Symptoms
The cervical cancer guidelines ... and exploring other methods of control—such as immunotherapy—for advanced cancers. Prevention remains key While the new patient guidelines focus primarily on cancer treatment rather than prevention, NCCN continues ...
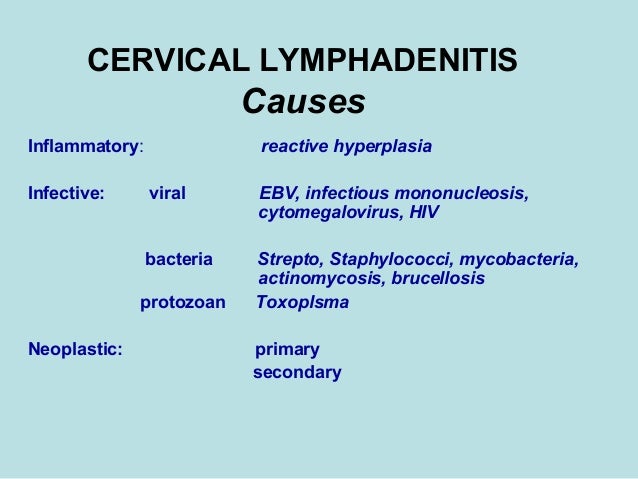
Causes
“This study provides a proof of concept of immunotherapeutic checkpoint inhibition in cervical cancer. If cemiplimab is approved, it will provide a second-line treatment option for women with recurrent cervical cancer,” Tewari said.
Prevention
Herbs For Cervical Cancer. Some herbs used in the treatment of cervical cancer include: #1. Tumeric. Tumeric is a member of the ginger family and has been used in the herbal medicine traditions and foods of India, China, Korea, and Japan for centuries. Tumeric is found in many anti-cancer formulas in traditional Chinese and Ayurvedic Medicine.
Complications
Top 5 Foods That Help to Prevent Cervical Cancer
- Carrots. Carrots are not just for the eyes: they contain both beta-carotene and carotenoids (a coincidence?) that directly defend against absorbing carcinogens into the body’s cells.
- Green Tea. Green Tea is a popular alternative drink that is also well known for its numerous health benefits in general.
- Beans. ...
- Lettuce. ...
- Whole Wheat Bread. ...
What are some common methods of cervical cancer treatment?
How do you cure cervical cancer?
What herbs are good for cervical cancer?
What is the natural diet for cervical cancer?

Can cervical cancer be cured completely?
Cervical cancer is curable, but it is difficult for doctors to know for sure that it will never come back following treatment. Therefore, doctors often use the term “remission” to describe cancer that has gone away and is no longer causing symptoms.
Is there any treatment for cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. If your doctor says that you have cervical cancer, ask to be referred to a gynecologic oncologist—a doctor who has been trained to treat cancers of a woman's reproductive system. This doctor will work with you to create a treatment plan.
What is the treatment for Stage 1 cervical cancer?
Stage 1 means that the cancer is only in the neck of the womb (cervix). The main treatment is surgery. You might also have combined radiotherapy and chemotherapy (chemoradiotherapy) if you have stage 1B cervical cancer.
What happens if you are diagnosed with cervical cancer?
The prognosis for invasive cervical cancer depends on the stage. More than 90% of women with stage 0 survive at least 5 years after diagnosis. Stage I cervical cancer patients have a 5-year survival rate of 80% to 93%. Women with stage II cervical cancer have a 5-year survival rate of 58% to 63%.
Will a hysterectomy cure cervical cancer?
Nearly half of cervical cancers are diagnosed at an early stage, meaning the tumors are small and have not spread beyond the cervix. Although there are other treatment options, radical hysterectomy is the most common treatment for early-stage disease, and cure rates for the disease are around 80%.
How long do you have to live if you have cervical cancer?
Survival for all stages of cervical cancer more than 60 out of every 100 (more than 60%) will survive their cancer for 5 years or more after diagnosis. more than 50 women out of every 100 (more than 50%) will survive their cancer for 10 years or more after diagnosis.
How long does it take for cervical cancer to go from Stage 1 to Stage 4?
Cervical cancer develops very slowly. It can take years or even decades for the abnormal changes in the cervix to become invasive cancer cells. Cervical cancer might develop faster in people with weaker immune systems, but it will still likely take at least 5 years.
What if cervical biopsy is positive?
However, if you recently had a cervical biopsy, you may need repeated Pap and HPV testing sooner. A positive test, on the other hand, means that cancer or precancerous cells have been found and further diagnosis and treatment may be needed.
What are the early warning signs of cervical cancer?
Early Warning Signs of Cervical CancerVaginal bleeding (either after intercourse, between periods or post-menopause)Abnormal vaginal discharge (heavy or with a foul odor)Pain during intercourse.Pelvic pain.Lower back pain.Pain and swelling in legs.Unexplained weight loss.Decreased appetite.
Does cervical cancer spread fast?
Usually, cervical cancer grows slowly, but sometimes it can develop and spread quickly. Cervical cancer is one of the cancers that can occur in young women.
Do you need chemo for cervical cancer?
As part of the main treatment for cervical cancer For some stages of cervical cancer, the preferred treatment is radiation and chemo given together (called concurrent chemoradiation). The chemo helps the radiation work better. Options for concurrent chemoradiation include: Cisplatin given weekly during radiation.
Is Stage 1 cervical cancer curable?
Stage I cervical cancer is curable for the majority of patients if surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy are appropriately used. A variety of factors ultimately influence a patient's decision to receive treatment of cancer.
What is the test for cervical cancer?
A Pap test can detect abnormal cells in the cervix, including cancer cells and cells that show changes that increase the risk of cervical cancer. HPV DNA test.
What is a punch biopsy?
Punch biopsy, which involves using a sharp tool to pinch off small samples of cervical tissue. Endocervical curettage, which uses a small, spoon-shaped instrument (curet) or a thin brush to scrape a tissue sample from the cervix.
What tests are done to determine if you have cervical cancer?
Your cancer's stage is a key factor in deciding on your treatment. Staging exams include: Imaging tests.
What is a wire loop?
Electrical wire loop, which uses a thin, low-voltage electrified wire to obtain a small tissue sample. Generally this is done under local anesthesia in the office. Cone biopsy (conization), which is a procedure that allows your doctor to obtain deeper layers of cervical cells for laboratory testing.
What is palliative care?
Palliative care is specialized medical care that focuses on providing relief from pain and other symptoms of a serious illness. Palliative care specialists work with you, your family and your other doctors to provide an extra layer of support that complements your ongoing care.
What is the instrument used to check for abnormal cells?
A special magnifying instrument (colposcope) is used to check for abnormal cells. During the colposcopic examination, your doctor is likely to take a sample of cervical cells (biopsy) for laboratory testing. To obtain tissue, your doctor may use:
What is cone shaped?
Typically, the cone-shaped piece includes tissue from both the upper and lower part of the cervix. If cervical cancer is suspected, your doctor is likely to start with a thorough examination of your cervix. A special magnifying instrument (colposcope) is used to check for abnormal cells. During the colposcopic examination, ...
How to treat cervical cancer?
Stage IVB cervical cancer is not usually considered curable. Treatment options include radiation therapy with or without chemo to try to slow the growth of the cancer or help relieve symptoms . Most standard chemo regimens include a platinum drug (cisplatin or carboplatin) along with another drug such as paclitaxel (Taxol), gemcitabine (Gemzar), or topotecan. The targeted drug bevacizumab (Avastin) may be added to chemo or immunotherapy alone with pembrolizumab (Keytruda) may also be an option.
What is the treatment for a tumor that has grown into blood vessels?
If the cancer has grown into blood or lymph vessels, one treatment option is a cone biopsy (with negative margins) with removal of pelvic lymph nodes. Another option is a radical trachelectomy along with removal of the pelvic lymph nodes.
What is stage IA1?
Stage IA1. Treatment for this stage depends on whether or not you want to be able to have children (maintain fertility) and whether or not the cancer has grown into blood or lymph vessels (called lymphova scular invasion).
What is the best treatment for cancer after birth?
Surgery options after birth for early-stage cancers include a hysterectomy, radical trachelectomy, or a cone biopsy. If the cancer is stage IB or higher, then you and your doctor must decide whether to continue the pregnancy. If not, treatment would be radical hysterectomy and/or radiation. Sometimes chemotherapy can be given during ...
What is the goal of cancer treatment?
No matter which type of treatment your doctor recommends, it's important that you understand the goal of treatment (to try to cure the cancer, control its growth, or relieve symptoms ), as well as its possible side effects and limitations.
What is the best treatment for pelvic cancer?
If the cancer has recurred in the center of the pelvis only, extensive surgery (s uch as pelvic exenteration) may be an option for some patients, and offers the best chance for possibly curing the cancer (although it can have major side effects). Radiation therapy (sometimes along with chemo) might be another option.
What is the procedure for a woman who wants to have children after cancer?
A cone biopsy is the preferred procedure for women who want to have children after the cancer is treated. If the edges of the cone don’t contain cancer cells (called negative margins), the woman can be watched closely without further treatment as long as the cancer doesn’t come back. If the edges of the cone biopsy have cancer cells (called ...
What is the difference between a gynecologic oncologist and a radiation oncologist
Different treatments may be provided by different doctors on your medical team. Gynecologic oncologists are doctors who have been trained to treat cancers of a woman’s reproductive system. Surgeons are doctors who perform operations. Medical oncologists are doctors who treat cancer with medicine. Radi ation oncologists are doctors who treat cancer ...
What is the treatment for cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. If your doctor says that you have cervical cancer, ask to be referred to a gynecologic oncologist —a doctor who has been trained to treat cancers of a woman’s reproductive system.
What is the treatment for a swollen vein?
Surgery: Doctors remove cancer tissue in an operation. Chemotherapy: Using special medicines to shrink or kill the cancer. The drugs can be pills you take or medicines given in your veins, or sometimes both.
What is the purpose of information about cancer?
Doctors use this information to plan treatment and to monitor progress.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment