/at-doctors-appointment-physician-shows-to-patient-shape-of-kidney-with-focus-on-hand-with-organ--scene-explaining-patient-causes-and-localization-of-diseases-of-kidney--stones--adrenal--urinary-system-1139659904-11800ef8290e467cb7b8397e159b37ae.jpg)
- Medicines to control your blood pressure and adjust the electrolytes in your blood
- Treatments to keep the right amount of fluid in your body (e.g. diuretics to make you pee out extra fluid)
- If the AKI is severe and your kidneys completely stop working, going on dialysis for a short period of time. ...
- When you return home, following a kidney-friendly eating plan to help your kidneys heal. Your doctor may refer you to a registered dietitian.
Can you heal the kidney naturally and reverse kidney disease?
Aug 04, 2021 · Treatment / Management. The management of prerenal kidney failure is dependent on the stage of AKI, underlying etiology, and the setting where it is identified. In an outpatient setting, patients who stage as 2 or 3 by the KDIGO criteria with AKI should be sent to the emergency department (ED) for further evaluation.
What causes prerenal acute renal failure?
Search the Healthwise Knowledgebase . Help: Healthwise Index: Topic Contents. Topic Overview; Related Information; Credits; This information does not replace the advice of a docto
Can prerenal acute renal failure be prevented?
Jun 02, 2020 · Treatment of Acute Kidney Injury: Correction of Hypovolemia: Individualized fluid therapy : Avoid positive fluid balance: Isotonic Saline: Albumin: Vasopressor support (MAP > 65 mmHg) Noradrenaline: Vasopressin: Terlipressin: Discontinue nephrotoxins and Adjust drugs to renal function: NSAIDs: ARBs, ACEis: Contrast: Metformin: Aminoglycosides: Vancomycin
What are the stages of acute kidney injury?
Mar 01, 2022 · PRERENAL CAUSES. Prerenal acute kidney injury is associated with decreased renal perfusion and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) caused by intravascular volume depletion secondary to hypovolemia ...
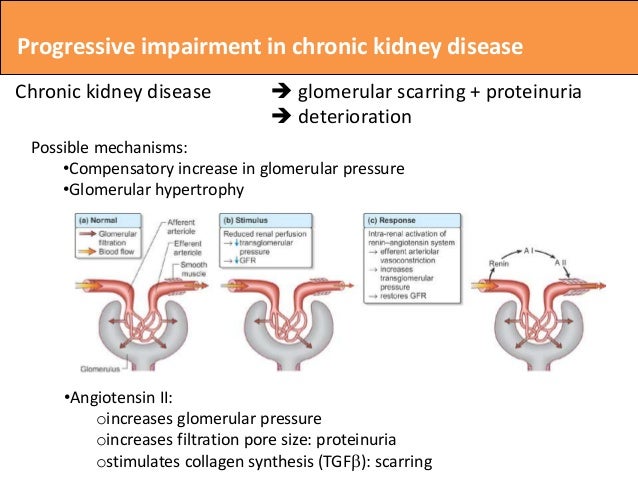
What treatment is used for acute kidney injury?
Is Prerenal acute kidney injury reversible?
Can kidney injury be cured?
How is intrinsic AKI treated?
...
Acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
- Severe infection (sepsis).
- Surgery, especially cardiovascular or abdominal surgery.
- Direct injury to the kidney.
- Severe burns.
- Severe muscle injury or extreme physical exertion.
What causes Prerenal failure?
Is Ginger good for kidneys?
Is drinking a lot of water good for your kidneys?
What fruit is good for kidneys?
What percentage of acute kidney injury is attributed to prerenal causes?
Approximately 70 percent of community-acquired cases of acute kidney injury are attributed to prerenal causes. 10 In these cases, underlying kidney function may be normal, but decreased renal perfusion associated with intravascular volume depletion (e.g., from vomiting or diarrhea) or decreased arterial pressure (e.g., from heart failure or sepsis) results in a reduced glomerular filtration rate. Autoregulatory mechanisms often can compensate for some degree of reduced renal perfusion in an attempt to maintain the glomerular filtration rate. In patients with preexisting chronic kidney disease, however, these mechanisms are impaired, and the susceptibility to develop acute-on-chronic renal failure is higher. 11
What are the symptoms of acute renal injury?
Patients with severe cases, however, may be symptomatic and present with listlessness, confusion, fatigue, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, weight gain, or edema. 15 Patients can also present with oliguria (urine output less than 400 mL per day), anuria (urine output less than 100 mL per day), or normal volumes of urine (nonoliguric acute kidney injury). Other presentations of acute kidney injury may include development of uremic encephalopathy (manifested by a decline in mental status, asterixis, or other neurologic symptoms), anemia, or bleeding caused by uremic platelet dysfunction.
What is acute kidney injury?
Acute kidney injury is characterized by abrupt deterioration in kidney function, manifested by an increase in serum creatinine level with or without reduced urine output. The spectrum of injury ranges from mild to advanced, sometimes requiring renal replacement therapy.
What is the most important noninvasive test in the initial workup of acute kidney injury?
Urinalysis is the most important noninvasive test in the initial workup of acute kidney injury. Findings on urinalysis guide the differential diagnosis and direct further workup ( Figure 1 12).
What is renal ultrasonography?
Renal ultrasonography should be performed in most patients with acute kidney injury, particularly in older men, to rule out obstruction (i .e., a postrenal cause). 17, 18 The presence of postvoid residual urine greater than 100 mL (determined by a bladder scan or via urethral catheterization if bladder scan is unavailable) suggests postrenal acute kidney injury and requires renal ultrasonography to detect hydronephrosis or outlet obstruction. To diagnose extrarenal causes of obstruction (e.g., pelvic tumors), other imaging modalities, such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, may be required.
Why is renal biopsy important?
Renal biopsy is particularly important when clinical assessment and laboratory investigations suggest a diagnosis that requires confirmation before disease-specific therapy (e.g., immunosuppressive medications) is instituted. Renal biopsy may need to be performed urgently in patients with oliguria who have rapidly worsening acute kidney injury, hematuria, and red blood cell casts. In this setting, in addition to indicating a diagnosis that requires immunosuppressive therapy, the biopsy may support the initiation of special therapies, such as plasmapheresis if Goodpasture syndrome is present.
Is acute kidney injury a chronic disease?
Patients with acute kidney injury are more likely to develop chronic kidney disease in the future. They are also at higher risk of end-stage renal disease and premature death. 25 – 27 Patients who have an episode of acute kidney injury should be monitored for the development or worsening of chronic kidney disease.
What causes acute kidney injury?
Causes of prerenal acute kidney injury include: 1 Severe blood loss and low blood pressure related to major cardiac or abdominal surgery, severe infection ( sepsis ), or injury. 2 Medicines that interfere with the blood supply to the kidneys. Medicines such as ACE inhibitors and common pain medicines ( NSAIDs ) commonly cause prerenal acute kidney injury in people who already have an increased risk for kidney problems. 3 Severe dehydration caused by excessive fluid loss. 4 Severe burns. 5 Pancreatitis and liver diseases, such as cirrhosis , that create fluid shifts in the abdomen.
Can NSAIDs cause kidney problems?
Medicines such as ACE inhibitors and common pain medicines ( NSAIDs ) commonly cause prerenal acute kidney injury in people who already have an increased risk for kidney problems.
What causes post renal acute kidney injury?
Postrenal acute kidney injury is due to extrarenal obstruction of urinary flow. Causes include neurogenic bladder; retroperitoneal fibrosis; and the tumor burden of bladder, prostate, or cervical cancer. Prostatic hypertrophy is the most common cause in older men. 11
What causes post renal injury?
POSTRENAL CAUSES. Postrenal acute kidney injury is due to extrarenal obstruction of urinary flow. Causes include neurogenic bladder; retroperitoneal fibrosis; and the tumor burden of bladder, prostate, or cervical cancer. Prostatic hypertrophy is the most common cause in older men. 11.
What is acute kidney injury?
Acute kidney injury is defined as the sudden loss of kidney function over hours to days resulting in the inability to maintain electrolyte, acid-base, and water balance.
Can renal ultrasonography show post renal injury?
Renal ultrasonography may show evidence of a postrenal cause of acute kidney injury but should be performed only when the history suggests the presence of urinary tract obstruction. 23 Renal biopsy is reserved for patients with intrinsic acute kidney injury of unclear etiology or when diagnostic confirmation is necessary before initiating disease-specific therapy.
Why is urine output difficult to assess?
Urine output can be difficult to accurately assess because of collection and documentation errors. Serum creatinine or urine output can be used for diagnosis of acute kidney injury, although patients who meet diagnostic criteria for both are at increased risk of mortality from renal replacement therapy and hospitalization. 7, 19
What is the purpose of urinalysis and urine microscopy?
Urinalysis in combination with urine microscopy provides insight into the location and cause of acute kidney injury. Table 4 summarizes common findings and associated diagnoses based on urine evaluation. 21
What is a review of medications requiring discontinuation, dose adjustment, or monitoring?
A review of medications requiring discontinuation, dose adjustment, or monitoring is critical to the management of acute kidney injury ( Table 5 and Table 6). 12 In addition, the implementation of pharmacist-led quality-improvement programs is associated with reductions in nephrotoxic exposures and rates of acute kidney injury in the hospital setting. 34
What is the filter of the kidney?
The filters of the kidney ( glomeruli) The blood vessels within the kidney ( vasculature) The small tubes that connect the glomeruli to the area within the kidney that collects newly made urine ( tubules) The space adjacent to the glomeruli, vasculature, and tubules within the kidney ( interstitial space)
What is intrinsic renal state?
An intrinsic renal state is a condition in which kidney damage has occurred but not due to lack of adequate kidney blood flow (a prerenal state) or obstruction of urine outflow (a postrenal state). Advertisements. As with both prerenal and postrenal conditions, an intrinsic renal state will eventually lead to a loss of GFR.
What is the role of the kidneys in the body?
Postrenal Conditions. Final Word. The kidneys play a vital role in clearing body wastes and maintaining body fluid levels. Therefore, it is essential to have knowledge about the causes of kidney damage and avoid those habits that can harm your kidneys, such as a lack of fluid intake or sleep.
Does smoking cause CKD?
In addition to the use or overuse of certain over-the-counter and prescribed drugs, smoking has been associated with the development of CKD and accelerates the progression of CKD once established. (5) Additionally, smoking cessation has been associated with a slower rate of CKD progression .
Why does urine output increase?
For patients with partial urine outflow obstruction of one or both kidneys, urine output may increase as a result of changes to the affected kidney’s ability to concentrate the urine it is producing.
Where does the normal clearance of toxic substances from the body occur?
The normal clearance of certain excess or potentially toxic elements from the body occurs within healthy kidney tissue. Under certain conditions, slowed or even absent clearance of these substances may result.
What does it mean when your kidneys stop working?
Acute kidney injury means your kidneys stop working suddenly. AKI requires immediate treatment and may be reversible if diagnosed and treated quickly—unlike chronic kidney disease (CKD), which is kidney damage that typically progresses slowly over a period of time and is not reversible. Some people diagnosed with AKI will need dialysis ...
Can you get dialysis for AKI?
If you have AKI that requires dialysis, also referred to as AKI-D, you may be treated in the hospital—since many people with AKI are in the hospital already for an injury, illness, or other condition—or at a dialysis center, under the care of a nephrologist (kidney doctor). Each person's recovery is different, and the length of time you receive acute kidney injury dialysis will depend on how long it takes for your kidneys to recover.
What is AKI in medical terms?
Treatment for acute kidney injury (AKI) can vary by person and depends on the cause. After an AKI diagnosis, the primary goal of your care team is to treat whatever is causing your acute kidney injury, so your kidneys can regain function. Acute kidney injury is also sometimes called acute renal failure (ARF) or acute kidney failure (AKF).
Is AKI reversible?
AKI requires immediate treatment and may be reversible if diagnosed and treated quickly—unlike chronic kidney disease (CKD), which is kidney damage that typically progresses slowly over a period of time and is not reversible. Some people diagnosed with AKI will need dialysis until normal kidney function returns.
How does dialysis work?
Dialysis works by filtering toxins, waste, and fluid from your blood through a dialyzer inside a dialysis machine. Your blood is accessed through your catheter site and circulated through the machine and cleaned before being returned to your body.
What is dialysate used for?
A dialysate solution is used in the filtering process to remove unwanted substances from your bloodstream. During your dialysis treatment your care team will be monitoring you closely. Before and after treatment, your weight and blood pressure will be taken.
What medications can cause kidney damage?
Do not stop taking any medication without first talking to your doctor. Common medications with possible risks for people with AKI include: NSAIDs —nonsteroidal anti -inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are common pain relievers that can be harmful to damaged kidneys. NSAIDs include: ibuprofen and naproxen, among others.
How to differentiate AKI from CKD?
The best way to differentiate between AKI and CKD is to look at the baseline SCr or GFR. AKI refers to an abrupt increase in SCr or drop in GFR from baseline. It is possible to have AKI on CKD. If previous laboratory values are not available history, physical examination and clinical investigations may be helpful.
What causes AKI?
Prerenal AKI is probable the most common type and is caused by hemodynamic changes resulting in reduced perfusion of kidneys.
How severe is AKI?
How severe is this patient's AKI? 1 AKIN Stage I: increase in SCr >0.3 (26 μmol/L) OR >50% – 100% from baseline, urine putput <0.5 mL/kg/hr for >6 hours 2 AKIN Stage II: Increase in SCr >100% – 200% from baseline, urine output <0.5 mL/kg/hr for >12 hours 3 AKIN Stage III: Increase in SCr >200 from baseline OR SCr >4 after a rise of at least 0.5 mg/dL OR on renal replacement therapy, urine putput <0.3 mL/kg/hr for >24 hours or anuric >12 hours

Diagnosis
Terminology
Cause
Epidemiology
Adverse effects
Signs and symptoms
Availability
Medical uses
Management
Clinical significance
Treatment
- The main indication for use of diuretics is management of volume overload. Intravenous loop diuretics, as a bolus or continuous infusion, can be helpful for this purpose. However, it is important to note that diuretics do not improve morbidity, mortality, or renal outcomes, and should not be used to prevent or treat acute kidney injury in the absen...
Contraindications
Prognosis
Resources