The activated sludge process is a type of biological wastewater treatment process for treating sewage or industrial wastewaters using aeration and a biological floc
Flocculation
Flocculation, in the field of chemistry, is a process wherein colloids come out of suspension in the form of floc or flake; either spontaneously or due to the addition of a clarifying agent. The action differs from precipitation in that, prior to flocculation, colloids are merely suspended in a liquid and not actually dissolved in a solution.
Protozoa
Protozoa is an informal term for single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, which feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Historically, the protozoa were regarded as "one-celled animals", because they often possess ani…
What is the purpose of Return Activated Sludge?
Process description
- Bioreactor and final clarifier. ...
- Sludge production. ...
- Process control. ...
- Package plants. ...
- Oxidation ditch. ...
- Deep shaft / Vertical treatment. ...
- Surface-aerated basins. ...
- Sequencing batch reactors (SBRs) Sequencing batch reactors (SBRs) treat wastewater in batches within the same vessel. ...
What is returned activated sludge?
return activated sludge (RAS) Settled activated sludge that is collected in the secondary clarifier or the membrane basin and returned to the aeration basin to mix with incoming raw or primary settled wastewater.
What is an activated sludge process?
Purpose
- In a sewage (or industrial wastewater) treatment plant, the activated sludge process can be used for one or several of the following purposes:
- oxidizing carbonaceous matter: biological matter.
- oxidizing nitrogeneous matter: mainly ammonium and nitrogen in biological materials.
- removing phosphate.
How does activated sludge work?
- The amount of undesired sludge is reduced.
- The sewage treatment plants re-seed themselves with beneficial bacteria.
- The activated sludge treatment process allows the emptying intervals to be longer.
- The process is very reliable.
- The process is more simple.
- Costs are reduced.
- The process can be odorless.
What is activated sludge?
When was activated sludge discovered?
What is pure oxygen sludge aeration?
How to reduce space in sewage treatment plant?
What is the mechanism of mixing sewage and sludge?
How is sewage treated in a short supply area?
How often is sludge blanket measured in a reactor?
See more
About this website

What is waste activated sludge in wastewater treatment?
The waste activated sludge process is a kind of sewage treatment that blows oxygen (or air) into unsettled, raw sewage, which digests pollutants and organic content to keep the biological system in balance. This process is called aeration and takes place in an aeration tank.
What is activated sludge How is it produced?
a When the BOD of sewage or waste is reduced significantly the effluent is then passed into a settling tank where the bacterial flocs are allowed to sediment. This sediment is called activated sludge.
What happens when activated sludge?
The organic matter, from the sludge is oxidized to carbon dioxide, water and ammonia. The ammonia is further converted to nitrates as the digestion process proceeds.
Why it is called activated sludge?
They aerated the waste-water continuously for about a month and were able to achieve a complete nitrification of the sample material. Believing that the sludge had been activated (in a similar manner to activated carbon) the process was named activated sludge.
What is the difference between primary sludge and activated sludge?
Solution : Activated sludge possesses flocs of decomposer microbes, whereas, primary sludge does not possess flocs. Unlike primary sludge a lot of decomposition occurs during formation of activated sludge.
What are the advantages of activated sludge process?
Advantages of Activated Sludge ProcessLow installation cost.Good quality effluent.Low land requirement.Loss of head is small.Freedom from fly and odor nuisance high degree of treatment.
How do you maintain activated sludge?
To control activated sludge, you need to "have a handle" either on aeration, sludge-wasting or return-sludge flow. Aeration-rate adjustment is probably the simplest way to go. It involves, however, more than measuring aeration-basin dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration once each day.
Activated Sludge Treatment Process Concept and System Design
Activated Sludge Treatment Process Concept and System Design ... Design
What is Waste Activated Sludge (WAS)? | WWD
One of the most commonly used sewage treatment processes is the activated sludge process, known as ASP.This article will look at the ASP in more detail, including how the process works, the benefits of this process, and activated sludge modifications.
What Is the Waste Activated Sludge Process?
The waste activated sludge process is a kind of sewage treatment that blows oxygen (or air) into unsettled, raw sewage, which digests pollutants and organic content to keep the biological system in balance. This process is called aeration and takes place in an aeration tank.
What is Waste Activated Sludge Used For?
Sewage and industrial wastewater treatment plants use the activated sludge process for several purposes: to oxidize nitrogenous materials, to oxidize carbonaceous materials, or to remove nutrients like phosphorus.
The Microbes in Activated Sludge
Activated sludge is termed 'activated' because many of its particles are active bacteria and protozoa. These microorganisms are needed in sewage treatment because they can digest sewage bacteria.
What are the Benefits of Waste Activated Sludge?
Activated sludge sewage treatment plants have a number of benefits compared to other types of sewage treatment, namely it is:
What Are the Issues with Waste Activated Sludge?
Like all forms of sewage treatment, activated sludge has its setbacks. Three common ones are:
Modifications of Activated Sludge
There is not one specific activated sludge process that is used across all sewage plants. Instead, different processes are used to address different problems or conditions. These processes have their own characteristics, including their aeration flow patterns and mixing, and how the microorganisms mix with sewage water.
The Bottom Line
The waste activated sludge process is one of the most effective sewage treatment options. Despite its drawbacks, this process is one of the most efficient and cost-effective processes that is relied upon by many municipalities.
What is activated sludge?
Activated sludge refers to a flocculent culture of organisms developed in aeration tanks under controlled conditions, according to WEF . Activated sludge is typically brown in color. Activated sludge is also known as waste activated biosolids or waste activated solids.
When was activated sludge first used?
The activated sludge process is designed to speed up the rate of decomposition of waste material in water and was first developed in 1914, according to the International Water Association.
What is a return sludge system?
The return sludge system includes pumps, a timer or variable speed drive, and a flow measurement device. An activated sludge system consists of the same components but in some cases, the waste activated sludge withdrawal is accomplished by adjusting valves on the return system.
What is the difference between a mechanical and a diffuser aeration system?
Mechanical aeration systems use agitators or mixers to mix air and mixed liquor. Diffused aeration systems use pressurized air released through diffusers near the bottom of the tank.
Is activated sludge sewage treatment centralized?
Activated sludge sewage treatment is ideally completed in a centralized treatment facility and the treatment of the sludge can occur in most climates. Colder environments reduce the treatment capacity, however.
What is activated sludge?
Activated sludge is also the name given to the active biological material produced by activated sludge plants. Excess sludge is called "surplus activated sludge" or "waste activated sludge" and is removed from the treatment process to keep the ratio of biomass to food supplied in the wastewater in balance. This sewage sludge is usually mixed with primary sludge from the primary clarifiers and undergoes further sludge treatment for example by anaerobic digestion, followed by thickening, dewatering, composting and land application.
When was activated sludge discovered?
The activated sludge process was discovered in 1913 in the United Kingdom by two engineers, Edward Ardern and W.T. Lockett, who were conducting research for the Manchester Corporation Rivers Department at Davyhulme Sewage Works. This development led to arguably the single most significant improvement in public health and the environment during ...
What is pure oxygen sludge aeration?
Pure oxygen activated sludge aeration systems are sealed-tank reactor vessels with surface aerator type impellers mounted within the tanks at the oxygen carbon liquor surface interface . The amount of oxygen entrainment, or DO (Dissolved Oxygen), can be controlled by a weir adjusted level control, and a vent gas oxygen controlled oxygen feed valve. Oxygen is generated on site by cryogenic distillation of air, pressure swing adsorption, or other methods. These systems are used where wastewater plant space is at a premium and high sewage throughput is required as high energy costs are involved in purifying oxygen.
How to reduce space in sewage treatment plant?
The space required for a sewage treatment plant can be reduced by using a membrane bioreactor to remove some wastewater from the mixed liquor prior to treatment. This results in a more concentrated waste product that can then be treated using the activated sludge process.
What is the mechanism of mixing sewage and sludge?
As the sewage rises the oxygen forced into solution by the pressure at the base of the shaft breaks out as molecular oxygen providing a highly efficient source of oxygen for the activated sludge biota. The rising oxygen and injected return sludge provide the physical mechanism for mixing of the sewage and sludge.
How is sewage treated in a short supply area?
Where land is in short supply sewage may be treated by injection of oxygen into a pressured return sludge stream which is injected into the base of a deep columnar tank buried in the ground. Such shafts may be up to 100 metres deep and are filled with sewage liquor.
How often is sludge blanket measured in a reactor?
In the reactor/aerator and clarifier system, the sludge blanket is measured from the bottom of the clarifier to the level of settled solids in the clarifier's water column; this, in large plants, can be done up to three times a day.
What is activated sludge?
The activated sludge is a process with high concentration of microorganisms, basically bacteria, protozoa and fungi, which are present as loose clumped mass of fine particles that are kept in suspension by stirring, with the aim of removing organic matter from wastewater. From: Resource-Efficient Technologies, 2016.
How does activated sludge work?
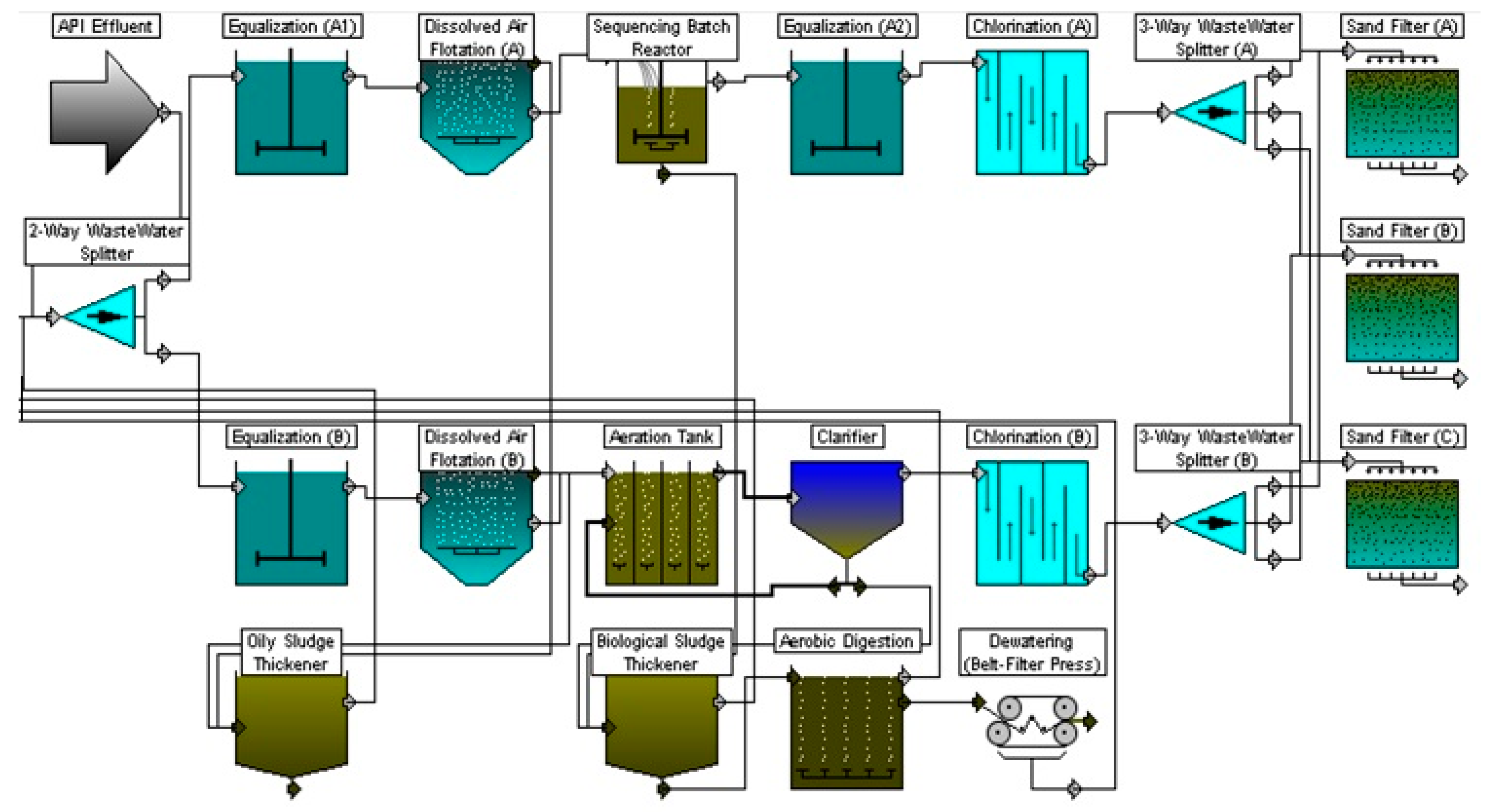
The activated sludge process (Fig 12.4) uses microorganisms to feed organic contaminants that are in wastewater to produce a high-quality effluent. The basic principle behind all activated sludge processes is that as microorganisms grow, they form particles that clump together. These particles, which are referred to as floc, are allowed to settle to the bottom of the tank, which results in a relatively clear liquid free organic material and suspended solids. The screened wastewater is mixed with varying amounts of recycled liquid that contains a high proportion of organisms that are taken from a secondary tank, and it becomes a product that is called mixed liquor. The next step for the mixture is to stir and inject it with large quantities of air to provide oxygen and keep the solids in suspension. After a period of time, the mixed liquor flows to a clarifier where it is allowed to settle. During this settling a portion of the bacteria is removed and the partially cleaned water flows on for additional treatment. The settled solids that resulted, the activated sludge, are then returned to the first tank to begin the process again. The basic activated sludge process consists of several interrelated components:
What is the major phenomenon responsible for PPCPs elimination in activated sludge process?
Biodegradation is suggested as the major phenomenon responsible for PPCPs elimination in activated sludge process. Therefore, to improve the degradation of PPCPs, an effective strategy must be adapted to increase the decomposition.
Why do activated sludge plants foam?
Foaming in activated sludge plants is caused by high SRTs, warm temperatures, low F:M ratios and high MLSS levels, as well as oil and grease and/or surfactants in the influent. Abundance of actinomycetes such as Nocardia or Microthrix are commonly related to foaming in activated sludge plants, and have been identified in a full-scale MBR plant subject to variable OLRs ( Smith, 2006 ). However, foam in MBR plants has been observed in the absence of actinomycetes. The degree of foaming is reported as being related to the protein EPS concentrations (Nakajima and Mishima, 2005). Foaming sludges also appear to yield lower membrane permeabilities ( Chang and Lee, 1998 ), attributed to the higher hydrophobicity of foaming activated sludge ( Section 2.3.6.4 ). Foaming thus provides an indication of sludge fouling propensity.
How many Ascaris eggs are in activated sludge?
The concentration of parasites in activated sludge treated effluents is usually low at less than 5 eggs/l, though higher numbers of around 60 Ascaris eggs/l have been reported ( Bhaskaran et al., 1956 ). Numbers of protozoan (oo)cysts in activated sludge effluents can be high despite relatively high removal rates.
What is activated sludge treatment?
Activated sludge treatment can define as the wastewater treatment plant, which eliminates the particulate matter like sand, unwanted inorganic and organic wastes and harmful microorganisms from the sewage waste. The process is followed by the primary, secondary and tertiary treatment methods.
What is activated sludge?
Activated sludge. It can define as waste formed in the secondary treatment by the oxidation of organic matter by the bacterial flocs under aerated condition. The coarse particles, colloids, suspended or dissolved matter etc. deposits at the bottom of the aeration basin is termed as sludge. This sludge contains active biomass ...
What is secondary treatment?
Secondary Treatment. It is the most crucial step of the wastewater treatment, which filters out the effluent from the waste activated sludge. The secondary treatment involves a series of operation, such as: Aeration tank: It a bioreactor which contains the primary or raw sludge and a microbial suspension.
What is the term for the average time wastewater remains in the aerobic digester?
This factor may affect the oxygen requirement, the susceptibility of the microorganisms to shock load, conditions within the bioreactor etc. Retention time . It can define as the average time, in which wastewater remains in the aerobic digester. It is also called hydraulic retention time or sludge retention time.
What are the variables used in activated sludge treatment?
Variables used in the Activated Sludge Treatment. While studying the activated sludge treatment, we must have an idea of the terms given below: Water pollution. It can define as the accumulation of invaluable physical, biological and chemical waste, which alters the appearance and potability of the water.
What is the term for sediment in wastewater treatment?
In the case of wastewater treatment, the sediment is called sludge. Flocculation. This method facilitates the clumping of particles suspended in a liquid, which generally appears as flocs that settle down towards the base of chamber or reactor.
What are water pollutants?
Water pollutants. It includes chemical wastes (like heavy metals, VOCs), physical wastes (like vegetable remainings, sand, gravel etc.) and biological waste (such as coliform bacteria in the human and animal’s faeces). Water pollutants change the water quality or make it undesirable or unpotable for human consumption. Activated sludge.
What is activated sludge?
Activate-sludge is that sludge which settle down in a secondary sedimentation tank after the sewage has been freely aerated and agitated for a certain time in an Aeration tank.
What are the functions of activated sludge?
The activated-sludge contains numerous bacteria and other microorganisms, when it is mixed with raw sewage saturated with oxygen, the bacteria perform the following function. Oxidize the organic solids. Promote coagulation and flocculation and convert dissolved, colloid and suspended solids into settle able solids.
Why is sludge returned to the aeration tank?
Most of the settled sludge is returned to the aeration tank (and is called return sludge) to maintain the high population of microbes that permits rapid breakdown of the organic compounds.
How long is the detention time for sewage?
The sewage is given treatment in the primary sedimentation tank. The detention time is kept as short as 1-1/2 hours. The settled sewage form the Primary Sedimentation Tank is the mixed with the required quantity of activated-sludge in the aeration tank.
What is activated sludge?
Activated sludge is also the name given to the active biological material produced by activated sludge plants. Excess sludge is called "surplus activated sludge" or "waste activated sludge" and is removed from the treatment process to keep the ratio of biomass to food supplied in the wastewater in balance. This sewage sludge is usually mixed with primary sludge from the primary clarifiers and undergoes further sludge treatment for example by anaerobic digestion, followed by thickening, dewatering, composting and land application.
When was activated sludge discovered?
The activated sludge process was discovered in 1913 in the United Kingdom by two engineers, Edward Ardern and W.T. Lockett, who were conducting research for the Manchester Corporation Rivers Department at Davyhulme Sewage Works. This development led to arguably the single most significant improvement in public health and the environment during ...
What is pure oxygen sludge aeration?
Pure oxygen activated sludge aeration systems are sealed-tank reactor vessels with surface aerator type impellers mounted within the tanks at the oxygen carbon liquor surface interface . The amount of oxygen entrainment, or DO (Dissolved Oxygen), can be controlled by a weir adjusted level control, and a vent gas oxygen controlled oxygen feed valve. Oxygen is generated on site by cryogenic distillation of air, pressure swing adsorption, or other methods. These systems are used where wastewater plant space is at a premium and high sewage throughput is required as high energy costs are involved in purifying oxygen.
How to reduce space in sewage treatment plant?
The space required for a sewage treatment plant can be reduced by using a membrane bioreactor to remove some wastewater from the mixed liquor prior to treatment. This results in a more concentrated waste product that can then be treated using the activated sludge process.
What is the mechanism of mixing sewage and sludge?
As the sewage rises the oxygen forced into solution by the pressure at the base of the shaft breaks out as molecular oxygen providing a highly efficient source of oxygen for the activated sludge biota. The rising oxygen and injected return sludge provide the physical mechanism for mixing of the sewage and sludge.
How is sewage treated in a short supply area?
Where land is in short supply sewage may be treated by injection of oxygen into a pressured return sludge stream which is injected into the base of a deep columnar tank buried in the ground. Such shafts may be up to 100 metres deep and are filled with sewage liquor.
How often is sludge blanket measured in a reactor?
In the reactor/aerator and clarifier system, the sludge blanket is measured from the bottom of the clarifier to the level of settled solids in the clarifier's water column; this, in large plants, can be done up to three times a day.

Overview
Purpose
Process description
- The activated sludge process is designed to speed up the rate of decomposition of waste material in water and was first developed in 1914, according to the International Water Association. The activated sludge process was first tested at the Manchester - Davyhulme Wastewater Treatment Plant, in a "mobile" pilot-plant. Most parts of the pilot-plant ...
Plant types
Aeration methods
The activated sludge process is a type of biological wastewater treatment process for treating sewage or industrial wastewaters using aeration and a biological floc composed of bacteria and protozoa. It uses air (or oxygen) and microorganisms to biologically oxidize organic pollutants, producing a waste sludge (or floc) containing the oxidized material. The general arrangement of a…
Recent developments
In a sewage (or industrial wastewater) treatment plant, the activated sludge process is a biological process that can be used for one or several of the following purposes: oxidizing carbonaceous biological matter, oxidizing nitrogenous matter: mainly ammonium and nitrogen in biological matter, removing nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus).
Issues
The process takes advantage of aerobic micro-organisms that can digest organic matter in sewage, and clump together (by flocculation) as they do so. It thereby produces a liquid that is relatively free from suspended solids and organic material, and flocculated particles that will readily settle out and can be removed.
The general arrangement of an activated sludge process for removing carbonaceous pollution i…
History
There are a variety of types of activated sludge plants. These include:
There are a wide range of types of package plants, often serving small communities or industrial plants that may use hybrid treatment processes often involving the use of aerobic sludge to treat the incoming sewage. In such plants the primary settlement stage of treatment may be omitted. In these plants, a biotic floc is created which provides the required substrate. Package plants are d…