Viral load tests are used to diagnose acute HIV infection, give health care providers treatment guidance, and monitor patient response to antiretroviral therapy (ART). The more HIV-1 viral particles in the blood, the faster the patient’s CD4+ T-cells are destroyed and the faster the progress toward AIDS.
How does HIV treatment work?
The main aim of HIV treatments is to reduce the viral load to the point where there are so few copies of the virus left that it is undetectable in the blood. When doctors say a person has detectable levels of HIV in a viral load test, it means there is a significant amount of HIV in their blood.
What is HIV viral load and how is It measured?
An HIV viral load is the amount of HIV measured in a volume of blood. The goal of HIV treatment is to lower viral load to be undetectable. That is, the goal is to reduce the amount of HIV in the blood enough so that it can’t be detected in a laboratory test. For people living with HIV, it can be helpful to know their own HIV...
What does it mean when your viral load is high?
When doctors say a person has detectable levels of HIV in a viral load test, it means there is a significant amount of HIV in their blood. This level will vary based on the stage of the condition and the stage of treatment. On first diagnosis of HIV, a person’s viral load is typically high.
What happens to viral load when HIV is not treated?
Shortly after contracting HIV, the viral load will drop as the immune system starts to fight the virus. Without treatment, the viral load will rise again as the virus starts to destroy specific immune system cells known as CD4 cells.

What does viral load have to do with HIV?
Viral load is the amount of HIV in the blood. A viral load test shows how much of the virus is in the body by measuring how many particles of HIV are in a blood sample. The results are given as the number of copies of HIV per millilitre of blood – for example 200 copies/ml.
How do you treat a viral load?
These steps may include:Taking antiretroviral medication regularly and as directed. When taken properly, antiretroviral medication reduces viral load, thus decreasing the risk of transmitting HIV to others. ... Getting tested for STIs. ... Using condoms during sex. ... Considering PrEP. ... Considering PEP. ... Getting tested regularly.
How is monitoring the viral load useful for management of HIV therapy?
Regular viral load measurements help to detect treatment failure earlier and may therefore reduce mortality and HIV transmission.
Does HIV treatment decrease viral load?
If taken as prescribed, HIV medicine reduces the amount of HIV in the body (viral load) to a very low level, which keeps the immune system working and prevents illness. This is called viral suppression—defined as having less than 200 copies of HIV per milliliter of blood.
What is the difference between viral load and CD4 count?
CD4 and viral load test results give essential information about the effect HIV is having on your body. A CD4 count tells you how many CD4 cells there are in a drop of blood. The more there are, the better. Viral load measures how much HIV there is in a drop of blood.
What is meant by viral load?
Viral load refers to the amount of virus that can be detected in an infected person. High viral loads are concerning because they can mean the person is more infectious.
How does a viral load test work?
Viral load tests measure the amount of HIV in a blood sample. This is reported as the number of copies of HIV per millilitre (copies/mL). Information about units of measure for blood tests. When viral load is very low on treatment (less than 200 copies/mL), the risk of transmission during sex becomes zero.
Why is viral load test done?
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Hepatitis Testing HIV viral load test indicates viral replication and is often conducted to monitor progress of antiretroviral therapy. In addition, CD4 lymphocyte counts are also measured to evaluate the immune system.
What makes viral load to increase?
Vaccinations, such as a flu jab, and infections can cause a temporary increase in your viral load. Talk to your doctor about whether you should delay your next viral load test – sometimes it is recommended to wait at least one month after having a vaccination or getting over an infection.
How is viral load calculated?
Viral load and how it is measured There are three main tests used to measure viral load. These are reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) tests, branched DNA (bDNA) tests, and nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NASBA) tests.
When is viral load highest?
What does seem clear is that people with symptoms of COVID-19 are more contagious. And that the viral load tends to peak in the week after their symptoms first appear.
What is the name of the new ARV pill?
The backbone of the new pill is dolutegravir, a remarkably powerful and safe ARV that inhibits HIV's integrase enzyme and has been too expensive for most poor and middle-income countries to afford.
What does it mean when a person has a higher number of CD4 cells?
Higher numbers of CD4 cells indicate that the person’s immune system is stronger and better able to fight off infections. When the viral load reaches less than 200 copies/ml of blood, doctors consider that HIV is undetectable.
What does it mean when a person has an undetectable viral load?
. An undetectable viral load means that a person has effectively zero risk of sexually transmitting the virus to an HIV-negative partner.
What is antiretroviral therapy?
Antiretroviral therapy aims to reduce a person’s viral load to undetectable levels. This is known as viral suppression. After starting antiretroviral therapy, a person’s HIV viral load tests will come back with low numbers. When this occurs, the treatment is working, and HIV is no longer progressing.
What happens to the viral load after HIV diagnosis?
Shortly after contracting HIV, the viral load will drop as the immune system starts to fight the virus. Without treatment, the viral load will rise again as the virus starts to destroy specific immune system cells known as CD4 cells.
What does it mean when you have a viral load test?
When doctors say a person has detectable levels of HIV in a viral load test, it means there is a significant amount of HIV in their blood. This level will vary based on the stage of the condition and the stage of treatment. On first diagnosis of HIV, a person’s viral load is typically high.
How does HIV affect CD4 cells?
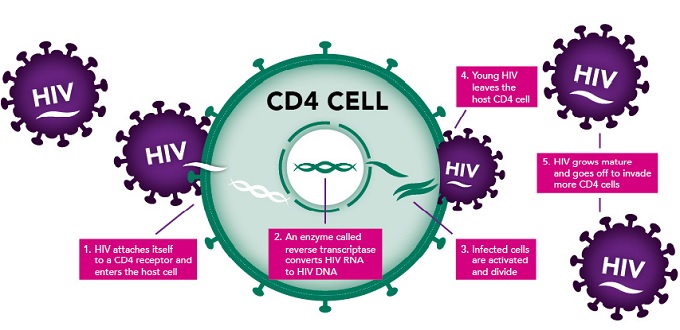
HIV hijacks the cellular machinery of CD4 cells to reproduce and shed more HIV, which means the viral load increases . As the HIV viral load increases, the number of healthy CD4 cells decreases as they are destroyed creating HIV copies . Treatment aims to produce a low viral load and a high CD4 count.
What does HIV treatment mean?
HIV treatments aim to reduce the viral load until the virus is no longer detectable, which mean it is also untransmittable . In this article, we discuss what viral load means for people living with HIV and their partners, the links between viral load and CD4 levels, and how doctors test and monitor these levels.
How many copies of HIV RNA can be found in a milliliter of blood?
They can find as few as 20 copies of HIV RNA in a milliliter of blood. Your doctor should use the same HIV viral load test each time, because tests made by different manufacturers might give you slightly different results. If your viral load changes, you want to be confident it's from what's happening inside you, not skewed by the testing method.
What is HIV test?
The test measures the number of HIV copies in a milliliter of blood. Your test results help your doctor follow what's happening with your infection, how well your treatment is working, and guide treatment choices. HIV viral load predicts how fast the disease will progress, while other tests, like the CD4 count, ...
How long does it take for a drug test to work?
When you start or change medicine, a test about 4 weeks afterwards helps your doctor decide how well it's working. An effective drug combination, taken as prescribed, can often drop the HIV viral load to one-tenth of what it was within a month.
Can you take condoms with HIV?
Continuing to take your medicine as prescribed to keep the virus undetectable is very important. When your HIV viral load is undetec table, there is little to no risk of infecting others, but most doctors still advise using condoms to prevent acquiring other strains of HIV and other sexually transmitted infections.
Can HIV antibodies be used to diagnose HIV?
The test can also help diagnose recent HIV infection in someone with inconclusive HIV antibody tests. However, in these cases, a subsequent positive HIV antibody test should be used to confirm the diagnosis. Keeping your viral load low will keep your immune system healthy, make complications of HIV less likely and help you live longer.
Does HIV help you live longer?
Keeping your viral load low will keep your immune system healthy, make complications of HIV less likely and help you live longer. It is possible if you adhere to your treatment to obtain a normal, or near-normal life expectancy.
Can HIV be detected?
The virus probably isn't actively reproducing as fast, and damage to your immune system may be slowed, but this is not optimal. A viral load that can't be detected -- less than 20 copies -- is always the goal of HIV treatment. This doesn't mean you're cured.
What is the goal of HIV treatment?
Generally, the higher the HIV viral load, the more CD4+ T-cells are being destroyed. The goals of HIV treatment are to keep CD4+ T-cell count high and viral load low. Routine viral load tests improve treatment quality and individual health outcomes for people living with HIV.
What is a viral load test?
Viral load tests are used to diagnose acute HIV infection, give health care providers treatment guidance, and monitor patient response to antiretroviral therapy (ART). The more HIV-1 viral particles in the blood, the faster the patient’s CD4+ T-cells are destroyed and the faster the progress toward AIDS.
What is the most important marker of treatment response?
Among patients on antiretroviral therapy, HIV viral load is the most important marker of treatment response. All patients should have their viral load measured at diagnosis and regularly thereafter. Increased or detectable viral loads in a patient on antiretroviral therapy indicates either nonadherence (most common) or development of drug resistance.
Where does HIV replication occur?
HIV replication occurs primarily in lymphoid tissue, but high levels of viremia can be detected in infected individuals. Early studies made it clear that the level of viremia at the "set point" (ie, after acute infection, but prior to significant immune decline) was associated with the rate of CD4 cell loss and hence the time to AIDS and death.
What is the ELISA technique?
Schematic of enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) technique. 1) viral antigen is bound to a solid substrate. 2) Patient serum with specific antibodies is added and binds to the antigen. 3) After removal of excess antibody, a detection antibody is added, to confirm binding of patient antibodies. of 1.
What is PCR in amplification?
Most rely on some form of nucleic acid amplification such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Internal standards of amplification targets of known concentration are compared to patient specimens in order to provide quantitation of viral load.
What is viral load?
Viral load can be considered a quantitative measure of viral RNA genomes in the peripheral circulation. The most common assays involve reverse transcription to convert viral RNA (which is readily destroyed by ubiquitous RNAses) to more easily manipulated DNA.
Why is nucleic acid amplification important?
Because nucleic acid amplification techniques are incredibly sensitive, it is crucial to avoid contamination of specimens in the laboratory. Not only is the specific quantitative analysis of viral load important in clinical management, but qualitative viral load tests are used in screening of blood donations.
What test can help determine if you have HIV?
If you receive a diagnosis of HIV / AIDS, several tests can help your doctor determine the stage of your disease and the best treatment, including: CD4 T cell count. CD4 T cells are white blood cells that are specifically targeted and destroyed by HIV. Even if you have no symptoms, HIV infection progresses to AIDS when your CD4 T cell count dips ...
What is HIV RNA?
Viral load (HIV RNA). This test measures the amount of virus in your blood. After starting HIV treatment the goal is to have an undetectable viral load. This significantly reduces your chances of opportunistic infection and other HIV -related complications.
How long does it take to get tested for HIV?
Most rapid HIV tests, including self-tests done at home, are antibody tests. Antibody tests can take three to 12 weeks after you're exposed to become positive. Nucleic acid tests (NATs). These tests look for the actual virus in your blood (viral load). They also involve blood drawn from a vein.
What are some examples of anti-HIV drugs?
Examples include efavirenz (Sustiva), rilpivirine (Edurant) and doravirine (Pifeltro).
What is the treatment for HIV?
However, there are many medications that can control HIV and prevent complications. These medications are called antiretroviral therapy (ART). Everyone diagnosed with HIV should be started on ART, regardless of their stage of infection or complications.
How to diagnose HIV?
Diagnosis. HIV can be diagnosed through blood or saliva testing. Available tests include: Antigen/antibody tests. These tests usually involve drawing blood from a vein. Antigens are substances on the HIV virus itself and are usually detectable — a positive test — in the blood within a few weeks after exposure to HIV.
What to do if you think you have HIV?
If you think you might have HIV infection, you're likely to start by seeing your family doctor. You may be referred to an infectious disease specialist — who additionally specializes in treating HIV / AIDS.
How long does it take for ART to become undetectable?
After starting ART viral load should then become undetectable (less than 50 copies/mL) within three months. Some people become undetectable after only a month. For some people this takes longer. How quickly viral load becomes undetectable depends on three main factors. How high viral load is when ART is started.
How long does it take for HIV to show symptoms?
Chronic infection. Chronic infection describes HIV infection after the first six months. Chronic infection can last for many years. It can take from 2-10 years until the majority of people get symptoms from having a damaged immune system.
What is the effect of Integrase inhibitors on HIV?
Which HIV drugs are in the combination. Integrase inhibitors reduce viral load quicker that other types of HIV drugs. A few weeks after infection, HIV viral load shoots up to very high levels. This is when someone is most infectious. Then your body fights back.
How long does it take for a virus to be detected?
The immune system reacts to viral load in the blood by producing antibodies to fight HIV. It usually takes 1-3 months after infection for antibodies to HIV to be strong enough to be detected on an HIV antigen test. Occasionally it can take longer.
What are the symptoms of HIV?
HIV can cause a range symptoms that include night sweats, fevers, weakness and tiredness and, more rarely, mouth ulcers.
How long does it take for HIV to multiply?
It then takes several hours for these newly infected cells to carry HIV to the lymph nodes. During the next few days or weeks, HIV continues to multiply in the lymph nodes. Lymph nodes packed with CD4 cells, which HIV uses to reproduce.
What happens after HIV builds up in the lymph nodes?
Seroconversion. After building up in the lymph nodes, the nodes burst sending HIV into the blood. This sends HIV throughout the body. HIV levels (viral load) become detectable in blood and reaches very high levels (often millions of copies/mL).