia. The mortality associated with febrile neutropenia is up to 11%, and can be as high as 50% in the setting of severe sepsis or septic shock. By risk stratifying neutropenia and the resultant neutropenic fever, the goal is to decrease the resultant morbidity and mortality (Taplitz et al., J Clin Oncol 36:3043–3054).
What foods should neutropenic patients avoid?
It is recommended to avoid undercooked meats, unpasteurized milk, unpasteurized cheese or unpeeled fruits and vegetables unless washed properly at home [1, 2]. Also, neutropenic patients in an outpatient setting should avoid contact with environments that have high concentrations of airborne fungal spores such as construction/renovation sites, intense gardening and digging [1, 2]. In the same line of thinking of minimizing exposure to plant matter, it is not recommended for neutropenic or impending neutropenic patients to utilize tobacco products or marijuana products due to the theoretical risk of fungal pneumonia.
What is the temperature of a neutropenic patient?
Fever in neutropenic patients is defined as a single oral temperature of ≥38.3 °C (101 °F) or a temperature of ≥38.0 °C (100.4 °F) sustained over a 1 h period.
Can neutropenic patients be inpatient or outpatient?
The management of neutropenic patients who present with fever can be divided into inpatient versus outpatient management. It is also important to identify patients presenting to the outpatient setting who will require inpatient referral [1] (Tables (Tables66and and77).
Does G-CSF decrease neutropenia?
The role of granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) in prophylaxis is at times controversial. G-CSF has shown to decrease length and degree of neutropenia and reduce the risk of febrile neutropenia in solid tumors however it has not shown to decrease the risk of febrile neutropenia or reduce mortality in hematological malignancies. The recommendation overall is to give G-CSF in patients who are on chemotherapy regimens known to have a 20% increase risk of febrile neutropenia or in presence of comorbidities but lower risk [7].
What is clinical judgment in neutropenia?
Clinical judgment is recommended when determining which patients are candidates for outpatient management, using clinical criteria or a valida ted tool such as the Multinational Association of Support Care in Cancer risk index. In addition, psychosocial and logistic considerations are outlined within the guideline. The panel continued to endorse consensus recommendations from the previous version of this guideline that patients with febrile neutropenia receive initial doses of empirical antibacterial therapy within 1 hour of triage and be monitored for ≥ 4 hours before discharge. An oral fluoroquinolone plus amoxicillin/clavulanate (or clindamycin, if penicillin allergic) is recommended as empirical outpatient therapy, unless fluoroquinolone prophylaxis was used before fever developed. Patients who do not defervesce after 2 to 3 days of an initial, empirical, broad-spectrum antibiotic regimen should be re-evaluated and considered as candidates for inpatient treatment.
What is the ANC in chemo?
Neutropenia, a decrease in the absolute neutrophil count (ANC), occurs frequently in recipients of chemotherapy. 1 Neutrophils are critical in providing host defense against infection, particularly bacterial and fungal infections.
How long after FN do you defervesce?
Should low-risk outpatients with FN who do not defervesce after 2 to 3 days of an initial empirical broad-spectrum antibiotic regimen (ie, patients who are experiencing persistent neutropenic fever) be considered for hospitalization or continue to be treated on an outpatient basis?
Can FN be treated with carbapenem?
Patients with FN who are infected by fluoro quinolone-resistant, gram- negative path ogens that are also coresistant to β-lactams/cephalosporins should be treated as inpatients with a carbapenem-based regimen that likely requires multiple doses per day.
Is neutropenia a result of infection?
In the absence of an alternative explanation, clinicians should assume that fe ver in a patient with neutropenia from cancer therapy is the result of an infection. The initial diagnostic approach should maximize the chances of establishing clinical and microbiologic diagnoses that may affect antibacterial choice and prognosis. A systematic evaluation should include the following:
What is the ANC of neutrophils?
Neutropenia is typically defined as an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) count of less than 1500; real neutropenia is less than 1000; and severe neutropenia is less than 500. Patients with a count of lower than 100 are considered to be at the highest risk of infection. There are several contributing causes to the high rate ...
Is AML a disease?
Patients with acute myeloid leukemia are extremely susceptible to infection, especially due to the prevalence of neutropenia. Patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) are extremely susceptible to infection, especially due to the prevalence of neutropenia.
What is the temperature of a neutropenic patient?
Fever in a neutropenic patient is defined as a sustained temperature > 38°C (100.4°F) for an hour or a single temperature >38.3°C (101°F).
What pathogens have been isolated from neutropenic patients with cancer?
Note that other rare pathogens such as Mycobacteria, Toxoplasma, Malaria, Nocardia, Babesia, Strongyloides, have been isolated from neutropenic patients with cancer.
How long does it take for neutropenia to go away after antibiotics?
Start antifungal therapy after 4-7 days of empiric antibiotic therapy on high-risk patients who have persistent or recurrent fever, are expected to have a total duration of neutropenia > 7 days, and there is no source of infection.
What are the signs of a neutropenic IV line?
Neutropenic patients with IV catheters and recent line sites should be examined for subtle infection signs such as: slight tenderness, erythema, exudate, fluctuance. These signs may represent a “tunnel” infection. Think about infected clot when there is difficulty drawing blood or infusion via a catheter in these patients. Rigors or chills associated with infusion through the IV catheter may represent IV line related infection.
What is the absolute neutrophil count?
Neutropenia is defined as absolute neutrophil count (ANC) < 500 cells/microL, or ANC <1000 cells/microL with a predicted decrease to <500 cell/microL. The term “profound” neutropenia is referred to an ANC ≤ 100 cells/microL. Fever in a neutropenic patient is defined as a sustained temperature > 38°C ...
How long does neutropenia last?
Profound neutropenia (ANC ≤ 100 cells/microL) that is anticipated to last for more than 7 days
Can a neutropenic patient have fever?
Be aware that occasionally a neutropenic patient may not present with fever. In these patients (most commonly elderly and patients receiving steroids) other symptoms such as hypotension, hypothermia, new unexplained organ dysfunction, or clinical deterioration/mental status changes are the primary signs of infection.
Which cell is the primary source of acute myelogenous leukemia?
Acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) evolves from the myeloid stem cell, which impacts the neutrophils, erythrocytes, monocytes, and platelets. Lymphoblastic leukemia, both acute and chronic, evolves from the lymphoid stem cell (lymphocytes).
What is CBC in leukemia?
The healthcare provider orders a complete blood count (CBC) with differential. After reviewing the client's symptoms, the nurse would expect to find which result on the client's CBC report?
Where does leukemia come from?
Test taking tips: leukemia comes from the work leukocyte.
What does Brian's physical exam and laboratory results indicate?
The healthcare provider explains to Brian that his physical exam and laboratory results indicate a potential diagnosis of leukemia. What diagnostic test or procedure would be performed to make a definitive diagnosis and determine the extent of the disease process?
What are the symptoms of neutropenic fever?
Characteristics and symptoms of neutropenic fever: When a person is neutropenic (has low white blood cells or neutrophils) the usual signs of infection (redness, swelling and pus formation) are absent. Pain and tenderness may be the only other indicators of infection.
What is a fever in chemo?
Fever and Chemotherapy. Fever is an abnormally high body temperature. Usually defined by 3 oral temperatures greater than 38°C or 100.4°F in a 24-hour period, or one temperature greater than 38.5°C or 101.3°F. Fever is the body's response to infection. However, only in about half of all patients with cancer, who develop a fever, ...
What is the best medicine for fever?
Over-the-counter medications such as acetaminophen (Tylenol ®) are used to treat fever related to flu-like syndrome. This may be prescribed to be taken around the clock, or prior to when expected fever may occur.
What temperature does a fever spike after a chill?
The fevers associated with FLS usually peak at 40°C or 104°F and often spike after a severe chill. This can mimic the clinical picture of sepsis (an infection in the blood), so it is important that patients who are receiving biologic therapy to be aware of the usual course of fever after treatment.
What are the symptoms of infection in biologics?
Pain and tenderness may be the only other indicators of infection. If a patient is taking biologic therapy where fever is a likely side effect of the treatment knowing the timing of the fever and its association with the treatment will help to evaluate if infection may also be present.
How to decrease white blood cell count after chemotherapy?
If you are receiving chemotherapy that is likely to decrease your white blood cell count, check your temperature twice a day if you feel warm. Fever related to flu-like syndrome: Take a lukewarm (tepid) bath if you have a fever. Also, you can use cold or ice packs on your body for comfort.
Is fever related to chemo?
During this time the body's normal defenses against infections are down, and fever needs to be further evaluated immediately. Chemotherapy and fever are sometimes related because fever can also be present in patients who are receiving chemo treatments and biologic therapy as part of the " flu-like syndrome (FLS).".
