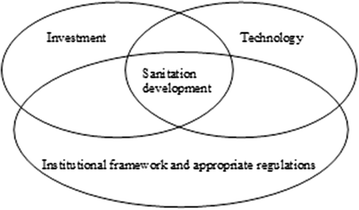
The key players operating in the tertiary water and wastewater treatment technologies market are Suez Environment S.A. (France), Veolia Environment SA (France), Xylem, Inc. (U.S.), DuPont de Nemours, Inc. (U.S.), Evoqua Water Technologies Corporation (U.S.), 3M Company, Inc. (U.S.), Pentair plc (U.K.), Calgon Carbon Corporation (U.S.), Kurita Water Industries, Ltd. (Japan), Bio-Microbics, Inc. (U.S.), ASIO, spol. s r.o. (Czech Republic), Scinor Water America, LLC (U.S.), Elgressy Engineering Services Ltd. (Israel), Outotec Oyj (Finland), Blue Eden CleanTech Solutions, Inc. (Canada), Membracon Ltd. (U.K.), Lamor Corporation Ab (Finland), and Ozone Tech Systems (Sweden).
What is tertiary water treatment?
Tertiary water treatment is the final stage of the multi-stage wastewater cleaning process. This third stage of treatment removes inorganic compounds, bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Removing these harmful substances makes the treated water safe to reuse, recycle, or release into the environment.
What are the most employed filtering materials in wastewater tertiary treatment?
Sand, activated carbon, and zeolite are the most employed filtering materials in wastewater tertiary treatment. Sand filtration is a conventional wastewater treatment process characterized by its simplicity, low energy inputs, and easy maintenance.
What are the different types of water treatment?
The treatment processes are mainly physicochemical in nature and include disinfection, oxidation, chemical dosing for water quality correction, chemically aided settling, filtration, softening, activated carbon treatment, ion exchange, and reverse osmosis.
What are the different types of tertiary treatment?
Tertiary treatment may take several different forms depending on the quality of the final effluent required. Near bathing waters (European Bathing Waters Directive 76/160/EEC), UV irradiation is the most common method and has become a more favoured option in reducing the number of viable bacteria.
Which country has the most wastewater treatment plants?
Total Waste Water Treatment#35 Countries1#1 ChileView data2#2 NetherlandsView data3#3 LuxembourgView data4#4 GermanyView data31 more rows
Which country has the best wastewater treatment system?
Wastewater Treatment ResultsCountryCurrent RankBaseline RankMalta11Netherlands33Luxembourg55Spain6693 more rows
What is tertiary water treatment used for?
The purpose of tertiary treatment is to provide a final polishing treatment stage prior to discharge or reuse of the wastewater. Chlorination – A water treatment method that destroys harmful bacteria, parasites, and other organisms. Chlorination also removes soluble iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide from the water.
Where is tertiary treatment required?
Tertiary treatment of wastewater is practiced for additional protection of wildlife after discharge into rivers or lakes. Even more commonly, it is performed when the wastewater is to be reused for irrigation (e.g., food crops, golf courses), for recreational purposes (e.g., lakes, estuaries), or for drinking water.
How does Germany treat their water?
Germany is the European country with the highest waste water reprocessing and recycling rate. More than 96 per cent of the waste water from private households or public facilities is discharged into nearby sewage treatment plants for processing.
Which country uses the new water for recycled water?
Australia, Israel, Namibia, Singapore, and South Africa incorporate water reuse into their water management programs to support water availability, security, and sustainability. These countries reuse wastewater that is treated to various levels for domestic, agricultural irrigation, and industrial water use.
What is an advantage of using tertiary treatment?
Tertiary treatment improves the quality of wastewater before it is reused, recycled or discharged to the environment. Industrial wastewater can contain high numbers of inorganic compounds. These are harmful to rivers and lakes as they are of mineral origin rather than biological.
Why is tertiary treatment important?
The main purpose of the tertiary treatment is to ensure that the treated water which is to be released on to the environment is biologically accepted by all other fresh water organisms such as weeds and algae.
What is the main role of tertiary treatment of wastewater?
Tertiary treatment is the next wastewater treatment process after secondary treatment. This step removes stubborn contaminants that secondary treatment was not able to clean up. Wastewater effluent becomes even cleaner in this treatment process through the use of stronger and more advanced treatment systems.
What is a tertiary treatment system?
Tertiary treatment is the third, and final, stage in a standard wastewater management system. Once effluent has been treated in the primary and secondary stages by removing suspended solids, pH balancing and reducing its biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), it is ready to enter the tertiary stage.
Which of the following is major objective of tertiary treatment?
The tertiary treatment process is used to improve the quality of the effluent which has resulted from primary and secondary treatment processes. After the tertiary treatment, the water can be safely discharged into the environment (water bodies like rivers and lakes, etc.)
What is tertiary treatment?
Tertiary Treatment. Tertiary treatment refers to secondary treatment followed by a filtration step, such as media filtration, so that the turbidity and TOC concentrations are generally lower , and if coagulation with metal salts is used, then the phosphate concentration will also be reduced (Henriksen, 1963).
What is agricultural wastewater treatment?
Agricultural wastewater treatment for continuous confined animal operations (e.g. milk and egg production) may be performed in plants using mechanized treatment units. If sufficient land is available for ponds, settling basins, and facultative lagoons, then the operational cost is lower.
How to remove nitrates from water?
Nitrates can be removed from wastewater by natural processes in wetlands but also via microbial denitrification. Ozone wastewater treatment with an ozone generator is also becoming popular; the ozone generator decontaminates the water as ozone bubbles percolate through the tank, but this treatment is energy intensive.
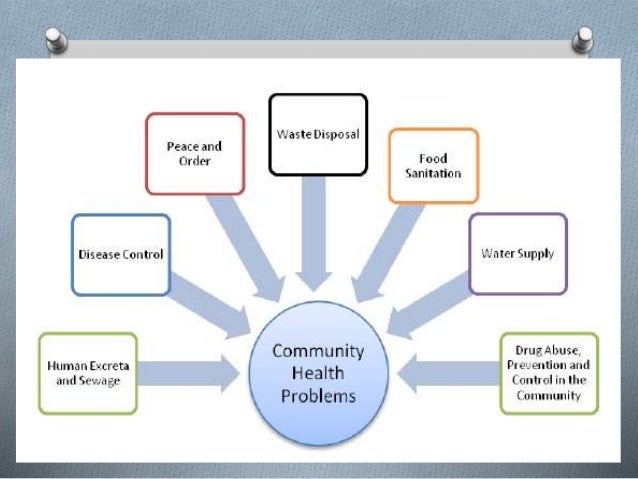
What are the risks of sewage treatment plants?
Common types of accidents include injuries from falls, deaths from drowning, and asphyxiation. Narrow walks or steps over tanks (particularly in darkness, rains, and wind), ladders, and spiral staircases are potential danger spots where the operator should be alert; overexertion during operation of valves, moving weights, and performing other arduous tasks should be avoided. All open tanks should be provided with guard rails to prevent accidental falls. Glass parts as well as moving parts should be protected by screen or guards. Adequate lighting within the plant and around the plant should be provided, which gives a better working facility, reducing accidents due to slipping, etc. Honeycomb grating be provided on open channels to avoid accidents due to falling or drowning. The staff should be trained and compelled to use helmets, gumboots, hand gloves, etc. Wherever necessary, precautionary boards/danger boards/sign boards should be displayed in the plant wherever necessary, drawing attention to the potential danger spots.
What is tertiary treatment?
Tertiary treatment includes the removal of the remaining inorganic compounds (phosphate, sulfate, ammonium) and other refractory organic compounds by one or more physical separation methods, such as carbon adsorption, deep-bed filtr ation, and in some cases, membrane-based techniques, such as reverse osmosis or electrodialysis.
When is tertiary treatment necessary?
Usually tertiary treatment of wastewater is only regarded as necessary when the nutrient concentrations in the effluent have to be reduced i.e., if the mill discharges to very sensitive recipients. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter.
What are the two types of chemical treatments?
There are two different types of chemical treatments, flocculation and precipitation , as they involve different types of purification mechanisms. Flo cculation, is based on an addition of ferric ions, aluminum ions, or/and long-chained polymers to the effluents.
What chemicals are used in lignin treatment?
The chemicals that are used are usually aluminum (Al) salts, ferric (Fe 3+) salts, and lime (CaO). The chemical treatment gives a further reduction of some recalcitrant compounds such as high-molecular degradation products from lignin.
Is tertiary treatment more proprietary than secondary treatment?
Tertiary treatment processes are more commonly proprietary than secondary treatment processes, usually being newer (or at least new variants on old processes). Secondary treatment was developed in large part to deal with the 1912 Reports of the UK Royal Commission.
Is toxicity a target in membrane filtration?
In membrane filtration and adsorption processes the toxicity is not targeted as such, but just removed from the water. The AOPs need to target the moieties that are essential to the toxic activity in order to be able to influence the specific toxic effect of a given compound [117].
Israel leads world in water recycling
Israel owns all the water in the country from limited freshwater, to underground water, and seawater. This means that if you chose to dig a well in Israel, you would need the approval of the authorities.
18,000 WWTPs and millions of kilometers of pipes
While Israel reuses almost all of its wastewater, Europe recycles merely 60%. The future goal is, naturally, to recycle the entire volume.
Three countries with the top water quality
Countries at the top of the European Environmental Agency’s list also ranked first on global scale.
Worst situation is in the regions
Now you know which country recycles the most and what is the wastewater treatment situation in Slovakia. In conclusion, see the latest findings on which countries treat the least wastewater based on the data by Utrecht University. The university suggests that the low treatment level is related to low income in the regions.
What is the primary treatment of wastewater?
Primary treatment of wastewater involves filtering out large solid contaminants. Secondary treatment then purifies the wastewater through biofiltration, aeration, and oxidation. These are all processes that help to remove sediment from the water.
What is tertiary treatment?
Tertiary Treatment of Wastewater – Methods and Process. Tertiary water treatment is the final stage of the multi-stage wastewater cleaning process. This third stage of treatment removes inorganic compounds, bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
What is the final stage of tertiary wastewater treatment?
The final stage of the tertiary wastewater treatment process involves removing the chlorine that was used to disinfect the water. This step is very important because chlorine is harmful to aquatic life. Chlorine also reduces biological water quality when it is present in high concentrations. To remove the chlorine, a compound called sodium ...
What is the purpose of chlorination in wastewater treatment?
Chlorination in wastewater treatment kills bacteria and viruses, and eliminates parasites such as Giardia and Cryptosporidium, which can cause very serious illnesses. In summary, this process disinfects water so that it is safe to reuse or recycle.
What is the third stage of sewage treatment?
This third stage of treatment removes inorganic compounds, bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Removing these harmful substances makes the treated water safe to reuse, recycle, or release into the environment. To find out how tertiary sewage treatment works, take a look at this overview of the methods and processes involved in ...
What is the process of adding chlorine to wastewater?
Disinfection. An important part of wastewater treatment involves the addition of chlorine to the final effluent before discharge. This process injects chlorine into the headworks of a serpentine effluent detention chamber.
What is secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment removes 85 to 90% of BOD, TSS, and the small portion of nitrogen, phosphorus, and heavy metals from wastewater. Tertiary treatment of wastewater is the third stage of the wastewater treatment and is also known as an advanced treatment.
What is membrane technology?
Membrane technology is used to treat a variety of wastes including sewage, organic and inorganic matter and water-soluble oil wastes. The membrane processes are classified on the basis of driving force and separation mechanism such as Multi Filtration (MF), Ultrafiltration (UF), Nano filtration (NF), Reverse Osmosis (RO), and Forward Osmosis (FO)
How does tertiary wastewater treatment work?
What Is Tertiary Wastewater Treatment, and How Does It Work? In the wastewater industry, plants often focus on primary and secondary treatments, which do most of the work of preparing wastewater for discharge into the environment. Tertiary treatment is also critical in many situations. It affords the peace of mind of knowing ...
What happens to wastewater after tertiary treatment?
Once the wastewater has undergone tertiary treatment, it is ready for discharge back into the environment. Many municipalities have specific requirements about the discharge of treated water, and tertiary treatment should be sufficient to meet those standards, keep the environment clean, and preserve human health.
What are tertiary filtration components?
Tertiary filtration components can contain a few different materials. Sand and activated carbon filters are common, and filters can also contain fine woven cloth. The filters also come in a few different types, including bag filters, drum filters and disc filters: Bag filters: Bag filters are ideal for wastewater treatment plants ...
Why is chlorine used in wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment plants can dump chlorine into the wastewater to kill harmful microorganisms like bacteria and viruses.
What is wastewater treatment?
Most wastewater treatment systems consist of at least two main treatment processes: primary and secondary treatment, with some additional preliminary methods. Primary treatment, which typically removes 50% to 70% of the suspended solids in wastewater, uses physical processes like filtration and settling to remove grit, debris, oil, ...
What is secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment applies additional biological processes like aeration and activated sludge treatment to break down dissolved and suspended biosolids using good bacteria. Tertiary treatment adds a third, more advanced and rigorous level of treatment.
Why do plants use tertiary treatment?
Many treatment plants use tertiary treatment specifically to make the water safe for human ingestion. After tertiary treatment, the water has undergone sufficient purification to be as clean and healthy as drinking water.
What are the most common treatment options for water?
Some of the most common treatment options are solar water disinfection, chlorination, ceramic and biosand water filters, and membrane filters . The first type of treatment is Solar Water Disinfection (SODIS).
How much does it cost to build a water treatment facility?
Many countries are not able to afford the cost of constructing and maintaining water treatment facilities that can cost anywhere from $45,000 for small scale or low flow treatment to millions of dollars for large scale start-up alone (Marshall).
How many people in the world don't have clean water?
It’s easy to take for granted the clean water we get everyday, but access to clean and safe drinking water is a major issue many people face today. According to the World Health Organization, 1 in 3 people globally do not have access to safe drinking water. Because of the Environmental Protection Agency’s passage of the Clean Water Act in 1972 and the Safe Drinking Water Act in 1974, any water supplied to the public in the United States must meet minimum standards to ensure safe water and public health. Water that is discharged in the environment must also meet standards set by the EPA. However, many countries don’t have these regulations in place to ensure clean water to the entire population. Contaminants unable to be seen by the human eye can cause disease and sickness among a population. In fact, contaminated drinking water causes about 485,000 deaths a year (WHO, 2019). These deaths and even more cases of illness, such as Cholera, Giardia, and Dysentery, are caused by unclean drinking water due to the lack of sufficient water treatment technology.
What is the first step in water treatment?
Coagulation and Flocculation: This is generally the first step in water treatment. In this process, chemicals are added to the water which promotes the clumping of particles in the water. Contaminants in the water stick together to form larger clumps that can be more easily removed.
How many people die from drinking contaminated water?
In fact, contaminated drinking water causes about 485,000 deaths a year (WHO, 2019). These deaths and even more cases of illness, such as Cholera, Giardia, and Dysentery, are caused by unclean drinking water due to the lack of sufficient water treatment technology.
What are the nutrients in water?
Nutrients like nitrates or phosphates are also widely found in water and can affect the way blood carries oxygen. This is especially dangerous to babies who could develop “blue baby syndrome,” and causes oxygen not to be properly distributed throughout the body (CDC).
How many people do not have access to safe drinking water?
According to the World Health Organization, 1 in 3 people globally do not have access to safe drinking water. Because of the Environmental Protection Agency’s passage of the Clean Water Act in 1972 and the Safe Drinking Water Act in 1974, any water supplied to the public in the United States must meet minimum standards to ensure safe water ...