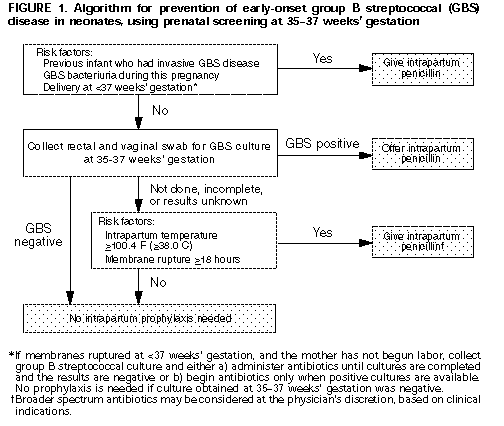
Children with suspected atypical pneumonia can be treated with macrolides. Children allergic to penicillin will be treated with other antibiotics as needed for the specific pathogen. Hospitalized, immunized children can be treated with ampicillin or penicillin G
Benzylpenicillin
Benzylpenicillin, also known as penicillin G, is an antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes pneumonia, strep throat, syphilis, necrotizing enterocolitis, diphtheria, gas gangrene, leptospirosis, cellulitis, and tetanus. It is not a first-line agent for pneumococcal meningiti…
Full Answer
What is the most common treatment for pneumonia?
· The duration of treatment exceeded recommendations in European guidelines. Empiric monotherapy with penicillin-G/V was commonly used and not associated with increased mortality in patients with mild to moderate pneumonia. Our results are in agreement with current conservative antibiotic strategy as outlined in the Danish guidelines.
What does medication treat pneumonia?
· Children with suspected atypical pneumonia can be treated with macrolides. Children allergic to penicillin will be treated with other antibiotics as needed for the specific pathogen. Hospitalized, immunized children can be treated with ampicillin or penicillin G.
What is the treatment for strep pneumonia?
Evaluating a patient who reports a penicillin or another ß-lactam antibiotic allergy involves three steps: 1) obtaining a thorough medical history, including previous exposures to penicillin or other ß-lactam antibiotics (658); 2) performing a skin test evaluation by using the penicillin major and minor determinants; and 3) among those who have a negative penicillin skin test, performing …
How long to treat community acquired pneumonia?
· Consensus guidelines from several organizations recommend empiric therapy with macrolides, fluoroquinolones, or doxycycline. Patients who are hospitalized should be switched from parenteral...

How do you treat pneumonia if you are allergic to penicillin?
Alternative antibiotics are doxycycline (a tetracycline), clarithromycin (a macrolide) and erythromycin (an alternative macrolide in pregnancy), for people with low-severity community-acquired pneumonia and penicillin allergy, or when amoxicillin may not be appropriate, for example, if an atypical infection is ...
How do you treat pneumonia without penicillin?
There are several different antibiotics are effective at treating this bacterial infection.Azithromycin. Azithromycin is a first-line treatment for healthy adults under age 65 with bacterial pneumonia. ... Clarithromycin. Clarithromycin is another macrolide antibiotic that is commonly used for pneumonia. ... Tetracycline.
What is the antibiotic of choice for pneumonia?
In otherwise uncomplicated pneumonia, azithromycin is the initial drug of choice, as it covers most of the potential etiologic agents, including Mycoplasma species.
What is the drug of choice for community-acquired pneumonia with penicillin sensitivity is?
Tigecycline was approved by the FDA in 2009 for adults with CAP caused by S pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible isolates), including cases with concurrent bacteremia, H influenza (beta-lactamase-negative isolates), and Legionella pneumophila.
What is the first line treatment for pneumonia?
Pneumonia should be treated with antibiotics. The antibiotic of choice for first line treatment is amoxicillin dispersible tablets. Most cases of pneumonia require oral antibiotics, which are often prescribed at a health centre.
What is the treatment for Covid pneumonia?
Are There Treatments for COVID-19 Pneumonia? Pneumonia may need treatment in a hospital with oxygen, a ventilator to help you breathe, and intravenous (IV) fluids to prevent dehydration.
Can you have ceftriaxone if allergic to penicillin?
Cross-Reactivity with Cephalosporins In most clinical settings, patients with reported penicillin allergy are precluded from treatment with such cephalosporin antibiotics as ceftriaxone.
What is the most common treatment for pneumonia?
Antibiotics. These medicines are used to treat bacterial pneumonia. It may take time to identify the type of bacteria causing your pneumonia and to choose the best antibiotic to treat it. If your symptoms don't improve, your doctor may recommend a different antibiotic.
Is azithromycin used for pneumonia?
Azithromycin is equally effective as treatment of atypical pneumonia in adult patients if given for 3 or 5 days at the same total dose.
Can you take azithromycin if allergic to penicillin?
Our patients did not show any reaction to azithromicin. This antibiotic is therefore a valid alternative to penicillin and/or cephalosporin in patients allergic to these two drugs.
Why do we give azithromycin in pneumonia?
Azithromycin may be effective in eradicating atypical organisms, but such bacteria are the causative organism in less than 20% of cases of pneumonia. The most common organism associated with CAP is Streptococcus pneumoniae. Since the 1990s, resistance to macrolides has been reported in S.
Does doxycycline treat pneumonia?
Background Doxycycline has a high degree of activity against many common respiratory pathogens and has been used in the outpatient management of lower respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia.
Can you get rid of pneumonia without antibiotics?
Mild cases of pneumonia can go away on their own if you manage your symptoms and get adequate rest. Home treatment for pneumonia includes getting plenty of rest, drinking adequate fluids, steamy baths or showers, fever reducers, and avoiding smoking. In severe cases of pneumonia, hospitalization may be needed.
What is the most common treatment for pneumonia?
Antibiotics. These medicines are used to treat bacterial pneumonia. It may take time to identify the type of bacteria causing your pneumonia and to choose the best antibiotic to treat it. If your symptoms don't improve, your doctor may recommend a different antibiotic.
Can pneumonia be treated at home?
Mild pneumonia can usually be treated at home with rest, antibiotics (if it's likely be caused by a bacterial infection) and by drinking plenty of fluids. More severe cases may need hospital treatment.
Can bacterial pneumonia go away by itself?
Bacterial pneumonia is treated with antibiotic therapy, while viral pneumonia will usually get better on its own.
What is the best medicine for pneumonia?
Healthy adults under 65 years with pneumonia are typically treated with a combination of amoxicillin plus a macrolide like Zithromax (azithromycin) or sometimes a tetracycline like Vibramycin (doxycycline).
What to do if you have pneumonia?
If you’ve been diagnosed with bacterial pneumonia, you’ll likely be prescribed antibiotics to treat it. Antibiotics kill bacteria or render them unable to replicate.
Do you have to take antibiotics if you feel better?
Taking your medication as prescribed, especially for antibiotics, is incredibly important. Even if you’re feeling better, you need to take the entire course.
How do doctors choose antibiotics?
Doctors typically choose your antibiotics prescription based on what medicines they think will be most effective and cause the fewest side effects.
What are the factors that influence a person's ability to fight off infections?
Your health history: A history of smoking, lung diseases, or other conditions may influence a person's ability to fight off infections.
Can a hospitalized child be treated with cephalosporin?
Hospitalized children and infants who are not fully vaccinated may be treated with a cephalosporin.
What is the treatment for pseudomonas?
Hospitalized adults with Pseudomonas will be treated with a combination of an antipseudomonal beta-lactam plus an antipseudomonal fluoroquinolone.
What is the true rate of penicillin allergy?
Moreover, in studies that have incorporated penicillin skin testing and graded oral challenge among persons with reported penicillin allergy, the true rates of allergy are low, ranging from 1.5% to 6.1% ( 665 – 667 ). Studies in preoperative surgical patients with reported penicillin allergy, evaluated for cardiovascular surgery ( 668) or orthopedics ( 669 ), have rates of skin test positivity <8.5%. However, when patients with high-risk penicillin allergy histories are excluded, 99% of patients could receive ß-lactams. In hospitalized patients and other populations with comorbidities, the typical rates of validated penicillin allergy among patients who report a history of penicillin allergy are 2.5%–9.0% ( 670 – 673 ).
What is the determinant of penicillin?
Penicillin skin testing with a major determinant analog (penicilloyl-polylysine) and minor determinants (benzylpenicilloate, benzylpenilloate, or benzylpenicillin isomers of penicillin) are used for skin test evaluation for IgE-dependent penicillin allergy and can reliably identify persons at high risk for IgE-mediated reactions to penicillin ( 658, 660, 676 ). Until recently, penicillin skin testing in the United States only included the major determinant benzyl penicillin poly-L-lysine (Pre-Pen) in addition to penicillin G. This test identifies approximately 90%–99% of the IgE-mediated penicillin-allergic patients. Because the remaining 1%–10% of penicillin-allergic patients who are not captured by this penicillin skin test are due to minor determinants IgE antibodies, the standard practice is to follow skin testing with an observed oral challenge of amoxicillin 250 mg with 1 hour of observation. If the skin test and oral challenge are both negative, the risk for IgE-mediated anaphylaxis approaches zero and is equivalent to that of a person who has never reported an allergy to penicillin.
What is desensitization for penicillin?
Desensitization is required for persons who have a documented penicillin allergy and for whom no therapeutic alternatives exist (e.g., syphilis during pregnancy and persons with neurosyphilis). Modified protocols might be considered on the basis of the clinical syndrome, drug of choice, and route of administration ( 687 – 690 ). Patients might require referral to a specialty center where desensitization can be performed.
Is it safe to take penicillin while pregnant?
Penicillin skin testing during pregnancy is considered safe. For pregnant persons who report a penicillin or ß-lactam allergy, penicillin allergy is an important consideration in treating syphilis during pregnancy and the potential for group B streptococcal infection and preoperative prophylaxis if a cesarean delivery is required. However, oral challenges should not be performed unless in a setting where additional support services are available.
Can you give penicillin to someone with STI?
Persons with high-risk symptom histories (e.g., anaphylaxis within the previous 10 years) should not be administered penicillin or a ß-lactam antibiotic in an ambulatory setting. Furthermore, these persons with high-risk symptoms should not receive penicillin skin testing or amoxicillin oral challenge in an ambulatory STI setting and should be referred to an allergist for further evaluation.
Is penicillin allergy testing needed for STI?
STI programs and clinicians should promote increased access to penicillin allergy testing. Allergy testing is being provided by clinicians in primary care and hospital settings. If appropriate, STI programs and ambulatory settings should consider developing expanded access to penicillin or ß-lactam allergy assessment.
Can you be allergic to penicillin?
Patients often are incorrectly labeled as allergic to penicillin and are therefore denied the benefit of a ß-lactam therapy. The presence of a penicillin allergy label considerably reduces prescribing options for affected patients. Moreover, penicillin allergy labels lead to the use of more expensive and less effective drugs and can result in adverse consequences, including longer length of hospital stay and increased risk for infection. Multiple studies have described that persons with reported penicillin or another ß-lactam antibiotic allergy have higher rates of surgical-site infections, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections, and higher medical care usage ( 653, 662 – 664 ).
What causes pneumonia?
Typical pneumonia usually is caused by bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae. Atypical pneumonia usually is caused by the influenza virus, mycoplasma, chlamydia, legionella, adenovirus, or other unidentified microorganism. The patient’s age is the main differentiating factor between typical and atypical pneumonia; young adults are more prone to atypical causes, 5, 6 and very young and older persons are more predisposed to typical causes.
What is pneumonia in lungs?
Pneumonia is an inflammation or infection of the lungs that causes them to function abnormally. Pneumonia can be classified as typical or atypical, although the clinical presentations are often similar. Several symptoms commonly present in patients with pneumonia.
What percent of patients with Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 infection have Legionella antigens?
Legionella antigens were found in the urine of 48 percent of patients with suspected Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 infection. 14 Table 2 2, 8, 11, 13 includes the sensitivity and specificity of diagnostic tests for CAP.
When should fluoroquinolones be used?
Respiratory fluoroquinolones should be used when patients have failed first-line regimens, have significant comorbidities, have had recent antibiotic therapy, are allergic to alternative agents, or have a documented infection with highly drug-resistant pneumococci. C. 8, 9, 28, 29.
What is a chest radiograph for pneumonia?
Chest radiography (posteroanterior and lateral views) has been shown to be a critical component in diagnosing pneumonia. 8 According to the latest American Thoracic Society (ATS) guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of adults with CAP, “all patients with suspected CAP should have a chest radiograph to establish the diagnosis and identify complications (pleural effusion, multilobar disease).” 8 Chest radiography may reveal a lobar consolidation, which is common in typical pneumonia; or it could show bilateral, more diffuse infiltrates than those commonly seen in atypical pneumonia. However, chest radiography performed early in the course of the disease could be negative.
Why should the pneumonia severity index be used?
The Pneumonia Severity Index should be used to assist in decisions regarding hospitalization of patients with CAP.
What are the symptoms of community acquired pneumonia?
Patients with community-acquired pneumonia often present with cough, fever, chills, fatigue, dyspnea, rigors, and pleuritic chest pain. When a patient presents with suspected community-acquired pneumonia, the physician should first assess the need for hospitalization using a mortality prediction tool, such as the Pneumonia Severity Index, combined with clinical judgment. Consensus guidelines from several organizations recommend empiric therapy with macrolides, fluoroquinolones, or doxycycline. Patients who are hospitalized should be switched from parenteral antibiotics to oral antibiotics after their symptoms improve, they are afebrile, and they are able to tolerate oral medications. Clinical pathways are important tools to improve care and maximize cost-effectiveness in hospitalized patients.
What are the symptoms of pneumonia?
Presenting symptoms of pneumonia are typically cough, pleuritic chest pain, fever, fatigue, and loss of appetite. Children and the elderly have different presenting features of pneumonia, which include headache, nausea, abdominal pain, and absence of one or more of the prototypical symptoms. Knowledge of local bacterial pathogens and their antibiotic susceptibility and resistance profiles is the key for effective pharmacologic selection and treatment of pneumonia.
What is considered a nonresolving pneumonia?
Pneumonia is considered “nonresolving” if there is an inadequate clinical response despite antibiotic treatment .11The incidence of treatment failure is 6% to 15% and is associated with a 5-fold increase in mortality.29IDSA broadly classifies nonresponse into 2 different groups: (1) progressive pneumonia characterized by clinical deterioration and (2) persistent pneumonia with absence or delay of clinical stability.11Progressive pneumonia with deterioration is characterized by respiratory failure and/or septic shock and typically occurs within 72 hours. Persistent pneumonia with absent or delayed response is typically considered after a time period of 72 hours, because this is often regarded as the median time required for clinical stability.11, 29
How long should you be on a fluoroquinolone?
Patients should be treated for a minimum of 5 days and should be clinically stable with resolving symptoms before treatment is discontinued.11, 18Patients with high severity of infection or with extrapulmonary manifestations may benefit from longer duration of therapy, such as 7 to 10 days or until improving.11, 12
What is the probability of pneumonia?
No individual component of the history or physical examination is useful in diagnosing pneumonia, but the presence of multiple findings is required (Table 2). In adults presenting with acute cough, the baseline probability of pneumonia is only 5%. Absence of any vital sign abnormality (blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate) reduces the predicted probability of pneumonia to 1%.8A chest radiograph should be ordered for any patient with abnormal vital signs defined as temperature higher than 100°F, heart rate higher than 100 bpm, or respiratory rate higher than 20 bpm. Imaging should also be obtained for physical examination abnormalities of crackles or decreased breath sounds in a patient without asthma.10Infectious Disease Society of America 2016 Guidelines recommend imaging with a demonstrable infiltrate to confirm the diagnosis of pneumonia and to exclude other causes of cough and fever such as acute bronchitis.11Although X-ray imaging is a mainstay of diagnosis of pneumonia, the British Thoracic Society recommends the entire clinical picture should be considered when making a decision to treat.12A systematic review found that among patients who are sick enough to be admitted with a clinical diagnosis of CAP but have a normal initial chest radiograph, approximately 1 in 10 will develop radiographic evidence of pneumonia within 72 hours.8In such cases, it is appropriate to treat the patient empirically for pneumonia and repeat imaging in 24 to 48 hours.11Community resources and access to imaging may also affect decision to treat without imaging.
Can corticosteroids be used for CAP?
In recent years, there has been emerging data supporting the use of adjunctive corticosteroids in the inpatient treatment of CAP. As this is an area of research, multiple recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses have been published, some with conflicting findings. A 2011 Cochrane review that included relevant CAP studies through the year 2010 showed that corticosteroid use accelerates time to symptom resolution and clinical stability, with infrequent adverse effects.19Similarly, a 2015 systematic review by Siemieniuk and colleagues20included studies from 2011 through mid-2015. Their analysis of 13 randomized controlled trials found significantly decreased mortality in severe pneumonia, decreased need for mechanical ventilation, decreased occurrence of acute respiratory distress syndrome, decreased time to clinical stability, and shorter duration of hospitalization.20Hyperglycemia requiring treatment occurred more frequently in patients treated with corticosteroids.20, 21The most recent IDSA and BTS guidelines do not make recommendations regarding the routine use of adjunctive corticosteroid for CAP.11, 12Given the variations in dose and route of administration, an optimal agent and dose is unknown. Further research is needed to determine steroid dosing and duration, as well as what patient populations are most likely to benefit from its use.20, 21
What are the symptoms of penicillin allergy?
There are very few cases in which allergy testing or desensitization for penicillin is dangerous. These cases are called severe hypersensitivity syndromes. They are rare, but they include these syndromes: 1 Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic syndrome (DRESS) 2 Stevens-Johnson syndrome 3 Serum sickness 4 Toxic epidermal necrolysis 5 Hemolytic anemia 6 Acute interstitial nephritis
How many people are allergic to penicillin?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, less than 1 percent of people have a true penicillin allergy, even though about 10 percent of people tell their doctors they are allergic to penicillin. Sometimes, a common reaction to penicillin (such as an upset stomach or diarrhea) is mistaken for an allergy.
What happens if you don't have a reaction to penicillin?
If you don't have a reaction to the oral challenge or the skin testing, there is almost a 100 percent chance you are not allergic. Serious reactions to skin testing or an oral challenge are rare.
How long does it take for penicillin to go away?
If the test is positive, you may have some local swelling and itching, but this reaction will go away within an hour or so. If you don't have a skin reaction to penicillin, there is a 95 percent chance you are not allergic.
Is penicillin the best antibiotic?
Sometimes penicillin is the best drug to treat a certain infection. Using other drugs—called broad-spectrum antibiotics—instead of penicillin can be more expensive and less effective. These drugs are also more likely to cause antibiotic resistance and result in an infection that is very hard to treat. Using a broad-spectrum antibiotic ...
When was penicillin discovered?
Penicillin was discovered in 1828 . Today, the family of penicillin drugs includes more than 15 different antibiotics, such as: These antibiotics can be given by mouth or injection to treat many types of bacterial infections. Amoxicillin, for example, is one of the most common oral penicillins.
Is penicillin desensitization dangerous?
This type of desensitization wears off, but it can be followed by allergy shots from an allergist that will give you long-lasting protection. There are very few cases in which allergy testing or desensitization for penicillin is dangerous. These cases are called severe hypersensitivity syndromes.