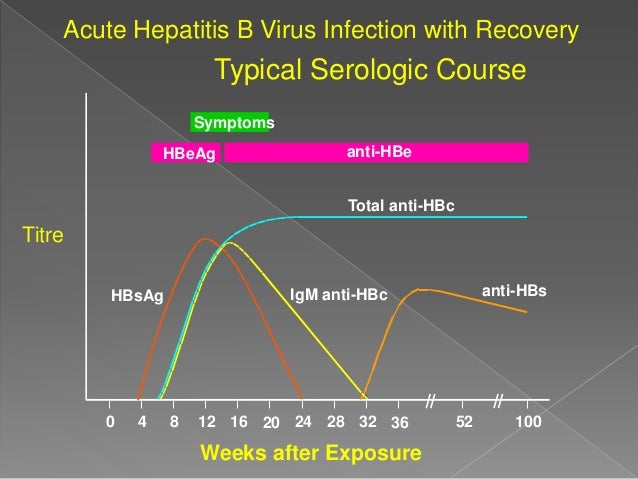
Precautions
Type1 interferon (IFN) signaling exerts anti-proliferative and anti-viral effects through a cell surface cognate receptor consisting of two subunits, the interferon alpha receptor subunit 1 (IFNAR1) and IFNAR2 [22].
What are the effects of interferon?
A TNF inhibitor is a pharmaceutical drug that suppresses the physiologic response to tumor necrosis factor (TNF), which is part of the inflammatory response.TNF is involved in autoimmune and immune-mediated disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa and refractory asthma, so TNF inhibitors may be used in their ...
Is Entocort a TNF alpha inhibitor?
What is the Treatment Course with Interferon?
- Treatment is administered via direct injection into Peyronie’s plaque every 2 weeks.
- 2 million U of interferon-a2b injected every 2 weeks for 6 to 12 treatments.
- About 50% of men respond to therapy.
- Absolute change of 9 degrees, a relative reduction of 20% from 42 degrees to around 30 degrees.
- Treatment is effective for dorsal and ventral curvature.
What does interferon treat?
What is interferon beta-1a? Interferon beta-1a is used to treat relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis in adults (including clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease). interferon beta-1a will not cure MS, it will only decrease the frequency of relapse symptoms.
What does interferon beta 1a used for?

Why are some patients treated with alpha interferons?
Interferon alpha helps stimulate the body's immune system to fight some types of cancer by strengthening the immune system, reducing the ability of the cancer cells to defend themselves from the immune system and by slowing down or stopping the cancer cells from dividing.
How is interferon treatment administered?
You get interferon as a shot under your skin or into a muscle. A doctor can give you the shot or teach you how to give it to yourself at home. Interferon is also sometimes given through a vein in your arm (infusion). The number of shots or infusions you need depends on the condition you have.
Can interferons be used for COVID-19?
The Panel recommends against the use of interferon alfa or lambda for the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19, except in a clinical trial (AIIa).
What is the main action of interferon alpha?
IFN-α is an antiviral cytokine of the type I IFN innate immune response of most cell types. IFN-α exhibits anti-viral activity via the induction of protective genes that inhibit viral replication and impede viral dissemination.
Where is interferon injected?
You can inject interferon beta-1a in areas of your body with a layer of fat between the skin and muscle, such as your thigh, the outer surface of your upper arms, your stomach, or your buttocks. If you are very thin, only inject in your thigh or the outer surface of your arm for injection.
How long does interferon treatment last?
Interferon treatment for hepatitis C would typically last 24–48 weeks (6–12 months). Interferons caused many long-term side effects partly because of this long treatment time. Using the drug for this length of time gave side effects a chance to develop and get worse.
How do interferons work against viruses?
Interferon is secreted by cells in response to stimulation by a virus or other foreign substance, but it does not directly inhibit the virus's multiplication. Rather, it stimulates the infected cells and those nearby to produce proteins that prevent the virus from replicating within them.
What is an example of interferons currently being researched or used in a clinical trial?
Zidovudine is an antiviral agent. When given with interferon alpha may help lower the levels and control disease so that cancer does not get worse or come back. Interferon alpha is a man-made copy of a protein that is produced by the body in response to infections.
Is interferon still used?
As well as occurring naturally in the body, interferon is also used as a treatment for various health disorders, including multiple sclerosis (MS), some types of cancer, and hepatitis C.
How much does interferon treatment cost?
The total cost of the IFN treatment regimen was estimated to range between US$1,120 and US$1,962 and the total cost of the Peg-IFN treatment regimen between US$2,156 and US$5,887 ( Table 3).
How do interferons protect against viral infection and healthy cells?
Virally infected cells produce and release small proteins called interferons, which play a role in immune protection against viruses. Interferons prevent replication of viruses, by directly interfering with their ability to replicate within an infected cell.
Is interferon an immunotherapy?
Interferon is a type of immunotherapy patients receive as adjuvant therapy to reduce the risk of melanoma relapse.
How to avoid interferon alfa-2a?
Avoid driving and doing other tasks or actions that call for you to be alert until you see how interferon alfa-2a affects you. Have blood work checked as you have been told by the doctor. Talk with the doctor. Have an eye exam as you have been told by your doctor.
What is interferon Alfa-2A used for?
Uses of Interferon Alfa-2a: It is used to treat cancer. It is used to treat hepatitis B and C infections. It is used to treat advanced HIV -associated Kaposi's sarcoma . It may be given to you for other reasons.
How to prevent pregnancy while taking interferon?
Talk with the doctor. If you are a man and have sex with a female who could get pregnant, protect her from pregnancy. Use birth control that you can trust. Use birth control that you can trust to prevent pregnancy while taking interferon alfa-2a. Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan on getting pregnant.
Can you take interferon while pregnant?
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan on getting pregnant. You will need to talk about the benefits and risks of using interferon alfa-2a while you are pregnant. Hepatitis infection: This medicine does not stop the spread of diseases like HIV or hepatitis that are passed through blood or having sex.
Can you share interferon with others?
Do not share your drugs with others and do not take anyone else's drugs. Some drugs may have another patient information leaflet. Check with your pharmacist. If you have any questions about interferon alfa-2a, please talk with your doctor, nurse, pharmacist, or other health care provider.
Can interferons cause relapse?
Relapse of drug addiction has also happened. Alpha interferons may also cause or make infections, blood flow problems, or autoimmune diseases worse. Sometimes, these may be deadly. If you think you have any of these health problems, call your doctor right away.
Can interferons cause mental health problems?
Alpha interferons may cause mental health problems or make them worse. Suicide or suicidal thoughts, thoughts of hurting others, depression, forceful actions, hallucinations, and other mood or behavior problems have happened during treatment and within 6 months after the last dose.
How is interferon alfa given?
How Interferon Alfa Is Given: By injection under the skin (subcutaneous, SubQ) By injection through a vein (intravenously, by IV) By injection into a muscle (intramuscular, IM) There is no oral ( by mouth) form of interferon alfa. Due to differences in dosage, you should not change brands of interferons.
What is interferon alfa?
This is a type of treatment that mobilizes the body's immune system to fight cancer. The therapy mainly consists of stimulating the immune system to help it do its job more effectively.
How does interferon alfa affect cancer?
There are several ways that interferon alfa fights cancer; directly by interfering with the cancer cells ability to divide, and indirectly by modifying the body's response to the cancer cells.
Can you take aspirin with interferon alpha?
Do not take aspirin or products containing aspirin unless your doctor specifically permits this.
Does interferon alfa go away?
Important things to remember about the side effects of interferon alfa: Side effects are almost always reversible and will go away after treatment is complete. There is no relationship between the presence or severity of side effects and the effectiveness of the medication.
Can you get pregnant while taking interferon?
For both men and women: Do not conceive a child (get pregnant) while taking interferon alfa. Barrier methods of contraception, such as condoms, are recommended. Discuss with your doctor when you may safely become pregnant or conceive a child after therapy. Do not breast feed while taking this medication.
Can you get immunizations with interferon?
Do not receive any kind of immunization or vaccination without your doctor's approval while taking interferon alpha.
What is interferon used for?
Interferons are currently used clinically to treat viral infections such as hepatitis C, cancers including non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis. This activity outlines the different types of interferons, namely interferon alpha, beta, and gamma. It discusses the pharmacological properties of different interferons, their medical uses, methods of administration, potential adverse effects, and other properties. It also highlights the important role that providers play in terms of correctly administering and dosing interferon medication, regularly monitoring patients for adverse effects, and counseling patients on the importance of medication adherence.
How often should I take interferon?
For chronic viral hepatitis treatment, administer 10 MIU of interferon-alpha is administered three times a week subcutaneously for 24 weeks in combination with ribavirin. For non-Hodgkin lymphoma, hairy cell leukemia, and multiple myeloma, 3 MIU of interferon-alpha is administered subcutaneously until tumor progression stops. In treating renal cell carcinoma, administer 10 MIU of interferon-alpha until the cessation of tumor progression. For chronic myeloid leukemia, 10 MIU of interferon-alpha is administered three to five times a week subcutaneously in combination with cytarabine until tumor progression stops. For melanoma treatment, give 3 to 10 MIU of interferon-alpha three times a week subcutaneously as adjuvant therapy. Interferon-alpha is also used to treat condylomata acuminata, Behcet disease, and Kaposi sarcoma with varying schedules. [14]
How do interferons affect the immune system?
Interferons exhibit immune-modulatory effects by initiating signaling cascades that lead to the expression of gene products such as MHC class 1, B2 microglobulin, and others. Alpha and beta interferons bind to the IFNA receptor, which has two parts, IFNAR1 and IFNAR2. IFNAR1 has a low affinity for interferon on its own, but binding is enhanced when accompanied by IFNAR2. Phosphatases SHP-1 and 2 associate with IFNAR1 and exhibit negative feedback in the activation of JAK signaling. IFNAR2 has three variants, short, soluble, and long-form. The long-form leads to activation of the JAK-STAT pathway and antiviral response. When stimulated by interferon, protein complexes form and translocate to the nucleus and activate STATs. This, in turn, leads to the dimerization of IFNAR1 and IFNAR2, which triggers a phosphorylation cascade. First, the JAK kinase, Tyk 2, which is associated with IFNAR1, is immediately phosphorylated by JAK1, another JAK kinase bound to IFNAR2. Activation of Tyk2 then phosphorylates JAK1, leading to phosphorylation of IFNAR1 and 2. Next, STAT2 binds to IFNAR1 at specific phosphorylated residues. Afterward, STAT2 is phosphorylated by JAK kinases, creating a port for STAT1, which is also phosphorylated. After becoming phosphorylated, the STATS dissociate and bind to the interferon regulatory factor 9, which forms the major interferon transcription factor, ISGF-3. IGSF-3 then translocates to the nucleus and binds to ISRE, initiating transcription of interferon-inducible genes. For interferon-gamma, there are different DNA regulatory sequences called gamma-activated sequence elements, which are present in promoters of interferon-gamma stimulated genes. [12]
What type of interferons are used for hepatitis C?
Ischemic colitis with type I interferons used in the treatment of hepatitis C and multiple sclerosis: an evaluation from the food and drug administration adverse event reporting system and review of the literature.
What are the roles of interferons in the immune system?
Interferons are particularly important in fighting viral infections but also play a vital role in tumor suppression, upregulation of MHC Class 1 and 2, signal transduction, and activation of immune cells, including natural killer cells and macrophages. Interferons can broadly be classified into three main subtypes, interferon-alpha, beta, and gamma, with interferon-alpha and beta belonging to the Type 1 interferon subclass and interferon-gamma belonging to the Type 2 subclass.[11] More recently, there has been the discovery of a third subclass of interferons, namely Type 3, which includes interferon lambda. [10]
How often is Interferon Beta 1A given?
Interferon-beta 1a and 1b are used to treat multiple sclerosis. Interferon-beta 1b is administered subcutaneously in a 250 ug dose every other day. Interferon-beta 1a is administered intramuscularly once per week at a dose of 30 mcg and subcutaneously three times a week at a dose of 22 to 42 mcg. [3]
What are the roles of interferons in the replication of a virus?
Interferons exhibit antiviral activity at many stages of the viral replication cycle, including entry, transcription, RNA stability, translation, maturation, and release. This action is under the mediation of the expression of antiviral genes. Interferons stimulate the expression of PKR through an ISRE and GAS in the promoter of the PKR gene. The kinase activity of the PKR gene, in turn, phosphorylates the translation initiation factor eIF2-a at Ser51. eIF2-a-GTP is necessary for the initiation of viral translation. PKR also plays roles in cell proliferation, tumor suppression, and signal transduction through the regulation of serine phosphorylation of STAT1 and the phosphorylation of IkB, which leads to the activation of NF-kB-dependent genes. Additionally, the 2-5 A oligosynthetase/RNAse L system is strongly induced by interferons. RNAse Ls are activated by double-stranded RNAs and degrade all single-stranded RNA, thereby inhibiting viral replication. The Mx proteins are a family of GTPases induced by interferons and assemble into oligomeric and interfere with transcription in negative-sense virus replication. An additional protein involved in inhibiting viral replication that is induced by interferons is the guanylate binding protein. [12]
Recommendations
The COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel (the Panel) recommends against the use of systemic interferon beta for the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 (AI).
Rationale
Many of the early studies that evaluated the use of systemic interferons for the treatment of COVID-19 were conducted in early 2020, before the widespread use of remdesivir and corticosteroids.
Clinical Trials
See ClinicalTrials.gov for a list of clinical trials that are evaluating the use of interferons for the treatment of COVID-19.
Adverse Effects
The most frequent adverse effects of systemic interferon include flu-like symptoms, nausea, fatigue, weight loss, hematological toxicities, elevated transaminases, and psychiatric problems (e.g., depression, suicidal ideation). Interferon beta is better tolerated than interferon alfa, but it can cause similar types of adverse effects. 6,7
Drug-Drug Interactions
Additive toxicities may occur when systemic interferons are used concomitantly with other immunomodulators and chemotherapeutic agents. 6,7
Considerations in Pregnancy
According to analyses of data from several large pregnancy registries, exposure to interferon beta-1b prior to conception or during pregnancy does not lead to an increased risk of adverse birth outcomes (e.g., spontaneous abortion, congenital anomaly). 8,9 Exposure to interferon beta-1b did not influence birth weight, height, or head circumference.
Considerations in Children
There are currently not enough data on the use of interferons to treat respiratory viral infections in children to make any recommendations for treating children with COVID-19.
When to inject Interferon Alfa-2b?
It is best to inject the medication at around the same time of day on your injection days, usually in the late afternoon or evening.
What to do before using Interferon Alfa-2b?
Before you use interferon alfa-2b for the first time, you or the person who will be giving the injections should read the manufacturer's information for the patient that comes with it. Ask your doctor or pharmacist to show you or the person who will be injecting the medication how to inject it.
How long can you keep interferon in the refrigerator?
However, you may mix the medication in advance, store it in the refrigerator, and use within 24 hours. Be sure to take the medications out of the refrigerator and allow it to come to room temperature before you inject it.
How long does it take to take melanoma medication?
malignant melanoma, inject the medication intravenously for 5 consecutive days for 4 weeks, then subcutaneously three times per week for 48 weeks.
What happens if you take Interferon Alfa 2b?
Interferon alfa-2b injection may cause or worsen the following conditions that may be serious or life-threatening: infections; mental illness, including depression, mood and behavior problems, or thoughts of hurting or killing yourself or others; ischemic disorders (conditions in which there is poor blood supply to an area of the body) such as angina (chest pain) or heart attack; and autoimmune disorders (conditions in which the immune system attacks one or more parts of the body that may affect the blood, joints, kidneys, liver, lungs, muscles, skin, or thyroid gland). Tell your doctor if you have an infection; or if you have or have ever had an autoimmune disease, psoriasis (a skin disease in which red, scaly patches form on some areas of the body), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE or lupus; an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks healthy parts of the body), sarcoidosis (a condition in which small clumps of immune cells form in various organs such as the lungs, eyes, skin, and heart and interfere with the function of these organs), or rheumatoid arthritis (RA; a condition in which the body attacks its own joints, causing pain, swelling, and loss of function); cancer; colitis (inflammation of the intestine); diabetes; heart attack; high blood pressure; high triglyceride levels (fats related to cholesterol); HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) or AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome); irregular heartbeat; mental illness including depression, anxiety, or thinking about or trying to kill yourself; or heart, kidney, pancreas, or thyroid disease.
How long does genital wart treatment last?
genital warts, inject the medication intralesionally three times weekly on alternate days for 3 weeks, then treatment may be continued for up to 16 weeks.
Where to inject interferon?
If you are injecting this medication subcutaneously, inject interferon alfa-2b anywhere on your stomach area, upper arms, or your thighs, except near your waistline or around your navel (belly button). Do not inject your medication into skin that is irritated, bruised, reddened, infected, or scarred.
When was interferon first used?
In 1986 , the first lab-made interferon was created to treat certain types of cancer. It was one of the earliest treatments to work with your immune system to fight illness and was later approved as a treatment for several other conditions, including hepatitis and multiple sclerosis.
How do you get interferon?
You get interferon as a shot under your skin or into a muscle. A doctor can give you the shot or teach you how to give it to yourself at home. Interferon is also sometimes given through a vein in your arm (infusion). The number of shots or infusions you need depends on the condition you have.
Why are interferons called interferons?
And they trigger killer immune cells to fight those invaders. Interferons got their name because they "interfere" with viruses and keep them from multiplying. In 1986, the first lab-made interferon was created to treat certain types of cancer.
What does interferon do to your body?
Interferons alert your immune system to fight viruses and cancer. Learn how they work and when your doctor might recommend them.
What is interferon gamma-1b?
Interferon gamma-1b (Actimmune) treats chronic granulomatous disease, which affects the way your immune system works, and severe malignant osteopetrosis, which affects your bones. Certain types of interferon medications have a chemical called polyethylene glycol (PEG) added to them.
What are the three types of interferons?
Almost every cell in your body makes interferons. There are three main types: Interferon-alpha (or interferon-alfa) Interferon-beta. Interferon-gamma. Cells that have been infected with viruses or other germs give off interferon-alpha and interferon-beta as a warning signal to your immune system. That triggers immune cells called white blood cells ...
How to help your immune system fight cancer?
Alert your immune system so it can go after the virus or cancer. Help your immune system recognize the virus or cancer. Tell immune cells to attack. Stop virus and cancer cells from growing and dividing. Help healthy cells fight infection.