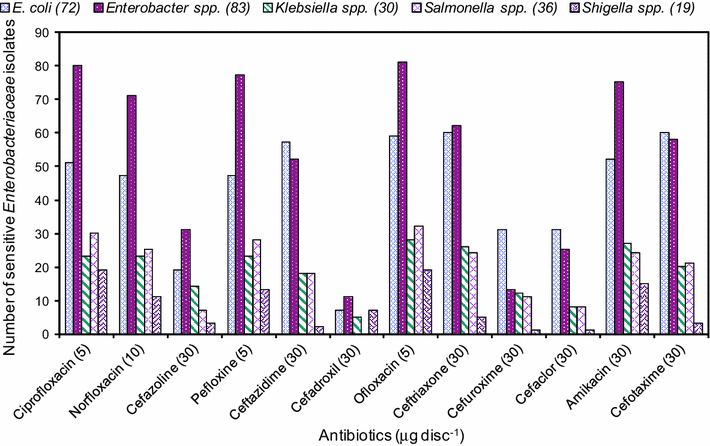
We further demonstrated that while wastewater treatment significantly reduced the abundance of integrons and the diversity of associated gene cassettes, a large fraction of integrons persisted in wastewater effluents and were consequentially discharged into downstream natural environments.
Full Answer
Does wastewater treatment affect the diversity of integrons in plant cells?
We further demonstrated that while wastewater treatment significantly reduced the abundance of integrons and the diversity of associated gene cassettes, a large fraction of integrons persisted in wastewater effluents and were consequentially discharged into downstream natural environments.
How can ecosystems and biodiversity help water management?
Some specific objectives of water management that ecosystems and biodiversity can assist in achieving are: Urban water management - Protecting biodi- versity, natural vegetation and other ecosystem attributes in catchment areas is part of proper land-use management.
What is IUCN doing to support freshwater biodiversity?
Through the EU-funded BIOFRESH project, IUCN is providing key scientific data on the status and trends of global freshwater biodiversity to develop an information platform for scientists and ecosystem managers from around the world. IUCN is also supporting biodiversity research for the Trans-boundary Waters Assessment Programme (TWAP).
Does genetic diversity make populations more resistant to disease?
So much for survival of the fittest – diversity is the key: a team of researchers from the Leibniz-Institute of Freshwater Ecology and Inland Fisheries (IGB) has succeeded in demonstrating experimentally that genetic diversity makes populations more resistant to disease.
Why is surface water treated differently than ground water?
Why do people use water treatment units?
How does a water treatment unit work?
What are the steps of water treatment?
What is a water softener?
What is the most common type of water treatment system?
Why is chlorine added to water?
See more
About this website

Drinking Water Standards and Regulations | Public Water Systems ...
Education and information about water regulations, water standards, Safe Drinking Water Act, Surface Water Treatment Rule, National Primary Drinking Water Regulations (NPDWR), National Secondary Drinking Water Regulations (NSDWR), Unregulated Contaminants and Bottled Water.
Surface Water Treatment Rules | US EPA
Rule History. EPA has developed the Surface Water Treatment Rules (SWTRs) to improve your drinking water quality. The regulations provide protection from disease-causing pathogens, such as Giardia lamblia,Legionella, and Cryptosporidium.The regulations also protect against contaminants that can form during drinking water treatment.
Lecture 8: Water treatment processes - IIT Delhi
Treatment schematic (SW Potable drinking water) • Sequence of unit processes: pre-sedimentation mixing, flocculation, settling filtration adsorption disinfection
Abstract
Crop yield of monoecious species like maize (Zea mays L) relies on simultaneous flowering of male and female inflorescences to ensure pollination. Yet productivity may be reduced if environmental conditions reduce floral synchrony or if plants within a field do not overlap sufficiently in flowering periods.
References (43)
Agroecology derives much of its strength from interactions between disciplines that produce a holistic perspective on agricultural systems and issues.
Why is surface water treated differently than ground water?
Typically, surface water requires more treatment and filtration than ground water because lakes, rivers, and streams contain more sediment and pollutants and are more likely to be contaminated than ground water.
Why do people use water treatment units?
Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: Remove specific contaminants. Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system. Improve the taste of drinking water.
How does a water treatment unit work?
Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: 1 Remove specific contaminants 2 Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system 3 Improve the taste of drinking water
What are the steps of water treatment?
Today, the most common steps in water treatment used by community water systems (mainly surface water treatment) include: Coagulation and flocculation are often the first steps in water treatment. Chemicals with a positive charge are added to the water.
What is a water softener?
Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water. A water softener typically uses sodium or potassium ions to replace calcium and magnesium ions, the ions that create “hardness.”. Distillation Systems.
What is the most common type of water treatment system?
The most common types of household water treatment systems consist of: Filtration Systems. A water filter is a device which removes impurities from water by means of a physical barrier, chemical, and/or biological process. Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water.
Why is chlorine added to water?
After the water has been filtered, a disinfectant (for example, chlorine, chloramine) may be added in order to kill any remaining parasites, bacteria, and viruses, and to protect the water from germs when it is piped to homes and businesses.
How many species depend on freshwater habitats?
All of these services from nature contribute to our water security, our health and our livelihoods. “IUCN scientists estimate that up to one million species rely on freshwater habitats and millions more, including human beings, rely on food, freshwater and many other services supplied by these precious ecosystems,” says Julia Marton-Lefèvre, ...
Why is water important to life?
Water is life. Our well-being, food security, health, sanitation and most economic activities directly depend on it – but it is nature that makes it possible for us to use it. Nature provides us with infrastructure that complements man-made levees, dams, canals and reservoirs in a cost-effective and sustainable way.
What are the three things that help us store water?
Aquifers, soils, lakes and wetlands store water. Wetlands and soils filter it. Rivers transport it. Floodplains and wetlands lower flood peaks in downstream cities. Mangroves, coral reefs protect coasts against storms and flooding. All of these services from nature contribute to our water security, our health and our livelihoods.
What is the theme of the International Day of Biological Diversity?
Today we celebrate the International Day for Biological Diversity. Its theme, Water and Biodiversity, coincides with the designation of 2013 as the International Year of Water Cooperation and highlights the indispensible role of nature in our water security and the sustainable development of our planet.
What happens when ecosystems degrade?
Where ecosystems degrade, biodiversity is lost and so is the precious natural infrastructure we depend on. If we fail to account for ecosystem services - invest in them, protect them and sustain them – we will no longer be able to rely on them for our water security and sustainable development. If we invest in nature and its services, it will offer us solutions for water security and other development challenges.
Why is genetic diversity important?
Genetic diversity helps protect against disease. So much for survival of the fittest – diversity is the key: a team of researchers from the Leibniz-Institute of Freshwater Ecology and Inland Fisheries (IGB) has succeeded in demonstrating experimentally that genetic diversity makes populations more resistant to disease.
How does genetic diversity affect cyanobacteria?
Genetic diversity in the host population slows down adaptation of parasites. If, on the other hand, the cyanobacteria were genetically diverse, these effects did not occur. The parasite failed to adapt, and the state of the disease remained unchanged.
Why do animal and plant species have different genetic variants?
Why is it that animal and plant species throughout the world have different genetic variants within their particular species, even though it is supposed to be the "fittest" gene pool that survives? According to a common theory in evolutionary biology, it is to enable the species to respond more effectively to changes in the environment, such as the occurrence of disease. However, experimental evidence to support this theory is very difficult to obtain: After all, it is virtually impossible to observe how evolutionary trends develop in most animal and plant species – their generation times are simply too long.
Why did the alpine marmot lose its genetic diversity?
After combining the results of comprehensive genetic analyses with data from fossil records, the researchers came to the conclusion that the alpine marmot lost its genetic diversity as a result of multiple climate-related adaptations during the last ice age.
What does lack of genetic variation mean?
After all, a lack of genetic variation can mean a reduced ability to adapt to change, rendering the affected species more susceptible to both diseases and altered environmental conditions -- including changes in the local climate.".
Why did they study the alpine marmot?
The researchers originally set out to study the alpine marmot's genome in order to gain a better understanding of the animal's lipid metabolism.
Did marmots survive the Ice Age?
It is possible that low genetic diversity played a role in this.". Outlining his plans for further research, he adds: "An important next step would be to study other animals more closely which, like the alpine marmot, managed to survive the ice age.
Is genetic diversity a key indicator of extinction?
Feb. 23, 2021 — Scientists have challenged the common assumption that genetic diversity of a species is a key indicator of extinction risk. The scientists demonstrate that there is no simple relationship between ...
Is the genetic diversity of a mammal lower than that of any other mammal?
In fact, the animal's genetic diversity is lower than that of any other wild mammal whose genome has been genetically sequenced. "We were very surprised by this finding. Low genetic diversity is primarily found among highly endangered species such as, for instance, the mountain gorilla.
Is the alpine marmot genetically diverse?
Results were unexpected: the species was found to be the least genetically diverse of any wild mammal studied to date. The alpine marmot has lost its genetic diversity during ice-age related climate events and been unable to recover its diversity since.
Why is surface water treated differently than ground water?
Typically, surface water requires more treatment and filtration than ground water because lakes, rivers, and streams contain more sediment and pollutants and are more likely to be contaminated than ground water.
Why do people use water treatment units?
Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: Remove specific contaminants. Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system. Improve the taste of drinking water.
How does a water treatment unit work?
Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: 1 Remove specific contaminants 2 Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system 3 Improve the taste of drinking water
What are the steps of water treatment?
Today, the most common steps in water treatment used by community water systems (mainly surface water treatment) include: Coagulation and flocculation are often the first steps in water treatment. Chemicals with a positive charge are added to the water.
What is a water softener?
Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water. A water softener typically uses sodium or potassium ions to replace calcium and magnesium ions, the ions that create “hardness.”. Distillation Systems.
What is the most common type of water treatment system?
The most common types of household water treatment systems consist of: Filtration Systems. A water filter is a device which removes impurities from water by means of a physical barrier, chemical, and/or biological process. Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water.
Why is chlorine added to water?
After the water has been filtered, a disinfectant (for example, chlorine, chloramine) may be added in order to kill any remaining parasites, bacteria, and viruses, and to protect the water from germs when it is piped to homes and businesses.