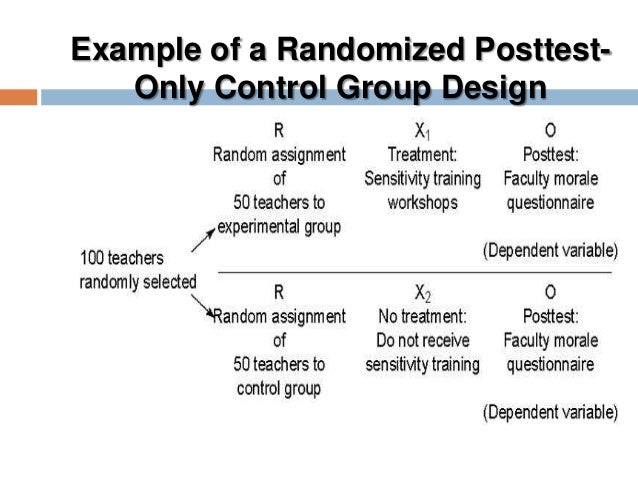
What is the experimental group in an experiment?
In a psychology experiment, the experimental group (or experimental condition) refers to the group of participants who are exposed to the independent variable. These participants receive or are exposed to the treatment variable. The data that are collected are then compared to the data from the control group, which did not receive the experimental treatment. 1 .
What are the treatment and control groups in a comparative experiment?
A control group is an experimental condition that does not receive the actual treatment and may serve as a baseline. A control group may receive a placebo or they may receive no treatment at all. A placebo is something that appears to the participants to be an active treatment, but does not actually contain the active treatment. For example, a placebo pill is a sugar pill that …
When subjects are randomly assigned to treatment or control groups?
A _____ group, which receives no treatment, allows researchers to determine if an experimental treatment has any effect. Scientists figure out if the findings support or disprove the hypothesis, scientists summarize the findings, and scientists seek to publish the results in scientific journals.
Which feature distinguishes experimental research from other types of research?
control group a comparison group that receives no treatment Post test in experimental research, the measurement of an outcome (dependent) variable after an experimental intervention or after a presumed independent variable has changes for some other reason. Pretest

What is a study that receives no treatment called?
Control group. A comparison group that receives no treatment. Posttest. In experimental research, the measurement of an outcome (dependent) variable after an experimental intervention or after a presumed independent variable has changed for some other reason.
What group receives no experimental treatment?
The control group is composed of participants who do not receive the experimental treatment. When conducting an experiment, these people are randomly assigned to be in this group.Oct 4, 2020
What is the control group?
control group, the standard to which comparisons are made in an experiment. Many experiments are designed to include a control group and one or more experimental groups; in fact, some scholars reserve the term experiment for study designs that include a control group.
When conducting an experiment the control group receives the treatment and the experimental group does not?
One group is exposed to the intervention (the experimental group, also known as the treatment group) and the other is not exposed to the intervention (the control group). In some cases, it may be immoral to withhold treatment from a control group within an experiment.
Which group receives the treatment?
experimental groupControl groups in experiments The treatment group (also called the experimental group) receives the treatment whose effect the researcher is interested in. The control group receives either no treatment, a standard treatment whose effect is already known, or a placebo (a fake treatment).Jul 3, 2020
What is experimental treatment in research?
1. in research, the conditions applied to one or more groups that are expected to cause change in some outcome or dependent variable. 2.
What is experimental group in research?
Put simply, an experimental group is the group that receives the variable, or treatment, that the researchers are testing whereas the control group does not. These two groups should be identical in all other aspects.Feb 22, 2022
What is experimental group?
In a psychology experiment, the experimental group (or experimental condition) refers to the group of participants who are exposed to the independent variable. These participants receive or are exposed to the treatment variable.Apr 24, 2020
What is control group and experimental group in research?
The control group and experimental group are compared against each other in an experiment. The only difference between the two groups is that the independent variable is changed in the experimental group. The independent variable is "controlled" or held constant in the control group.Jan 13, 2020
Is control group a treatment group?
In the design of experiments, treatments are applied to experimental units in a treatment group. In comparative experiments, members of a control group receive a standard treatment, a placebo, or no treatment at all. There may be more than one treatment group, more than one control group, or both.
What is treatment condition?
Quick Reference. In experimental design, a level of an independent variable or combination of levels of two or more independent variables. For example, in an experiment examining the effects of four different drugs on dreaming, research participants or subjects would receive a different drug in each treatment condition ...
What is the purpose of the placebo group?
The purpose of the placebo group in this study is to make the two groups equivalent except for the presence ...
What is ESC in medical terms?
ESC. A control group is an experimental condition that does not receive the actual treatment and may serve as a baseline. A control group may receive a placebo or they may receive no treatment at all. A placebo is something that appears to the participants to be an active treatment, but does not actually contain the active treatment.
What is an experimental group?
Experimental group. in an experiment, the group of subjects that receives the treatment or experimental manipulation. Comparison group. in an experiment, a group that has been exposed to a different treatment (or value of the independent variable) than the experimental group. control group.
What is the source of treatment misidentification in experiments and quasi-experiments?
Expectancies of experimental staff. A source of treatment misidentification in experiments and quasi-experiments that occurs when change among experimental subjects is due to the positive expectancies of the staff who are delivering the treatment rather than to the treatment itself; self-fulfilling prophecy.
What is the pretest in research?
in experimental research, the measurement of an outcome (dependent) variable prior to an experimental intervention or change in a presumed independent variable for some other reason. The pretest is exactly the same "test" as the post test, but it is administered at a different time.
What is a true experiment?
True experiment. Experiment in which subjects are assigned randomly to an experimental group that receives treatment or other manipulation of the independent variable, and a comparison group that does not receive the treatment or receives some other manipulation. Outcomes are measured in post test. Experimental group.
What is a quais-experimental design?
Quais-experimental design. a research design in which there is a comparison group that is comparable to the experimental group in critical ways, but subjects are not randomly assigned to the comparison and experimental groups. nonequivalent control group design.
What is treatment misidentification?
Treatment misidentification. a problem that occurs in an experiment when the treatment itself is not what causes outcome, but rather the outcome is caused by some intervening process that the researcher has not identified and is not aware of. selection bias.
What is matching in psychology?
Matching. a procedure for equating the characteristics of individuals in different comparison groups in an experiment. matching can be done on either an individual or an aggregate basis. For individual matching, individuals who are similar in terms of key characteristics are paired prior to assignment, and then the two members ...
What is the difference between experimental and control groups?
The experimental group gets the exposure/treatment which can be an agent involved in causation , prevention or treatment of a disease . The control group receives no treatment, a placebo treatment or another standard of care treatment depending on the objective of the study.
What is epidemiology research?
In epidemiology, researchers are interested in measuring or assessing the relationship of exposure with a disease or an outcome. As a first step, they define the hypothesis based on the research question and then decide which study design will be best suitable to answer that question. How the investigation is conducted by ...
What is a randomized control trial?
Randomized clinical trials or randomized control trials (RCT) are considered the gold standard of study design . In an RCT the researcher randomly assigns the subjects to a control group and an experimental group. Randomization in RCT avoids confounding and minimizes selection bias. This enables the researcher to have similar experimental and control groups thereby enabling them to isolate the effect of an intervention. The experimental group gets the exposure/treatment which can be an agent involved in causation, prevention or treatment of a disease. The control group receives no treatment, a placebo treatment or another standard of care treatment depending on the objective of the study. The groups are then followed prospectively to see who develops the outcome of interest. RCT’s are expensive, and researchers using this study design often face issues with the integrity of randomization due to refusals, drops outs, crossovers, and non-compliance.
What is cross sectional study?
Cross-sectional studies are observational in nature and give a snapshot of the characteristics of study subjects in a single point of time. Unlike cohort studies, cross-sectional studies do not have a follow-up period and therefore are relatively simple to conduct. As the exposure status and outcome of interest information is collected in ...
What is ecological fallacy?
The types of measures in ecological studies are aggregates of individual-level data. These studies, therefore, are subject to a type of confounding called ecological fallacy which occurs when relationships identified at group level data are assumed to be true for individuals.
What is relative risk in a cohort study?
Relative risk is the measure of effect for a cohort study. Cohort studies are subject to very low recall bias, and multiple outcomes can be studied simultaneously. One of the disadvantages of cohort studies is that they are more prone to selection bias.
What is a cohort study?
Cohort Studies. Cohort studies initially classify patients into two groups based on their exposure status. Cohorts are followed over time to see who develops the disease in the exposed and non-exposed groups. Cohort studies can be retrospective or prospective.
What distinguishes experimental research from other types of research?
The major feature that distinguishes experimental research from other types of research is that the researcher manipulates the independent variable. There are a number of experimental group designs in experimental research. Some of these qualify as experimental research, others do not.
What is quasi experimental research?
In this case, quasi-experimental research involves using intact groups in an experiment, rather than assigning individuals at random to research conditions. (some researchers define this latter situation differently.
Why does causal comparative research not meet the standards of an experiment?
It does not meet the standards of an experiment because the independent variable in not manipulated. The statistics by themselves have no meaning. They only take on meaning within the design of your study.
What is a regression class?
Regression (Statistical Regression) — A class that scores particularly low can be expected to score slightly higher just by chance. Likewise, a class that scores particularly high, will have a tendency to score slightly lower by chance. The change in these scores may have nothing to do with the treatment.
What is experimental research?
Commonly used in sciences such as sociology, psychology, physics, chemistry, biology and medicine, experimental research is a collection of research designs which make use of manipulation and controlled testing in order to understand casual processes.
What is it called when you drop out of an experiment?
If particular types of individuals drop out or refuse to participate more often than individuals with other characteristics, this is called differential attrition.
What is pre experimental design?
Pre-experimental design is a research format in which some basic experimental attributes are used while some are not. This factor causes an experiment to not qualify as truly experimental. This type of design is commonly used as a cost effective way to conduct exploratory research.
What are ethical issues in conducting experiments?
Ethical issues in conducting experiments relate to withholding the experimental treatment from some individuals who might benefit from receiving it, the disadvantages that might accrue from randomly assigning individuals to groups. This assignment overlooks the potential need of some individuals for beneficial treatment. Ethical issues also arise as to when to conclude an experiment, whether the experiment will provide the best answers to a problem, and considerations about the stakes involved in conducting the experiment.
Why is experimental research important?
The aim of experimental research is to predict phenomenons. In most cases, an experiment is constructed so that some kinds of causation can be explained. Experimental research is helpful for society as it helps improve everyday life.
What is the best method for establishing causation?
“The best method — indeed the only fully compelling method — of establishing causation is to conduct a carefully designed experiment in which the effects of possible lurking variables are controlled. To experiment means to actively change x and to observe the response in y” .
Why can't you do experiments?
Taking for instance a situation wherein you are enthusiastic about the effects of an individual’s culture or the tendency of helping strangers, you cannot do the experiment. The reason for this is simply because you are not capable of manipulating the individual’s culture.
What is treatment in comparative studies?
In comparative experiments, members of a control group receive a standard treatment, a placebo, or no treatment at all. There may be more than one treatment group, more than one control group, or both.
What is a clinical control group?
In a superiority trial, the clinical control group is the older medication rather than the new medication.
Is it statistically efficient to randomly assign twins?
In studies of twins involving just one treatment group and a control group, it is statistically efficient to do this random assignment separately for each pair of twins, so that one is in the treatment group and one in the control group.
Can a third control group be used to measure the placebo effect?
In such cases, a third, non-treatment control group can be used to measure the placebo effect directly, as the difference between the responses of placebo subjects and untreated subjects, perhaps paired by age group or other factors (such as being twins).
What is the primary way that researchers accomplish this kind of control of extraneous variables across conditions?
The primary way that researchers accomplish this kind of control of extraneous variables across conditions is called random assignment, which means using a random process to decide which participants are tested in which conditions. Do not confuse random assignment with random sampling.
Why are within-subjects experiments important?
Within-subjects experiments have the advantage of controlling extraneous participant variables, which generally reduces noise in the data and makes it easier to detect a relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
How to do a within subject experiment?
In a within-subjects experiment, each participant is tested under all conditions. Consider an experiment on the effect of a defendant’s physical attractiveness on judgments of his guilt. Again, in a between-subjects experiment, one group of participants would be shown an attractive defendant and asked to judge his guilt, and another group of participants would be shown an unattractive defendant and asked to judge his guilt. In a within-subjects experiment, however, the same group of participants would judge the guilt of both an attractive and an unattractive defendant.
What is a randomized clinical trial?
In research on the effectiveness of psychotherapies and medical treatments, this type of experiment is often called a randomized clinical trial. There are different types of control conditions. In a no-treatment control condition, participants receive no treatment whatsoever.
What is the strictest definition of random assignment?
In its strictest sense, random assignment should meet two criteria. One is that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to each condition (e.g., a 50% chance of being assigned to each of two conditions). The second is that each participant is assigned to a condition independently of other participants.
What is a treatment in psychology?
In psychological research, a treatment is any intervention meant to change people’s behavior for the better. This includes psychotherapies and medical treatments for psychological disorders but also interventions designed to improve learning, promote conservation, reduce prejudice, and so on.
What happens if participants in the treatment condition end up better off than participants in the control condition?
If participants in the treatment condition end up better off than participants in the control condition—for example, they are less depressed, learn faster, conserve more, express less prejudice—then the researcher can conclude that the treatment works.
