
management of otitis externa
- prescribe suitable eardrops e.g. containing antibiotic and anti-inflammatory: Gentisone-HC contains gentamicin and...
- oral antibiotics may occasionally be prescribed with topical treatment. Use flucloxacillin (if not penicillin allergic)...
- note that review of the evidence suggests no clinical benefit with the use of oral antibiotics plus...
- antibiotic ear drops – this can treat an underlying bacterial infection.
- corticosteroid ear drops – this can help to reduce swelling.
- antifungal ear drops – this can treat an underlying fungal infection.
- acidic ear drops – this can help kill bacteria.
What is primary treatment for otitis externa (OE)?
- Assessing the severity of symptoms (for example, pain, itch, hearing loss, and ear discharge).
- Managing any aggravating or precipitating factors (such as diabetes mellitus, dermatitis, or ear trauma).
- Offering paracetamol or ibuprofen for symptomatic relief (plus codeine for severe pain).
- Treating infection, usually with a topical preparation.
Are ear drops safe to take while on antibiotics?
Ear drops can be helpful when treating an ear infection, but there are times when you shouldn’t use them. For example, if you or your child has a perforated eardrum, you should avoid the use of certain ototoxic ear drops (those that have a toxic effect on the ear and the ear’s nerve supply) because fluid from the drops can get deep into the ear and cause more problems.
What are otic drops?
US Brand Name
- Antibiotic Otic
- Cort-Biotic
- Cortisporin
- Cortomycin
- Oti-Sone
- Pediotic
What are the names of antibiotic ear drops?
To use the ear drops:
- Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water.
- Shake the bottle well before using it.
- Lie down or tilt your head so that the infected ear faces up. ...
- Drop the prescribed number of drops into the ear canal. ...
- Your doctor may insert a gauze or cotton wick inside your ear and may want you to keep the wick moistened with this medicine. ...
How do you apply antibiotic ear drops?
Tips for using ear drops correctlyWarm the ear drop bottle in your hands. ... Lie down with your affected ear facing up.Gently pull your ear back to help straighten the ear canal.Hold the dropper over the ear and squeeze out recommended drops (typically 4 to 5 drops of antibiotics per dose).More items...•
Which antibiotic is best for otitis externa?
Common topical antibiotics indicated for otitis externa include:Polymyxin B, neomycin, and hydrocortisone 3 to 4 drops to the affected ear four times a day.Ofloxacin 5 drops to the affected ear twice daily.Ciprofloxacin with hydrocortisone 3 drops to the affected ear twice daily.
What is the best ear drops for otitis externa?
Ciprofloxacin and dexamethasone combination ear drops is used to treat ear infections, such as acute otitis externa and acute otitis media. Otitis externa, also known as swimmer's ear, is an infection of the outer ear canal caused by bacteria.
How long do you let antibiotic ear drops sit in your ear?
Lie down with the affected ear up. Put enough drops in the ear canal to fill it up. Once the drops are in place, stay in this position for 3-5 minutes. Use a timer to help measure the time.
How do you use ofloxacin ear drops?
For ear infections:Adults and teenagers (12 years of age and older)—Place 10 drops in each affected ear two times a day for ten to fourteen days, depending on the infection.Children 1 to 12 years of age—Place 5 drops in each affected ear two times a day for ten days.More items...•
Does otitis externa need antibiotics?
Systemic Treatment Oral antibiotics are rarely needed2 but should be used when otitis externa is persistent, when associated otitis media may be present or when local or systemic spread has occurred.
Do antibiotic ear drops work for middle ear infections?
A middle ear infection may be treated with: Antibiotics, taken by mouth or as ear drops. Medication for pain.
Should you drain ear drops?
It is very important to make sure the drops reach all the way down to the eardrum. Lie on your side (or tilt) for 5 minutes then drain the drops out on a tissue for another 5 minutes to allow the entire canal to be coated. Wipe away excess and repeat with second ear if needed.
How long does it take for antibiotic ear drops to work?
Once I start using the eardrops how long should it take until I feel better? Most people feel better within 48 to 72 hours and have minimal or no symptoms by 7 days. Notify your doctor if your pain or other symptoms fail to respond within this time frame.
How many drops of ear drops should I use?
To apply ear drops, wash your hands first. To avoid contamination, do not touch the dropper tip or let it touch your ear or any other surface. Lie on your side or tilt the affected ear upward. Hold the dropper directly over the ear and place 5 to 10 drops into the ear canal.
What is the best treatment for otitis externa?
Otitis externa can be caused by bacteria, fungi or other germs. Antibiotic ear drops are the treatment of choice. 3 The ear drops that your medical provider will prescribe will likely include antibiotics, steroids, or anti-inflammatory medication.
How to prevent otitis externa?
If you are prone to otitis external, wearing earplugs can help keep water out of your ears when you're swimming or bathing.
How long does it take for otitis externa to heal?
6 Whether your ear drops contain a steroid most of your inflammation should resolve within 48-72 hours after using antibiotic ear drops.
What are the symptoms of otitis externa?
You should avoid self-treatment as other ear conditions can cause symptoms that are similar to otitis externa, including: 1 Otalgia (ear pain) 2 Otorrhea (ear drainage) 3 Inflammation of the external ear canal
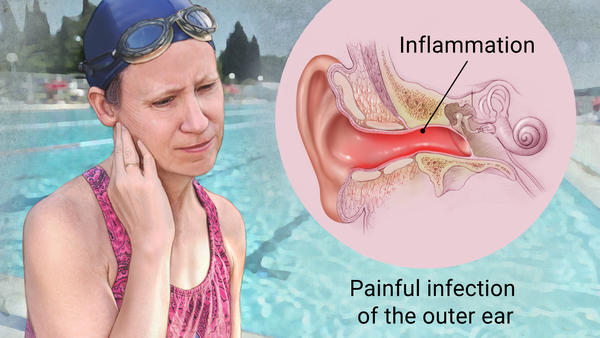
What is the name of the infection in the outer ear?
As of 2014, the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery published new guidelines to help standardize the treatment of otitis externa. As previously mentioned, otitis externa is an infection of the outer ear. It's called swimmer's ear because it often occurs when contaminated water sits in ...
Why is it important to treat otitis externa?
In addition to resolving the infection that causes otitis externa, treatments focus on controlling ear pain and other symptoms that accompany the condition.
What is swimmer's ear?
Learn about our Medical Review Board. John Carew, MD. on March 20, 2020. Acute otitis externa, more commonly called swimmer's ear, is an infection of the outer ear. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 1 in 123 Americans get swimmer's ear each year. 1 . While otitis externa can occur in any person ...
What is the treatment for acute otitis media?
The treatment of acute otitis media consists of analgesia, cleansing of the external auditory canal, and the application of antiseptic and antimicro bial agents. Local antibiotic and corticosteroid preparations have been found useful, but there have been no large-scale randomized controlled trials of their use.
What temperature is otitis externa?
Mild fever (up to 39°C) may be present; markedly higher temperatures suggest spread of the infection beyond the ear canal. Treatment. The treatment of uncomplicated acute otitis externa consists of cleansing the ear canal, topical antiseptic and antimicrobial treatment, and adequate analgesia.
What is malignant otitis externa?
Malignant (necrotizing) otitis externa is a destructive infection of the external auditory canal with invasive perichondritis and osteomyelitis of the lateral skull base, arising mainly in elderly men who are either diabetic or immunosuppressed .
What is the abscess in the hair follicle?
Chronic otitis externa often fails to respond to treatment administered for several weeks. Circumscribed otitis externa. Circumscribed otitis externa is an abscess-forming infection of a hair follicle (i.e., a furuncle) in the cartilaginous part of the external auditory canal, mostly due to Staphylococcus aureus.
What changes in the ear canal are seen in otitis externa?
The changes in the ear canal that are seen in otitis externa (e.g., hyperkeratosis of the epidermis, chronic granulation tissue, edema, or fibrosis of the dermis ) tend to narrow the canal. Epithelial cell migration normally rids the ear canal of cerumen, cellular detritus, and microorganisms.
How common is otitis externa?
Otitis externa is common all over the world, with a higher incidence in tropical than in temperate zones because of the higher temperature and humidity. Its lifetime prevalence is estimated at 10% (4). It affects adults most commonly, and children only rarely (generally aged 7 to 12) (e1).
How long does it take for otitis to heal?
Acetic acid is comparably effective to antibiotic or corticosteroid drops after 7 days of treatment, but significantly less effective if treatment is needed for 2–3 weeks (10) . Topical antibiotics. Acetic acid.
What are the primary outcomes of antibiotics?
The primary outcome measures were the rates of topical, oral, or a combination of antibiotic prescriptions for uncomplicated acute otitis externa (AOE) in primary care . The secondary outcome measures included the choice of prescribed antibiotics and the rate of oral antibiotic prescriptions without a valid indication.
What is the most common antibiotic prescribed?
The most frequent prescriptions were Amoxicillin or Ampicillin (34%), followed by Co-amoxiclav (amoxicillin/clavulanic acid) (19%), Flucloxacillin (15%), and macrolides (14%) [1]. Selwyn and Lau [11] found that 6% of patients were given only an oral antibiotic, usually Amoxicillin (11%).
Is antibiotic over prescribed for otitis externa?
Background: There is a perception among ear, nose, and throat (ENT) surgeons that oral antibiotics are over-prescribed for acute otitis externa (AOE), and the potential for topical therapy as first-line treatment is not fully realized in primary care.
Why does otitis externa come back?
irritation or an allergic reaction – otitis externa can occur because of a reaction to something that comes into contact with your ears , such as ear medication, ear plugs, shampoo or sweat. Otitis externa can also return after previous treatment if you don't complete the full course of recommended treatment.
What causes otitis externa?
Most cases of otitis externa are caused by a bacterial infection, although the condition can also be caused by: irritation. fungal infections. allergies. There are a number of things that can make you more likely to develop otitis externa, including: damaging the skin inside your ear. regularly getting water in your ear.
What does it mean when your ear hurts when you move it?
discomfort and pain in your ear that becomes worse when you move it – this is usually much milder than in short-term otitis externa. a thin, watery discharge from your ear. a lack of earwax. a build-up of thick, dry skin in your ear canal, known as stenosis, which can narrow your ear canal and affect your hearing.
How long does otitis externa last?
In some cases, the symptoms of otitis externa can persist for several months, or sometimes years. This is known as chronic otitis externa. Symptoms of chronic otitis externa can include: a constant itch in and around your ear canal.
What is the name of the condition where the hair follicle inside the ear becomes infected by bacteria
Symptoms of otitis externa. Otitis externa can cause a number of different symptoms affecting the ear and the surrounding area. Otitis externa sometimes occurs if a hair follicle inside the ear becomes infected by bacteria and develops into a spot (pimple) or boil.
Why is my ear red?
Otitis externa is often referred to as "swimmer's ear" because repeated exposure to water can make the ear canal more vulnerable to inflammation.
How to protect ears from water?
If you're a regular swimmer, consider using ear plugs when swimming or wearing a swimming cap to cover your ears and protect them from water. You should also try to avoid getting water, soap or shampoo into your ears when you have a shower or bath. Read more about preventing otitis externa.
What are the parts of the ear?
The ear has three parts to it: outer, middle, and inner. Otitis externa is an infection of the outer ear, which includes the opening of the ear and the ear canal, all the way to the eardrum.
Can acetic acid be used to treat otitis externa?
Over the counter ear drops can consist of acetic acid (vinegar) to acidify the ear canal, plus cortisone to heal inflammation. These usually are not strong enough to cure a bad otitis externa infection.
Drugs used to treat Otitis Externa
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Alternative treatments for Otitis Externa
The following products are considered to be alternative treatments or natural remedies for Otitis Externa. Their efficacy may not have been scientifically tested to the same degree as the drugs listed in the table above. However there may be historical, cultural or anecdotal evidence linking their use to the treatment of Otitis Externa.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.

Treatment
- Most cases of otitis externa are caused by shallow bacterial infections. Accordingly, many people with this condition might be treated with topical antibiotic preparations. Some preparations likewise consist of a corticosteroid active ingredient. The small amount of steroid that exists in t…
Usage
- This otic suspension is shown for usage in OE, along with for usage in otitis media in individuals with tympanostomy tubes.
Medical uses
- Hydrocortisone/neomycin/polymyxin is an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agent for otic use, offered as a solution or a suspension. It is utilized to treat steroid-responsive inflammatory conditions for which a corticosteroid is indicated and in which bacterial infection or a danger of bacterial infection exists. Otic ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone that hinders bacterial synthesis …
Chemistry
- Otic ofloxacin is a pyridine carboxylic acid derivative with broad-spectrum result that inhibits bacterial growth by preventing DNA gyrase. It is available as a 0.3 % (3 mg/mL) solution.
Mechanism of action
- Tobramycin interferes with bacterial protein synthesis by binding to 30S and 50S ribosomal subunits, thus causing problems in the bacterial cell membrane. Dexamethasone decreases inflammation by reducing migration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) and lowering capillary permeability. TobraDex is an ophthalmic option that may be utilized for OE. Ciprofloxac…
Introduction
- Inflammation and accumulated debris enable the development of bacterial types. This growth is combated by the usage of mild acidifying medications, such as acetic acid options. These representatives are useful for fungal OE or for moderate OE believed to be of bacterial origin. They can also be useful for avoidance.
Reactions
- Aluminum acetate has a drying result. Acetic acid works well in superficial bacterial infections of OE.
Pharmacology
- Acetic acid is anti-bacterial and antifungal; hydrocortisone is anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, and antipruritic. The combination of the 2 agents is economical and works well in dealing with superficial bacterial infections of OE.