Symptomatic management of patients with cough and laryngospasm due to a suspected sensory neuropathy may include the use of antiseizure medications such as gabapentin. MeSH terms Adolescent
- Try not to panic or gasp for air. Remaining calm can help you relax more through the laryngospasm.
- Take small sips of water. This will help wash away any irritants that may have come in contact with your vocal cords.
- Apply pressure behind your earlobes.
How do you treat laryngospasm in the throat?
Laryngospasm can sometimes occur after an endotracheal tube is removed from the throat. These are usually rare events and recurrence is uncommon, but if it happens, try to relax. Taking an antacid or acid inhibitor for a few weeks may help diagnose the problem by the process of elimination.
Can laryngospasm be reversed?
Left untreated, laryngospasm caused by anesthesia can be fatal. To reverse laryngospasm after surgery with anesthesia, your medical team can perform treatments to relax your vocal cords and ease your symptoms. Laryngospasms that are caused by other conditions — like asthma, stress or hypersensitivity— aren’t usually dangerous or life-threatening.
How is laryngospasm treated in children with Gerd?
Experts say that in infants with GERD, laryngospasm might be involved in sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). How Is Laryngospasm Treated? If GERD is the problem, treating the condition can help manage laryngospasm. Doctors often prescribe proton pump inhibitors such as Dexlansoprazole (Dexilant), Esomeprazole(Nexium), and Lansoprazole(Prevacid).
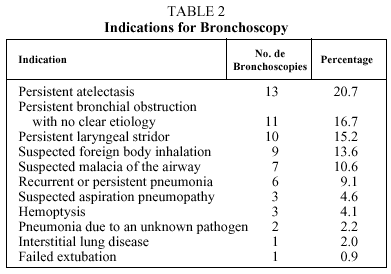
Is there any literature on the technique of laryngospasm notch?
However, a thorough literature search has not revealed any mention of it. The technique involves placing the middle finger of each hand in what I term the laryngospasm notch.
What medicine stops laryngospasm?
Pharmacologic interventions such as the use of lidocaine, midazolam, or propofol have emerged as potentially use- ful treatments for breaking or preventing laryngospasm.
How do you break a laryngospasm?
You want to push at a point as superior as you can go in this notch. Push both sides firmly inward towards the skull base. Simultaneously, push anteriorly similar to a jaw-thrust maneuver. This should break the laryngospasm within 1-2 breaths.
Is laryngospasm an emergency?
Laryngospasm is one of the more frightening events in anesthesia: the protective, reflex, spasmodic closure of the vocal cords that occurs when the vocal cords are stimulated.
Does laryngospasm go away?
The vocal cords are two fibrous bands inside the voice box (larynx) at the top of the windpipe (trachea). The onset of a vocal cord spasm is sudden, and just as suddenly, it goes away, usually after a few minutes. The breathing difficulty can be alarming, but it's not life-threatening.
How do you treat laryngospasm at home?
A few simple techniques may stop the spasm:Hold the breath for 5 seconds, then breathe slowly through the nose. Exhale through pursed lips. ... Cut a straw in half. During an attack, seal the lips around the straw and breathe in only through the straw and not the nose. ... Push on a pressure point near the ears.
How long can laryngospasm last?
Laryngospasms are rare and usually last for less than a minute. During that time, you should be able to speak or breathe. They're not usually an indicator of a serious problem and, generally speaking, they aren't fatal. You may experience a laryngospasm once and never have one again.
What causes a coughing spasm?
What causes coughing spasms? A cough has many causes, the most common of which is an upper airway infection, such as a common cold. Coughing spasms can be due to whooping cough (pertussis) or a chronic lung condition, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or asthma.
Why does my throat close when I cough?
The cause of the tightness can vary from an infection like strep throat to a more serious allergic reaction. If you have other warning signs, like trouble swallowing or breathing, throat tightness is an emergency that needs to be treated immediately. Tightness in your throat can take many forms.
How do you open your throat to breathe?
Breathe in gently through the nose. Stick your tongue out of your mouth, past the teeth & lower lip, in preparation to exhale. This forward stretch of the tongue helps to open the airway at the vocal cords.
How to relieve laryngospasm pain?
Forcefully push down and in toward the throat. The pressure should be forceful enough to be painful, and if it works, it should relieve the symptoms of laryngospasm immediately. Other treatments focus on addressing the underlying cause of laryngospasms.
How long does it take for a laryngospasm to stop?
Although extremely rare, if a laryngospasm does not stop after a minute or two, or if it causes a loss of consciousness, it should be treated as a medical emergency.
What is a laryngospasm?
People experiencing a laryngospasm have sudden difficulty breathing and talking. A laryngospasm is a muscle spasm in the vocal cords, sometimes called a laryngeal spasm. While a mild laryngospasm where you can still exhale air can be frightening, it is usually not dangerous, ...
Why do doctors think laryngospasms are reflexes?
Doctors think that a laryngospasm may be a reflex designed to prevent accidental drowning or suffocation.
What is it called when the vocal cords are pushed together?
Normally, the vocal cords separate when a person breathes, which is called abduction . A laryngospasm causes the vocal cords to be forcibly pushed together, called adduction. When the vocal cords spasm, they can fully or partially close the airway.
How to relieve vocal cord pain?
Push on a pressure point near the ears. This point, known as the laryngospasm notch, can force the vocal cords to relax. Locate the soft spot behind the earlobes and just above the jaw. Forcefully push down and in toward the throat. The pressure should be forceful enough to be painful, and if it works, it should relieve the symptoms of laryngospasm immediately.
How common is laryngospasm in children?
In children who have asthma or a respiratory infection, the incidence increases to about 10 percent.
What to do if you witness a laryngospasm?
If you witness someone having what appears to be a laryngospasm, make sure that they’re not choking. Urge them to stay calm, and see if they can nod their head in response to questions.
How long does a laryngospasm last?
Laryngospasms are rare and usually last for less than a minute. During that time, you should be able to speak or breathe. They’re not usually an indicator of a serious problem and, generally speaking, they aren’t fatal. You may experience a laryngospasm once and never have one again.
What is a sudden spasm of the vocal cord?
Laryngospasm refers to a sudden spasm of the vocal cords. Laryngospasms are often a symptom of an underlying condition. Sometimes they can happen as a result of anxiety or stress. They can also occur as a symptom of asthma, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), or vocal cord dysfunction.
How long does a sleep-related laryngospasm last?
Just like laryngospasms that happen while awake, a sleep-related laryngospasm will only last several seconds.
What is GERD in the esophagus?
GERD is characterized by stomach acid or undigested food coming back up your esophagus. If this acid or food matter touches the larynx, where your vocal cords are, it may trigger the cords to spasm and constrict.
What happens when your vocal cords stop working?
During a laryngospasm, your vocal cords stop in a closed position. You’re unable to control the contraction that’s happening at the opening to the trachea, or windpipe. You may feel like your windpipe is constricted slightly (a minor laryngospasm) or like you can’t breathe at all.
How to stop vocal spasms?
If you’re experiencing a tense feeling in your vocal cords and a blocked airway, try not to panic. Don’t gasp or gulp for air. Drink small sips of water to try to wash away anything that might have irritated your vocal cords.
How to treat laryngospasm in children?
In children who develop laryngospasm as a complication of anesthesia during surgery, treatment usually involves moving the head and neck to open the airway.
How long does it take for laryngospasm to go away?
Though it can be scary while it's happening, laryngospasm typically goes away within a couple of minutes.
What is the best treatment for a corrosive stomach?
Doctors often prescribe proton pump inhibitors such as Dexlansoprazole ( Dexilant ), Esomeprazole ( Nexium ), and Lansoprazole ( Prevacid ). These reduce the production of stomach acids, so that fluids from the stomach that do back up into the esophagus are less corrosive. Another option is prokinetic agents.
What causes laryngospasm?
Laryngospasm may be associated with different triggers, such as asthma, allergies, exercise, irritants (smoke, dust, fumes), stress, anxiety or commonly gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD. GERD is a condition that occurs when the ring-like muscle that normally closes to keep the stomach 's contents from backing up doesn't work right. With reflux, harsh acids from the stomach rise up into the esophagus and cause irritation.
What does it mean when you are unable to breathe?
When laryngospasm occurs, people describe the sensation of choking and are unable to breathe or speak. Sometimes, the episodes occur in the middle of the night. A person may suddenly awaken feeling as though they are suffocating. This condition is called sleep -related laryngospasm. It also is often related to GERD. Some people will actually lose consciousness during these episodes.
What is the procedure to stop stomach acid from backing up?
Patients who don't respond to these treatments may need surgery. One surgical option is fundoplication , a procedure that wraps the upper part of the stomach (fundus) around the esophagus to prevent acids from backing up.
How to stop GERD and LPR?
Eat smaller meals, and stop eating two to three hours before bedtime. If you smoke, quit.
How to treat laryngospasm?
To the Editor:-When considering the treatment of laryngospasm, standard textbooks of anesthesiology suggest virtually the same sequence: namely jaw thrust at the angle of the mandible while applying positive-pressure ventillation with oxygen, 100%, by bag and mask and, if that fails, administering succinylcholine, the recommended dose varying from 0.25 to 1 mg/kg intravenously or 4 mg/kg intramuscularly. [1-8] In addition, some texts recommend suctioning foreign material from the oropharynx, administering lidocaine, 1 to 1.5 mg/kg, and removing or avoiding any painful stimulus. One author recommended digital elevation of the tongue by inserting an index finger deep into the pharynx, a treatment of substantial risk to the therapist. [9]
Where is the laryngospasm notch?
Schematic illustration of laryngospasm notch bounded anteriorly by the condyle of the mandible, posteriorly by the mastoid process, and superiorly by the base of the skull. Digital pressure is applied firmly inwardly and anteriorly on each side of the head at the apex of the notch (see pressure point arrow), which is slightly cephalad to the plane of the earlobes (not shown).
Why does mandible stimulation work?
It works in part because forward displacement of the mandible corrects airway obstruction caused by the tongue falling back against the posterior pharyngeal wall. However, contrary to the recommendation that painful stimulation be avoided, an essential component of the treatment is the severe pain that the patient experiences because of the firm pressure that is applied to the ramus of the mandible, the facial nerve, and perhaps the deep lobe of the parotid gland. The parotid gland is innervated in part by the glossopharyngeal nerve, which in turn has connections with the vagus nerve and the superior cervical sympathetic ganglion by way of the petrosal ganglion. [10] The interconnections of the nerves at this location are complex and specific functions are not completely understood. It is likely that the painful stimulus relaxes the vocal folds and vocal cords by way of either the parasympathetic or sympathetic nervous systems.
Is laryngospasm better than lidocaine?
I believe this technique for treatment of laryngospasm is far superior to those recommended herein because it is absolutely reliable, it resolves the spasm more rapidly than positive pressure ventilation, and it is much quicker and safer than administering succinylcholine or lidocaine.
Is pain a part of the treatment of parotid gland?
However, contrary to the recommendation that painful stimulation be avoided , an essential component of the treatment is the severe pain that the patient experiences because of the firm pressure that is applied to the ramus of the mandible, the facial nerve, and perhaps the deep lobe of the parotid gland.
Does pressure elevate tongue from posterior pharyngeal wall?
Pressure and forward displacement of the mandible at these locations will elevate the tongue from the posterior pharyngeal wall but will not correct laryngospasm. To be effective for laryngospasm, the pressure must be firm and must be applied at the most cephalad portion of the laryngospasm notch.
What is the spasm in the vocal cord?
Laryngospasm (luh-RING-go-spaz-um) is a spasm of the vocal cords that temporarily makes it difficult to speak or breathe. The vocal cords are two fibrous bands inside the voice box (larynx) at the top of the windpipe (trachea). The onset of a vocal cord spasm is sudden, and just as suddenly, it goes away, usually after a few minutes. The breathing difficulty can be alarming, but it's not life-threatening.
Can vocal cord spasms be life threatening?
The breathing difficulty can be alarming, but it's not life-threatening. The cause of vocal cord spasms is often unknown, but conditions such as anxiety and acid reflux may be contributing factors or triggers.
Can acid reflux cause vocal spasms?
Some think acid reflux may cause a few drops of stomach acid backwash to touch the vocal cords, setting off the spasm. Recurrence is uncommon, but if it happens, try to relax. Taking an antacid or acid inhibitor for a few weeks can help diagnose the problem by the process of elimination.
How does voice therapy help with cough?
In such patients, voice therapy can help resolve these symptoms through behavior modification, self-awareness exercises, vocal hygiene training, and cough suppression behavior. Contact Us.
How does SLP therapy work?
Through self-awareness exercises and therapy , patients are often able to decrease laryngeal sensory hyper-responsiveness leading to such symptoms. The SLP therapy program has several components that include behavior modification, cough suppression behaviour, and vocal hygiene training. This treatment should be differentiated from voluntary symptom suppression which does not appear to be helpful. For more info, see references below.
How to avoid hyperventilation during exercise?
During the first week, exercises should be performed in isolation without any distractions; always sitting down using a clock as a timing device. Emphasize slow emptying of lungs during exhalation before repeating sequence to minimize risk of hyperventilation. Monitor # of repetitions achieved in one minute.
Is voice therapy good for laryngospams?
Although medical treatment can stil be pursued, in such patients it is becoming recognized that voice therapy ( under guidance from a qualified speech language patho logist or SLP ) is beneficial to reduce signficantly a persistent cough or laryngospams attacks. Keep in mind that not all SLP are qualified, but those minority who are voice therapy trained probably are.
Is respiratory retraining effective?
As a reminder, this respiratory retraining is most effective within the context of other therapeutic maneuvers under the guidance of a voice therapist, self-awareness practiced at all times, and diligence in performing every day .
Can a SLP help with laryngospasm?
Described here is one behavior modification program patients with chronic cough or laryngospasm can start at home, though ideally such patients should work with a qualified SLP to address all necessary components to alleviate a hyper-irritated voicebox successfully. When performing these exercises, it is not just the motions, but also the self-awareness of how everything feels (much like what one experiences when performing yoga or meditation) that is just as important.
