
What should you consider about electroconvulsive therapy?
You can find more information about:
- Depression by clicking here.
- Bipolar disorder by clicking here.
- Schizophrenia by clicking here.
What are the side effects of electroconvulsive therapy?
What are the side effects of ECT?
- Memory loss. Many people experience memory loss after having ECT. Some people find this only lasts for a short time and their memories gradually return as they recover from ECT.
- Immediate side effects. You may experience other side effects immediately after treatment. ...
- Longer-term side effects. Was this page useful? ...
Is ECT worth it?
Is ECT worth it? – The effectiveness of ECT Researchers and healthcare professionals have observed the life-changing and life-saving benefits of electroconvulsive therapy for decades and some of them describe modern ECT as the fastest and most effective way for patients to completely recover from depression.
Should we stop using electroconvulsive therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) has a long history and pre-dates current drug treatments in psychiatry. It continues to attract controversy about the balance between its efficacy and adverse effects in a highly polarised debate (e.g. Read Reference Read, Cunliffe and Jauhar 2019b).. The review in this month's Review Corner (Read Reference Read, Cunliffe and Jauhar 2019a) is written from a ...
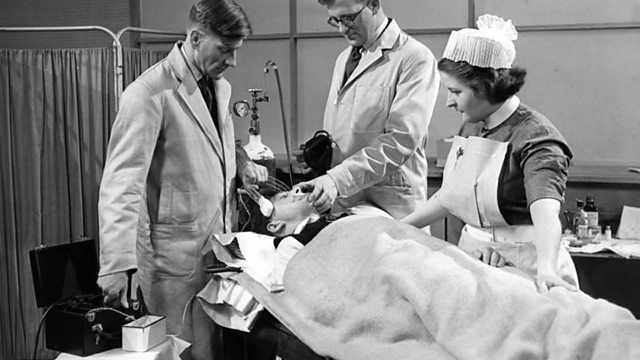
How does ECT work on the brain?
During ECT, a small amount of electrical current is passed through the brain while the patient is under general anesthesia. This current causes a seizure that affects the entire brain, including the parts that control mood, appetite, and sleep.
Is electroconvulsive therapy successful?
What is the Success Rate of Electroconvulsive Therapy? ECT is an effective medical treatment option, helping as many as 80-85 percent of patients who receive it. Most patients remain well for many months afterwards.
How long does it take for electroconvulsive therapy to work?
After two to three weeks, 71% of people who received ECT had a positive response to treatment. But only 28% who received the antidepressant had a positive response after four weeks of treatment.
Is electroconvulsive therapy still used today?
But electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is still being used -- more in Europe than the United States -- and it may be the most effective short-term treatment for some patients with depressive symptoms, a newly published review in the journal The Lancet suggests.
Why would electroconvulsive therapy be used?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: Severe depression, particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat.
Does electric shock therapy hurt?
No, the ECT procedure isn't painful. ECT involves general anesthesia, which means you're asleep while the procedure is happening. After the procedure, you may have some side effects, such as headache, nausea or sore muscles, but these are all normal.
What does electroconvulsive therapy feel like?
When you awaken, you may experience a period of disorientation lasting from a few minutes to several hours. Headaches, jaw pain, and muscle soreness may occur. ECT requires a series of treatments, often initiated two to three times a week for a few weeks and then the frequency is tapered down.
How does ECT reset the brain?
ECT, sometimes called shock therapy, is used mainly when antidepressant medication fails to treat severe depression. The procedure pushes small electric currents through the brain to trigger a brief seizure, which changes the brain's chemistry and, in many cases, reverses the symptoms of some types of mental illness.
Does ECT damage the brain?
The review of literature and present evidence suggests that ECT has a demonstrable impact on the structure and function of the brain. However, there is a lack of evidence at present to suggest that ECT causes brain damage.
What is the difference between electroshock therapy and electroconvulsive therapy?
Electroshock therapy, also known as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), is a treatment for severe major depression, bipolar depression, and other mental health conditions. Psychiatrists may recommend ECT when a person does not respond well to other treatments.
Do they shave your head for ECT?
During surgery prep, you'll have your head shaved. You may be kept unconscious throughout brain surgery with general anesthesia or stay awake with a local anesthetic used on your scalp. A sturdy frame will hold your head to prevent movement during surgery.
Why is ECT used as a last resort?
“The seizure is induced in a very controlled fashion, using a fairly precise delivery of an electric current.” Dr Davey says ECT is seen as a treatment option of last resort, to be used when nothing else has worked, or when there isn't time to find the right medication for a patient, a process that can take months.
How Does Electric Shock Treatment Work?
Patients under general anesthesia are given short bursts of electric pulses through nodes attached to the patient’s head. These small bursts of electricity trigger tiny seizures which, for reasons that have yet to be fully determined, can alleviate symptoms or even improve neurobiological health for longer-term relief. Here’s what is known so far:
What Is ECT Used To Treat?
Electroconvulsive therapy is most commonly used to treat severe depression. It has often been successful in the treatment of serious mental illness where other treatment methods have failed.
Electroconvulsive Therapy Side Effects
The most common side effects of ECT include confusion immediately after treatment (which only lasts a few hours at most and primarily only affects older adults) and memory loss. In most cases, the memory loss is temporary and short-term, leaving patients with difficulty recalling events immediately before treatment.
How does electroconvulsive therapy work?
How Electroconvulsive Therapy Works. With ECT, an electrical stimulation is delivered to the brain and causes a seizure. For reasons that doctors don't completely understand, this seizure helps relieve the symptoms of depression. ECT does not cause any structural damage to the brain.
How many ECT sessions are needed?
The number of required sessions varies. Many people have six to 12 sessions administered 2-3 times per week over a period of several weeks. After initial treatment, you might require further ECT treatments in addition to depression medicine and therapy to prevent your depression from returning.
What are the risks of ECT?
Risks and Side Effects of ECT. The most common side effect of ECT is short-term memory loss. However, some people report that they have long-term memory loss, as well. ECT also causes a brief rise in heart rate and blood pressure during the procedure, so it may not be recommended in people with unstable heart problems.
Does ECT work for depression?
Studies have shown that ECT works for many people who have treatment-resistant depression. One study of 39 people with treatment-resistant depression compared the effects of an antidepressant with ECT. After two to three weeks, 71% of people who received ECT had a positive response to treatment.
Does ECT cause brain damage?
ECT does not cause any structural damage to the brain. The procedure itself typically requires a stay in the hospital, although more and more it is being performed on an outpatient basis. During the procedure, you will be put to sleep under general anesthesia. You won't feel anything.
Is electroshock therapy a painless procedure?
In reality, it is a painless medical procedure performed under general anesthesia that is considered one of the most effective treatments for severe depression. It can be lifesaving.
Is ECT a life saving medication?
It can be lifesaving. ECT works quickly, which is why it's often the treatment of choice for people with highly severe, psychotic, or suicidal depression. For these people, waiting for antidepressants or therapy to work might be dangerous. However, the drawback is that the effects of ECT usually don't last, and further treatments will likely be ...
What is Electroconvulsive Therapy?
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment that involves sending brief electric currents to the brain, keeping the patient under general anesthesia. The whole process is operated by professional medical persons who have previous experience of doing this.
How Electroconvulsive Therapy Works?
In Electroconvulsive Therapy, small electric currents are sent to the brain. Those cause a seizure. Researchers haven’t found yet how the electric currents work to alter the symptoms of depression.
ECT Electrode Placement Techniques
Electroconvulsive Therapy includes the placement of electrodes near the brain of the patients. Depending on the point where to set the electrodes, ECT is divided into some common types. These are-
What is Electroconvulsive Therapy Used for?
Electroconvulsive Therapy is used to treat severe symptoms of some mental health issues. This is an effective therapy that has the ability to bring quick and significant improvement in mental health conditions.
How Long Does Electroconvulsive Therapy Last?
If you ask about the length of a single Electroconvulsive Therapy session, the answer is about 1 hour. This 1 hour includes the preparation for the therapy, time spent in the treatment room, and time spent in the recovery room.
How much does Electroconvulsive Therapy Cost?
Electroconvulsive Therapy is a costly therapy if you consider the cost of each session as it includes anesthesia and medical arrangement in each session. Let’s see the typical cost of ECT.
Is Electroconvulsive Therapy Safe?
Electroconvulsive Therapy is a great treatment option for people with mental health issues that medicine can’t cure. But as it includes the process of passing electricity through the brain, there is a question- is it safe?
Where is the Electroconvulsive Therapy Machine?
Electroconvulsive therapy machine on display at Glenside Museum in Bristol, England. ECT device produced by Siemens and used for example at the Asyl psychiatric hospital in Kristiansand, Norway from the 1960s to the 1980s.
What is ECT used for?
ECT is used to treat people who have severe or prolonged mania; NICE recommends it only in life-threatening situations or when other treatments have failed and as a second-line treatment for bipolar mania.
How many ECT machines are there in China?
As of 2012, there are approximately 400 ECT machines in China, and 150,000 ECT treatments are performed each year. Chinese national practice guidelines recommend ECT for the treatment of schizophrenia, depressive disorders, and bipolar disorder and in the Chinese literature, ECT is an effective treatment for schizophrenia and mood disorders. Although the Chinese government stopped classifying homosexuality as an illness in 2001, electroconvulsive therapy is still used by some establishments as a form of " conversion therapy ".
How long does it take for a person to relapse from ECT?
There is little agreement on the most appropriate follow-up to ECT for people with major depressive disorder. When ECT is followed by treatment with antidepressants, about 50% of people relapsed by 12 months following successful initial treatment with ECT, with about 37% relapsing within the first 6 months.
When did ECT become popular?
ECT became popular in the US in the 1940s. At the time, psychiatric hospitals were overrun with patients whom doctors were desperate to treat and cure. Whereas lobotomies would reduce a patient to a more manageable submissive state, ECT helped to improve mood in those with severe depression. A survey of psychiatric practice in the late 1980s found that an estimated 100,000 people received ECT annually, with wide variation between metropolitan statistical areas. Accurate statistics about the frequency, context and circumstances of ECT in the US are difficult to obtain because only a few states have reporting laws that require the treating facility to supply state authorities with this information. In 13 of the 50 states, the practice of ECT is regulated by law. In the mid-1990s in Texas, ECT was used in about one third of psychiatric facilities and given to about 1,650 people annually. Usage of ECT has since declined slightly; in 2000–01 ECT was given to about 1500 people aged from 16 to 97 (in Texas it is illegal to give ECT to anyone under sixteen). ECT is more commonly used in private psychiatric hospitals than in public hospitals, and minority patients are underrepresented in the ECT statistics. In the United States, ECT is usually given three times a week; in the United Kingdom, it is usually given twice a week. Occasionally it is given on a daily basis. A course usually consists of 6–12 treatments, but may be more or fewer. Following a course of ECT some patients may be given continuation or maintenance ECT with further treatments at weekly, fortnightly or monthly intervals. A few psychiatrists in the US use multiple-monitored ECT (MMECT), where patients receive more than one treatment per anesthetic. Electroconvulsive therapy is not a required subject in US medical schools and not a required skill in psychiatric residency training. Privileging for ECT practice at institutions is a local option: no national certification standards are established, and no ECT-specific continuing training experiences are required of ECT practitioners.
When was the ECT procedure first used?
The ECT procedure was first conducted in 1938 by Italian psychiatrist Ugo Cerletti and rapidly replaced less safe and effective forms of biological treatments in use at the time. ECT is often used with informed consent as a safe and effective intervention for major depressive disorder, mania, and catatonia.
Is electroconvulsive therapy required in medical school?
A few psychiatrists in the US use multiple-monitored ECT (MMECT), where patients receive more than one treatment per anesthetic. Electroconvulsive therapy is not a required subject in US medical schools and not a required skill in psychiatric residency training.
What is the treatment for ECT?
This typically means psychotherapy and/or medication or, in some circumstances, ongoing ECT treatments.
What is ECT therapy?
What is Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)? Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment most commonly used in patients with severe major depression or bipolar disorder that has not responded to other treatments. ECT involves a brief electrical stimulation of the brain while the patient is under anesthesia.
How often is TMS given?
TMS is usually administered four or five times a week for four-to-six weeks. Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) was developed as a treatment for seizure disorders but can also be used to treat depression that has not responded to other therapies.
What are the side effects of ECT?
The most common side effects of ECT on the day of treatment include nausea, headache, fatigue, confusion, and slight memory loss, which may last minutes to hours.
How long does a seizure last after a brain surgery?
The patient's brain is stimulated with a brief controlled series of electrical pulses. This causes a seizure within the brain that lasts for approximately a minute. The patient is asleep for the procedure and awakens after 5-10 minutes, much as from minor surgery.
What is consent process?
In situations where a person is too ill to make decisions for him or herself, the consent process is governed by state law (for example, a court-appointed guardian). Patients and their families should discuss all options for treatment with the psychiatrist before making a specific treatment decision.
Does TMS cause seizure?
It involves the use of rapidly alternating magnetic fields to stimulate specific areas of the brain. Unlike ECT, TMS does not cause a seizure and the patient remains awake through the noninvasive process. TMS typically only has mild side effects including headaches, muscle twitches and pain at the stimulation site.

Why It's Done
Risks
Self help information for family, friends and colleagues
- Loosen tight clothing
- Protect the person from injury
- If they have fallen, place something soft under their head
- Stay with them until they recover fully
Do not:
- Try to restrain the person
- Put anything between their teeth
- Move them, unless they are in danger
- Give them food to eat or drink
Person who have had seizure
- Avoid triggers
- Avoid unprotected heights and unsupervised areas of water
- Seizure lasts less than 5 minutes
- None of the below mentioned incidents occur during the episode
See a doctor immediately if you notice:
- Seizure lasts longer than five minutes
- Breathing or consciousness doesn't return after the seizure stops
- A second seizure follows immediately
- The seizure happened in water
- High fever
- Heat exhaustion
- Person is pregnant
- Person has diabetes
- Person is injured during the seizure
How You Prepare
What You Can Expect
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: 1. Severe depression,particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to e…
Results
- Although ECT is generally safe, risks and side effects may include: 1. Confusion.Immediately after treatment, you may experience confusion, which can last from a few minutes to several hours. You may not know where you are or why you're there. Rarely, confusion may last several days or longer. Confusion is generally more noticeable in older adults. 2. Memory loss.Some people hav…