
Hydroxychloroquine is effective in the long-term treatment of NPSLE. Immunosuppressive medicines help inhibit the activity of the immune system, which can be useful in treating NPSLE. Corticosteroids and other immunosuppressants are effective against active lupus.
Full Answer
What is an effective treatment for systemic lupus?
What's New in the Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Introduction. ...
- The Cellular Approach. ...
- The Cytokines Approach. ...
- Selective Inhibition of Intracellular Biochemical Pathways. ...
- Ongoing Clinical Trials. ...
- Other Potential Therapeutic Targets. ...
- Discussion. ...
- Author Contributions. ...
- Conflict of Interest. ...
- References. ...
How do you get systemic lupus erthematosus?
- use high-factor (50+) sunscreen – you can get it on prescription if you have lupus
- learn to pace yourself to avoid getting too tired
- try to stay active even on a bad day
- try relaxation techniques to manage stress – stress can make symptoms worse
- wear a hat in the sun
What is the best medicine for lupus?
- NSAIDs. These common drugs -- like aspirin, ibuprofen, naprosyn, or indomethacin, help reduce swelling, stiffness, and pain. ...
- Antimalarial drugs. ...
- Benlysta. ...
- Corticosteroids. ...
- Immunosuppressive drugs. ...
- New and experimental medications. ...
- Other medications. ...
What medications are used to treat lupus?
Saphnelo approved in the EU for the treatment of moderate to severe systemic lupus erythematosus
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). ...
- American College of Rheumatology. Guidelines for referral and management of systemic lupus erythematosus in adults. ...
- Touma Z, et al. ...
- Cornet A, et al. ...
- Morand EF, et al. ...
- Furie R, et al. ...
- Furie R, et al. ...
- Al Sawah S, et al. ...
- Kabadi S, et al. ...
- ClinicalTrials.gov. ...
How do immunosuppressants help lupus?
Immunosuppressants such as azathioprine, cyclophosphamide and methotrexate reduce lupus symptoms by lowering immune system activity. Azathioprine is used to treat lupus and is also used in the management of other immune diseases and organ transplantation.
What is used in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus?
Hydroxychloroquine should be used in all patients with lupus unless contraindicated. It is an antimalarial drug that inhibits toll-like receptors 7 and 9. These are potent drivers of type 1 interferon production. Hydroxychloroquine is useful in both cutaneous and systemic lupus.
Why is a patient given immunosuppressants to fight off lupus?
In people with lupus, the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues. Most immunosuppressives work to downregulate (suppress) this attack by interfering with the synthesis of DNA, the material in your cells that contains the blueprints for all of your genetic information.
How do immunosuppressive drugs work?
Immunosuppressants work in the following ways: They suppress or inhibit the immune system's activity and prevent it from attacking the transplanted organ, as it attacks any foreign cells, which could otherwise lead to severe damage to the organ. They stop the immune system from damaging healthy cells and tissues.
What is the most common treatment for lupus?
Lupus is mainly treated with medicine. The types of drugs that have been used to treat lupus include NSAIDs, corticosteroids and other immune system suppressing drugs, hydroxychloroquine, and the newest lupus drug, Benlysta.
What is the first treatment for lupus?
Early Progress With Lupus Treatment Involves Antimalarials and Corticosteroids. The first medication used for lupus, quinine (an antimalarial), was described by Payne in 1894 (Payne, 1894).
What to avoid while on immunosuppressants?
Basic Guidelines to Follow Avoid unpasteurized beverages, such as fruit juice, milk and raw milk yogurt. Avoid salad bars and buffets. Refrigerate pate, cold hot dog or deli meat (including dry-cured salami and deli prepared salads containing these items), eggs or seafood.
What is the most common side effect of immunosuppressive medications?
The most significant side effect of immunosuppressant drugs is an increased risk of infection. Other, less serious side effects can include loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, increased hair growth, and hand trembling. These effects typically subside as the body adjusts to the immunosuppressant drugs.
What are the three classes of immunosuppressant drugs?
Types of immunosuppressantsInduction immunosuppression. This approach includes all medications given immediately after transplantation in intensified doses for the purpose of preventing acute rejection. ... Maintenance immunosuppression. ... Anti-rejection immunosuppression.
Which drug is commonly used for immunosuppression?
Calcineurin Inhibitors: Tacrolimus and Cyclosporine. Antiproliferative agents: Mycophenolate Mofetil, Mycophenolate Sodium and Azathioprine. mTOR inhibitor: Sirolimus. Steroids: Prednisone.
Which conditions are treated using immunosuppressive therapy?
Immunosuppressive therapy conditions treatedInflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease and Ulcerative Colitis)Multiple sclerosis.Aplastic anemia.Lupus.Rheumatoid arthritis.Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS)
Why immunosuppressive drugs are used?
Immunosuppressant drugs are used to treat autoimmune diseases. With an autoimmune disease, the immune system attacks the body's own tissue. Because immunosuppressant drugs weaken the immune system, they suppress this reaction. This helps reduce the impact of the autoimmune disease on the body.
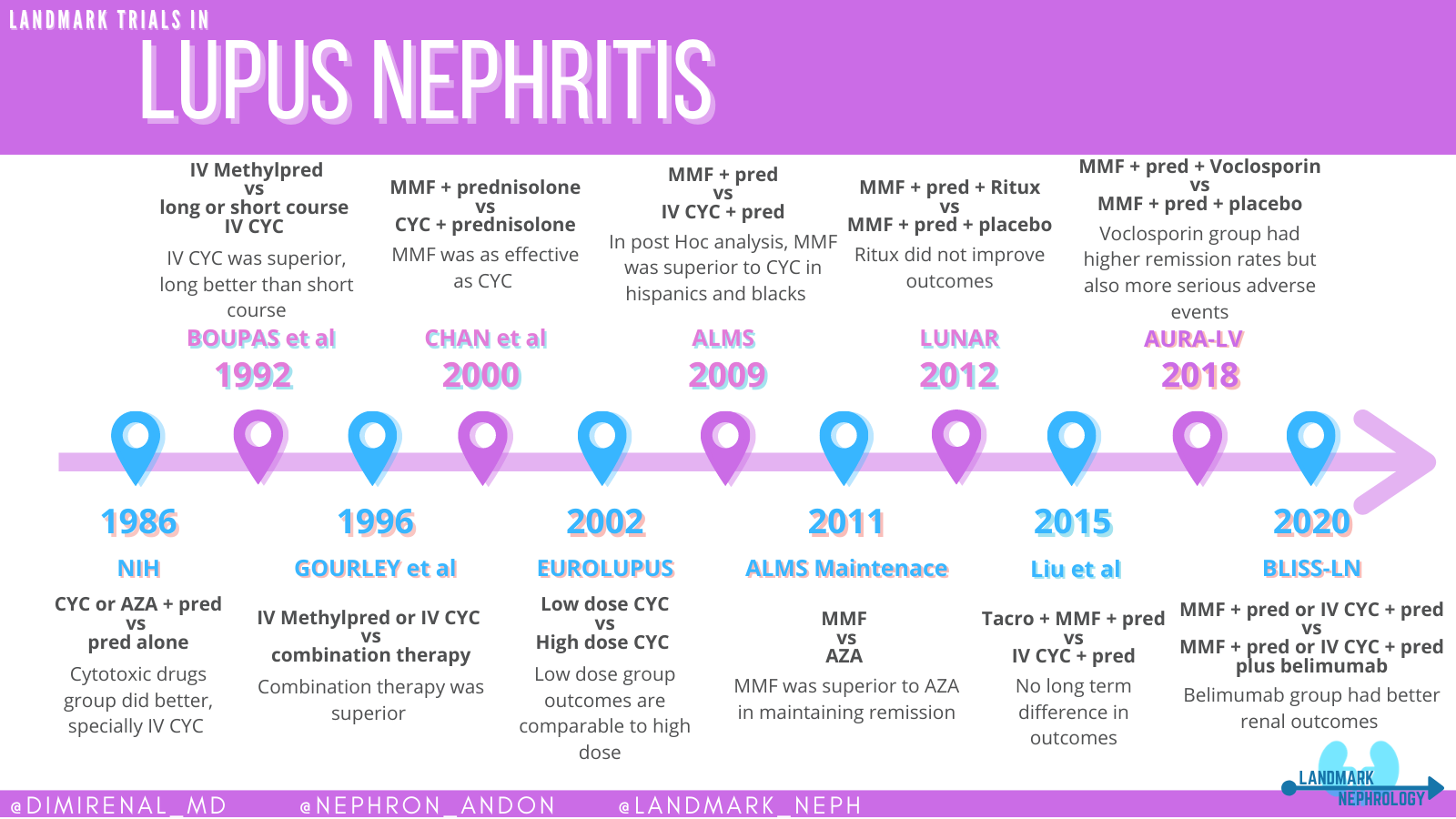
What is the best treatment for lupus nephritis?
In particular, hydroxychloroquine is associated with a higher rate of remission, fewer relapses, and reduced damage in the course of the disease, even in lupus nephritis. High-dose glucocorticoids should be given only when acutely indicated; immunosuppressives such as azathioprine, methotrexate, or mycophenolate mofetil may be administered to reduce glucocorticoids, according to the EULAR recommendations. Belimumab was recently approved as add-on therapy in autoantibody-positive SLE patients with high disease activity unresponsive to standard treatment. Short-term induction pulse therapy with low-dose intravenous cyclophosphamide, as well as continued mycophenolate mofetil treatment are advances in lupus nephritis.
How many criteria are needed for lupus nephritis?
For classification as SLE, four criteri a (at least one of them clinical and at least one immunological) have to be fulfilled or lupus nephritis has to be diagnosed histologically in the presence of ANA or anti-dsDNA antibodies. The SLICC criteria are not diagnostic criteria.
What are the manifestations of SLE?
Cutaneous manifestations occur in about 75% of patients with SLE in the course of the disease, and are the first sign in a quarter of cases (e10). Based on clinical and histological criteria, the skin lesions are divided into lupus erythematosus (LE)-specific (eTable) and LE-non-specific manifestations (e11, e12). The most frequent LE-specific manifestation is the acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (ACLE), which may occur as a butterfly rash or in the form of a generalized maculopapular exanthema. Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) displays a chronic course, typically characterized by inflammatory erythematous plaques with follicular hyperkeratosis and scarring (Figure 1a), leading to irreversible alopecia in hairy areas (Figure 1b). Approximately 5% of patients with DLE who initially show no systemic organ involvement will develop SLE. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE) is characterized by symmetric, annular, polycyclic, and/or papulosquamous/psoriasiform skin lesions without scarring on sun-exposed areas of the back, chest, and extensor surfaces of the arms (Figure 1c). The LE-non-specific manifestations include, among others, vascular skin lesions (e.g., periungual teleangiectasia, livedo racemosa, Raynaud syndrome).
What is SLE in medical terms?
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a heterogeneous autoimmune disease that may involve many different organs and display a variable clinical course. The diagnosis of SLE is based on characteristic clinical findings of the skin, joints, kidneys, and the central nervous system, as well as on serological parameters such as antinuclear antibodies (ANA), in particular antibodies to dsDNA (e1). The various clinical symptoms do not always occur simultaneously and may develop at any stage of the disease. In the early stages, physicians from various disciplines often propose several differential diagnoses, or identify only one aspect of the disease without recognizing the symptoms as part of SLE (1, e2). Fever, fatigue, and arthralgia are the most frequently occurring non-specific symptoms at disease onset; additional joint swelling or a "butterfly rash"”particularly in women of childbearing age”should prompt consideration of SLE (2). The aim of this article is to provide an updated review on the diagnosis and treatment of SLE, based on a selective survey of the literature in PubMed and the Cochrane Library, including current guidelines and the recommendations of experts with extensive experience in the management of this disease.
What are the non-specific symptoms of SLE?
Fever, fatigue, and arthralgia are the most frequently occurring non-specific symptoms at disease onset; additional joint swelling or a "butterfly rash"”particularly in women of childbearing age”should prompt consideration of SLE (2).
Is immunosuppression a co-med?
Adjunct treatment. Almost as important as immunosuppression is the co- medication, which is determined by the comorbidities (infections, arteriosclerosis, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, osteoporosis, avascular necrosis, and malignancies, among others) and the damage that has already occurred (13, 21, 30).
Is chloroquine good for SLE?
Hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine are licensed for the treatment of SLE. Apart from their good efficacy against arthritis and LE-specific skin lesions (8), antimalarials maintain SLE in remission, are associated with fewer disease flares, and reduce damage in the course of the disease (23, e18).
What is the best treatment for SLE?
In 2007, the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) released recommendations for the treatment of SLE. [ 64] In patients with SLE without major organ manifestations, glucocorticoids and antimalarial agents may be beneficial. [ 64] NSAIDs may be used for short periods in patients at low risk for complications from these drugs. Consider immunosuppressive agents (eg, azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, methotrexate) in refractory cases or when steroid doses cannot be reduced to levels for long-term use. [ 112]
What are EULAR recommendations for the management of SLE with neuropsychiatric manifestations?
EULAR recommendations for the management of SLE with neuropsychiatric manifestations support the evaluation and treatment of these symptoms in the same way as they are evaluated and treated in patients without SLE; if symptoms persist, management of these symptoms as an extension of SLE should be considered. [ 88, 64] For example, in patients with neuropsychiatric manifestations that may have an inflammatory etiology, immunosuppressive agents may be considered. [ 64]
Why is SLE considered a grounds for hospital admission?
Fever in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is grounds for hospital admission because of the difficulty of distinguishing a disease flare from infection in these immunocompromised hosts.
Why do SLE patients die from infections?
[ 140, 141] Overall, it is likely that the primary reason patients with SLE die of infections is immunosuppressive medications.Stress -dose steroid protocols should be used in patients who are receiving maintenance corticosteroids when they are admitted with infectious or perioperative stress.
How to avoid flares in SLE?
Patients with SLE should be educated to avoid triggers for flare. Persons with SLE should avoid ultraviolet light and sun exposure to minimize worsening of symptoms from photosensitivity. Diet modification should be based on the disease activity. A balanced diet is important, but patients with SLE and hyperlipidemia, for example, should be placed on a low-fat diet. Many patients with SLE have low levels of vitamin D because of less sun exposure; therefore, these patients should take vitamin D supplements. Exercise is important in SLE patients to avoid rapid muscle loss, bone demineralization, and fatigue. Smoking should also be avoided.
Where do SLE rashes occur?
Photosensitive systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) rashes typically occur on the face or extremities, which are sun-exposed regions. Although the interphalangeal spaces are affected, the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) and proximal interphalangeal (PIP) and distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints are spared.
When was belimumab approved?
In March, 2011, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of belimumab in combination with standard therapies (including steroids, nonbiologic DMARDS [eg, hydroxychloroquine, azathioprine, methotrexate]) to treat active autoantibody-positive SLE. [ 123] .
How to help someone with Lupus?
Connect with others who have lupus. Talk to other people who have lupus. You can connect through support groups in your community or through online message boards. Other people with lupus can offer unique support because they're facing many of the same obstacles and frustrations that you're facing.
What are the side effects of lupus?
Side effects include weight gain, easy bruising, thinning bones, high blood pressure, diabetes and increased risk of infection. The risk of side effects increases with higher doses and longer term therapy. Immunosuppressants. Drugs that suppress the immune system may be helpful in serious cases of lupus.
What does a low platelet count mean in a lupus test?
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate. This blood test determines the rate at which red blood cells settle to the bottom of a tube in an hour.
What are some examples of lupus drugs?
Examples include azathioprine (Imuran, Azasan), mycophenolate (Cellcept), methotrexate (Trexall, Xatmep, others), cyclosporine (Sandimmune, Neoral, Gengraf) and leflunomide (Arava). Potential side effects may include an increased risk of infection, liver damage, decreased fertility and an increased risk of cancer.
What are the tests for Lupus?
Laboratory tests. Blood and urine tests may include: Complete blood count. This test measures the number of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets as well as the amount of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells. Results may indicate you have anemia, which commonly occurs in lupus. A low white blood cell or platelet count may occur in ...
Can lupus be diagnosed by blood test?
Signs and symptoms of lupus may change over time and overlap with those of many other disorders. No one test can diagnose lupus. The combination of blood and urine tests, signs and symptoms, and physical examination findings leads to the diagnosis.
Does Rituximab cause depression?
Rarely, worsening of depression can occur. Rituximab (Rituxan, Truxima) may be beneficial for some people in whom other medications haven't helped. Side effects include allergic reaction to the intravenous infusion and infections. In clinical trials, voclosporin has been shown to be effective in treating lupus.
