:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/methicillin-resistant-staphylococcus-aureus-infections-1069436-01-d693749241d44b33b384b8b03cefa97f.png)
What can kill Staph aureus?
Aug 09, 2018 · The most important treatment is drinking plenty of fluids. Your healthcare provider may give you medicine to decrease vomiting and nausea. People with severe illness may require intravenous fluids. Antibiotics are not useful in treating this illness because the toxin is not affected by antibiotics. How can I prevent Staph food poisoning?
How long does it take staph infection to heal?
Feb 05, 2019 · Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a cause of staph infection that is difficult to treat because of resistance to some antibiotics. Staph infections—including those caused by MRSA—can spread in hospitals, other healthcare facilities, and in the community where you live, work, and go to school. You can help prevent ...
What happens if staph infection is untreated?
9. MRSA Decolonization Therapy. Decolonization therapy is the administration of antimicrobial or antiseptic agents to eradicate or suppress MRSA carriage. – Intranasal antibiotic or antiseptic (e.g., mupirocin, povidone-iodine) – Topical antiseptic (e.g., chlorhexidine) – +/- …
Which antibiotic is best for staph infection?
Mar 22, 2019 · Staphylococcus aureus (staph) is a germ found on people’s skin. Staph can cause serious infections if it gets into the blood and can lead to sepsis or death. Staph is either methicillin-resistant staph (MRSA) or methicillin-susceptible staph (MSSA). Staph can spread in and between hospitals and other healthcare facilities, and in communities.
See more
The glycopeptide drug vancomycin, and in some countries teicoplanin, is the most common drug used to treat severe MRSA infections. There are now other classes of antimicrobials available to treat staphylococcal infections, including several that have been approved after 2009.
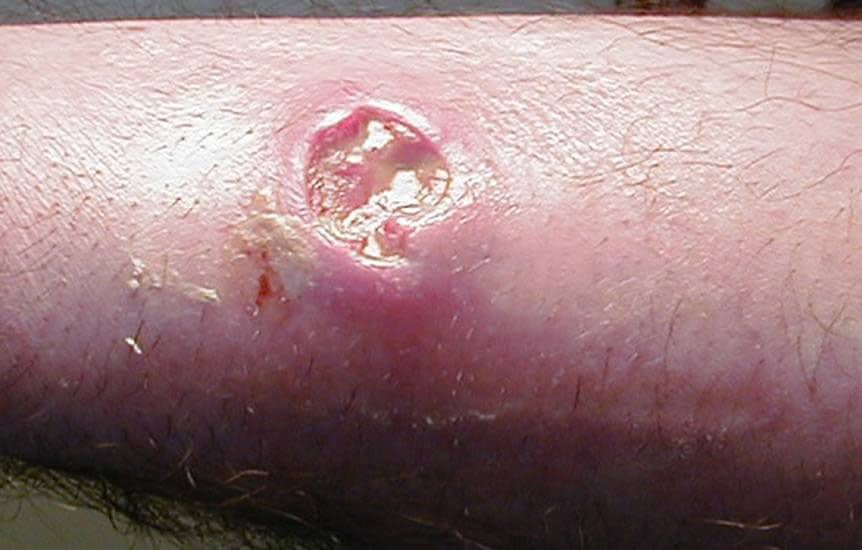
What is the best treatment for Staphylococcus aureus?
...
These include:
- methicillin.
- nafcillin.
- oxacillin.
- cloxacillin.
- dicloxacillin.
- flucloxacillin.
How can Staphylococcus be treated?
How do you get rid of Staphylococcus aureus?
How can Staphylococcus aureus be controlled?
Which injection can cure Staphylococcus?
...
Ceftriaxone as Home IV for Staph Infections.
| Primary Purpose: | Treatment |
| Official Title: | Ceftriaxone as Home Intravenous Therapy for Deep-Seated Staphylococcal Infections, a Randomized Non-Inferiority Trial |
What are the symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus?
- S. aureus can also cause serious infections such as pneumonia (infection of the lungs) or bacteremia (bloodstream infection). ...
- If you suspect you may have an infection with S. aureus contact your health care provider.
How long does it take to cure Staphylococcus aureus?
How can Staphylococcus be treated naturally?
Can staph go away on its own?
How long does staph infection last?
Is Staphylococcus aureus an STD?
What Is Staphylococcal Food Poisoning?
Staphylococcal food poisoning is a gastrointestinal illness caused by eating foods contaminated with toxins produced by the bacterium Staphylococcu...
How Do People Get Staphylococcal Food Poisoning?
People who carry Staph can contaminate food if they don’t wash their hands before touching it. Staph can also be found in unpasteurized milk and ch...
What Are The of Staphylococcal Food Poisoning?
Staphylococcal toxins are fast-acting, symptoms usually develop within 30 minutes to 6 hours. Patients typically experience vomiting, nausea, stoma...
How Do I Know If I Have Staphylococcal Food Poisoning?
Toxin-producing Staph can be identified in stool or vomit using specialized techniques. The toxins can also be detected in foods. Suspicion of stap...
How Is Staphylococcal Food Poisoning Treated?
For most patients, staphylococcal food poisoning is a brief illness. The most important treatment is plenty of fluids. Medicines may be given to de...
Are Sick Patients Contagious?
Patients with this illness are not contagious because the toxins are not transmitted from one person to another.
How Can Staphylococcal Food Poisoning Be ?
Staphylococcal food poisoning can be prevented by preventing the contamination of food with Staph. The following food safety tips(https://www.cdc.g...
Could Staphylococcal Toxins Be Used in A Bioterrorist Attack?
Staph toxins could be used as a biological agent either by contamination of food or water or by aerosolization (using pressure to produce a fine mi...
What happens if you eat staph?
If food is contaminated with Staph, the bacteria can multiply in the food and produce toxins that can make people ill. Staph bacteria are killed by cooking, but the toxins are not destroyed and will still be able to cause illness. Foods that are not cooked after handling, such as sliced meats, puddings, pastries, and sandwiches, ...
How many people have staph on their nose?
About 25% of people and animals have Staph on their skin and in their nose. It usually does not cause illness in healthy people, but Staph has the ability to make toxins that can cause food poisoning.
How to treat nausea and vomiting?
The most important treatment is drinking plenty of fluids. Your healthcare provider may give you medicine to decrease vomiting and nausea. People with severe illness may require intravenous fluids.
What are the steps to food safety?
The following tips that are part of the four steps to food safety – clean, separate, cook, and chill – also can help protect you and your loved ones from food poisoning:
Can you detect staph in stool?
Although laboratory tests can detect toxin-producing Staph in stool, vomit, and foods, these tests are usually not ordered except during an outbreak.
What is the most effective strategy for reducing rates of MRSA clinical isolates?
In adult ICUs, universal decolonization with intranasal mupirocin and daily CHG bathing was the most effective strategy for reducing rates of MRSA clinical isolates.
What are the logistical issues of MRSA decolonization?
A number of these are logistical issues, including determining what patient population the program will include, whether you will use targeted or universal decolonization, what antiseptic or antimicrobial agents will be used for decolonization, and how the order for the decolonization therapy will be entered. In addition, a plan for the assessment of adherence with the decolonization therapy program should be developed.
What is targeted decolonization?
Targeted decolonization: administration of MRSA decolonization therapy to persons known to be colonized with MRSA
What is decolonization therapy?
Decolonization therapy is the administration of antimicrobial or antiseptic agents to eradicate or suppress MRSA carriage
What is vertical infection control?
In contrast, “vertical” infection control strategies are those that only target a specific pathogen such as MRSA. Examples include active surveillance testing for MRSA in high-risk patient populations and decolonization of patients colonized with MRSA. Often studies examining this issue have combined vertical and horizontal strategies.
Does AST reduce MRSA?
AST by itself will not reduce MRSA transmission or infection
Can you take antibiotics for MRSA?
In some cases, usually in persons who have had recurrent MRSA infections, systemic antibiotics may also be administered at the same time as the intranasal and topical antiseptics. Several studies have assessed the impact of MRSA decolonization therapy and have found that decolonization is associated with reduction in MRSA carriage, transmission and infection. Persons who are decolonized can become colonized again.
Why are people at higher risk for staph infection?
People are at higher risk for staph infection when they have surgery or stay in healthcare facilities, have medical devices in their body, inject drugs, or when they come in close contact with someone who has staph.
How many bloodstream staph infections were there in 2017?
More than 119,000 bloodstream staph infections occurred in 2017.
How can healthcare facilities make MRSA and MSSA prevention a priority?
Healthcare facilities can make MRSA and MSSA prevention a priority by assessing the facility’s staph infection data, implementing prevention actions, and evaluating progress. Many hospitals have successfully prevented infections and spread.
Can staph cause sepsis?
Staph can cause serious infections if it gets into the blood and can lead to sepsis or death. Staph is either methicillin-resistant staph (MRSA) or methicillin-susceptible staph (MSSA). Staph can spread in and between hospitals and other healthcare facilities, and in communities. People are at higher risk for staph infection when they have surgery ...
What antimicrobials are used to treat S. aureus?
aureus treatment is marked by the development of resistance to each new class of antistaphylococcal antimicrobial drugs, including the penicillins, sulfonamides, tetracyclines, glycopeptides, and others, complicating therapy.
What is the most common antibiotic used for MRSA?
The glycopeptide drug vancomycin, and in some countries teicoplanin, is the most common drug used to treat severe MRSA infections. There are now other classes of antimicrobials available to treat staphylococcal infections, including several that have been approved after 2009.
What class of drugs are used for MRSA?
While infections caused by methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA) strains are usually treated with drugs in the ß-lactam class, such as cephalosporins, oxacillin or nafcillin, MRSA infections are treated with drugs in other antimicrobial classes.
What is CA MRSA?
CA-MRSA organisms, compared with health care-associated (HA-) MRSA strain types , are more often susceptible to multiple classes of non ß-lactam antimicrobials.
Is Staphylococcus aureus a bacterial infection?
Staphylococcus aureus, although generally identified as a commensal, is also a common cause of human bacterial infections, including of the skin and other soft tissues, bones, bloodstream, and respiratory tract.
How to prevent S. aureus infection?
Prevention of S. aureusinfections remains challenging. Despite many efforts, a routine vaccination for S. aureusinfections has remained elusive. As a result, efforts have relied on infection control methods such as hospital decontamination procedures, handwashing techniques, and MRSA transmission prevention guidelines. Topical antimicrobials such as mupirocin can be used to eliminate nasal colonization in some nasal carriers. However, usage is controversial.
What is Staphylococcus aureus?
Last Update: August 23, 2020. Continuing Education Activity. Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive bacteria that cause a wide variety of clinical diseases. Infections caused by this pathogen are common both in community-acquired and hospital-acquired settings. The treatment remains challenging due to the emergence of multi-drug resistant strains ...
What is the color of a staph?
Staphylococcus aureus is Gram-positive bacteria (stain purple by Gram stain) that are cocci-shaped and tend to be arranged in clusters that are described as “grape-like.” On media, these organisms can grow in up to 10% salt, and colonies are often golden or yellow (aureus means golden or yellow). These organisms can grow aerobically or anaerobically (facultative) and at temperatures between 18 C and 40 C. Typical biochemical identification tests include catalase positive (all pathogenic Staphylococcusspecies), coagulase positive (to distinguish Staphylococcus aureusfrom other Staphylococcusspecies), novobiocin sensitive (to distinguish from Staphylococcus saprophyticus), and mannitol fermentation positive (to distinguish from Staphylococcus epidermidis). [4][1] MRSA strains carry a mecgene on the bacterial chromosome, which is a component of the larger Staphylococcal chromosomal cassette mec(SCCmec) region, conferring resistance to multiple antibiotics depending on the SCCmectype.[2] The mecgene encodes the protein PBP-2a (penicillin-binding protein 2a). PBP-2a is a penicillin-binding protein (PBP), or essential bacterial cell wall enzyme that catalyzes the production of the peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall. PBP-2A has a lower affinity to bind to beta-lactams (and other penicillin-derived antibiotics) when compared to other PBPs, so PBP-2A continues to catalyze the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall even in the presence of many antibiotics. As a result, S. aureusstrains that synthesize PBP-2A can grow in the presence of many antibiotics, and these MRSA strains are resistant to many antibiotics. MRSA strains tend to be resistant to methicillin, nafcillin, oxacillin, and cephalosporins. [2][4]
What are the most common infections caused by S. aureus?
aureusare one the most common bacterial infections in humans and are the causative agents of multiple human infections, including bacteremia, infective endocarditis, skin and soft tissue infections (e.g., impetigo, folliculitis, furuncles, carbuncles, cellulitis, scalded skin syndrome, and others), osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, prosthetic device infections, pulmonary infections (e.g., pneumonia and empyema), gastroenteritis, meningitis, toxic shock syndrome, and urinary tract infections.[6] Depending on the strains involved and the site of infection, these bacteria can cause invasive infections and/or toxin-mediated diseases. [6][7] The pathophysiology varies greatly depending on the type of S. aureusinfection.[6] Mechanisms for evasion of the host immune response include the production of an antiphagocytic capsule, sequestering of host antibodies or antigen masking by Protein A, biofilm formation, intracellular survival, and blocking chemotaxis of leukocytes. [8][7] Binding of the bacteria to extracellular matrix proteins and fibronectin in infectious endocarditis is mediated by bacterial cell wall-associated proteins such as fibrinogen-binding proteins, clumping factors, and teichoic acids.[7] Also, Staphylococcal superantigens (TSST-1 or toxic shock syndrome toxin 1) are important virulence factors in infectious endocarditis, sepsis, as well as toxic shock syndrome. [9][10] Pneumonia infections are associated with the bacterial production of PVL (Panton-Valentine leukocidin), Protein A, and alpha-hemolysin, and infections are more common following influenza virus infection as well as a diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis. Prosthetic device infections are often mediated by the ability of S. aureusstrains to form biofilms as well as communicate using quorum sensing in a bacterial cell density-dependent manner. [11]
How long does it take to treat S. aureus?
When prescribing antibiotics, one should limit the duration to no more than 7 to 10 days for most infections. The reason is that the empirical prescription of antibiotics has led to the development of resistant strains. Pharmacists should coordinate with the clinician to target antimicrobial therapy, and nursing can chart the progress so modification to the regimen can be made if treatment is ineffective. This kind of interprofessional coordination is necessary to treat such infections with precision.
How to diagnose S. aureus?
In many cases, routine cultures will reveal the diagnosis (i.e.,blood, sputum); however, RT-PCR (real-time PCR) for 16S rRNA genes may be necessary in some cases. Drug susceptibility testing often is required to guide treatment. If patient samples are collected for pathogen identification in the microbiology laboratory, caution must be exercised as the presence of S. aureusin the skin or mucous membrane does not necessarily indicate infection because these organisms are frequently members of the normal flora. [4]
Is Staphylococcus aureus transmitted?
Transmission is typically from direct contact. However, some infections involve other transmission methods.[4] Staphylococcus aureus is a major bacterial human pathogen that causes a wide variety of clinical manifestations.[1] . Infections are common both in community-acquired as well as hospital-acquired settings and treatment remains challenging ...
How to diagnose staph infection?
To diagnose a staph infection, your doctor will: Perform a physical exam. During the exam, your doctor will closely examine any skin lesions you may have. Collect a sample for testing. Most often, doctors diagnose staph infections by checking a tissue sample or nasal secretions for signs of the bacteria. Other tests.
What antibiotics are used for staph infection?
Antibiotics commonly prescribed to treat staph infections include certain cephalosporins such as cefazolin; nafcillin or oxacillin; vancomycin; daptomycin (Cubicin); telavancin (Vibativ); or linezolid (Zyvox). Vancomycin increasingly is required to treat serious staph infections because so many strains of staph bacteria have become resistant ...
Why is vancomycin used for staph infections?
Vancomycin increasingly is required to treat serious staph infections because so many strains of staph bacteria have become resistant to other traditional medicines. But vancomycin and some other antibiotics have to be given intravenously.
What is the name of the antibiotic that is used to treat staph?
The emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains of staph bacteria — often described as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains — has led to the use of IV antibiotics, such as vancomycin or daptomycin, with the potential for more side effects.
What test is used to check for staph infection?
If you're diagnosed with a staph infection, your doctor may order an imaging test called an echocardiogram to check if the infection has affected your heart. Your doctor may order other imaging tests, depending on your symptoms and the exam results.
What to do if you have staph on your skin?
If you suspect you have a staph infection on your skin, keep the area clean and covered until you see your doctor so that you don't spread the bacteria. And, until you know whether or not you have staph, don't prepare food. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
What to do if you have a wound infection?
Wound drainage. If you have a skin infection, your doctor will likely make an incision into the sore to drain fluid that has collected there. Device removal. If your infection involves a device or prosthetic, prompt removal of the device is needed. For some devices, removal might require surgery.
What is the assignment of a strain to the genus Staphylococcus?
Assignment of a strain to the genus Staphylococcus requires it to be a Gram-positive coccus that forms clusters, has an appropriate cell wall structure (including peptidoglycan type and teichoic acid presence) and G + C content of DNA in a range of 30–40 mol%.
How many clusters are there in the genus Staphylococcus?
Taxonomy. The taxonomy is based on 16s rRNA sequences, and most of the staphylococcal species fall into 11 clusters: A twelfth group – that of S. caseolyticus – has now been removed to a new genus, Macrococcus, the species of which are currently the closest known relatives of Staphylococcus.
Why are S. sciuri oxidase positive?
Members of the S. sciuri group are oxidase -positive due to their possession of the enzyme cytochrome c oxidase. This group is the only clade within the staphylococci to possess this gene.
What is the abbreviation for coagulase negative staphylococci?
Common abbreviations for coagulase-negative staphylococci are CoNS, CNS, or CNST. The American Society for Microbiology abbreviates coagulase-negative staphylococci as "CoNS".
What is the name of the Gram positive bacteria that forms in grape-like clusters?
Staphylococcus is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical ( cocci ), and form in grape -like clusters. Staphylococcus species are facultative anaerobic organisms (capable of growth both aerobically and anaerobically).
What is the cause of antibiotic resistance?
aureus, or across different species of Staphylococcus has been attributed to horizontal gene transfer of genes encoding antibiotic/metal resistance and virulence. A recent study demonstrated the extent of horizontal gene transfer among Staphylococcus to be much greater than previously expected, and encompasses genes with functions beyond antibiotic resistance and virulence, and beyond genes residing within the mobile genetic elements.
How many species of staph are there?
Staphylococcus includes at least 40 species. Of these, nine have two subspecies, one has three subspecies, and one has four subspecies. Many species cannot cause disease and reside normally on the skin and mucous membranes of humans and other animals. Staphylococcus has been found to be a nectar-inhabiting microbe.
What is the impact of MRSA on the community?
The growing clinical impact of MRSA, particularly community-acquired infections, prompted the Infectious Diseases Society of America to develop its first treatment guidelines for MRSA.
What is MRSA in medical terms?
Assistant Clinical Professor, Division of Infectious Diseases, University of California. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) – both healthcare- and community-associated – has become an enormous public health problem. MRSA is responsible for about 60 percent of skin and soft tissue infections seen in emergency rooms, ...
Is there a golden bullet for MRSA?
Although a number of new drugs have been developed and FDA-approved, we have yet to discover the golden bullet. Of course, additional research is necessary on MRSA and as with all IDSA guidelines, these recommendations will evolve as new information and antibiotics become available.
