Most cases of metabolic alkalosis can be managed with fluid and electrolyte therapy. When metabolic alkalosis needs to be resolved quickly or when conventional therapy cannot be tolerated, mineral acid administration should be instituted.
Full Answer
What are the signs and symptoms of metabolic alkalosis?
Metabolic alkalosis does not present with any specific signs and symptoms. The symptoms which are experienced occur due to hypoventilation and hypokalemia which take place along with it. Due to hypokalemia, individuals often suffer from weakness, arrhythmias, polyuria and myalgia.When there is associated hypoventilation that occurs as compensatory mechanism, individuals suffer from muscle ...
How can you prevent metabolic acidosis?
You can do the following to reduce your risk of respiratory acidosis:
- Take sedatives as prescribed and never mix them with alcohol.
- Stop smoking. Smoking can damage your lungs and make breathing less effective.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Obesity can make it harder for you to breathe.
How can metabolic acidosis be compensated?
Metabolic compensation
- Diabetes treatment. Resolving metabolic acidosis caused by untreated or uncontrolled diabetes includes treatment for diabetes.
- IV sodium bicarbonate. Adding base to counter high acids levels treats some types of metabolic acidosis. ...
- Hemodialysis. Dialysis is a treatment for serious kidney disease or kidney failure. ...
- Other treatments for metabolic acidosis. ...
What is respiratory compensation for metabolic acidosis?
Respiratory compensation is the physiologic mechanism to help normalize a metabolic acidosis, however, compensation never completely corrects an acidemia. It is important to determine if there is adequate respiratory compensation or if there is another underlying respiratory acid-base disturbance.

What is the treatment for metabolic alkalosis?
Metabolic alkalosis is usually treated by replacing water and electrolytes (sodium and potassium) while treating the cause. Rarely, when metabolic alkalosis is very severe, dilute acid is given intravenously. In respiratory alkalosis, the first step is to ensure that the person has enough oxygen.
How do nurses treat metabolic alkalosis?
Nursing Interventions for Metabolic AlkalosisBased on the cause: vomiting (give antiemetic ex: Zofran, Phenergan), stop diuretics.Doctor may order Diamox (Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors): a diuretic which reduces the reabsorption of bicarb.Watch ABGs and signs of respiratory distress.More items...
What is first aid for person with symptoms of alkalosis?
The first step when treating respiratory alkalosis is to breathe and get enough oxygen. If you're hyperventilating, being able to slow down your breathing, breathing calmly, and easing anxiety will help restore your oxygen.
Which drugs cause metabolic alkalosis?
Active use of thiazides or loop diuretics in hypertension is the most common cause of metabolic alkalosis in hypertensive patients.
What is the treatment of metabolic acidosis?
Metabolic acidosis treatments may include : oral or intravenous sodium bicarbonate to raise blood pH. sodium citrate to treat metabolic acidosis due to distal renal tubular acidosis. insulin and intravenous fluids to treat ketoacidosis.
How do you increase blood bicarbonate?
One way to increase bicarbonate levels is through alkali therapy, which could include taking sodium bicarbonate. Your doctor could also suggest taking another similar supplement, such as calcium citrate, calcium carbonate, or calcium acetate. Taking sodium bicarbonate introduces sodium (salt) into your body.
How can you prevent alkalosis?
Reduce your risk for developing alkalosis by maintaining good health, eating a healthy diet, and staying hydrated. Choosing foods high in nutrients and potassium can help combat electrolyte deficiencies. Nutrients and potassium are primarily found in fruits and vegetables, as well as some other foods, such as: carrots.
Which of the following chemical agent is used for the treatment of acidosis or alkalosis?
Introduction. Sodium Citrate is a urine alkalinizing agent. After absorption it is metabolized to produce bicarbonate. It can be used to treat metabolic acidosis, where the generated bicarbonate buffers excess hydrogen ions in the blood, raising its p H.
How to diagnose metabolic alkalosis?
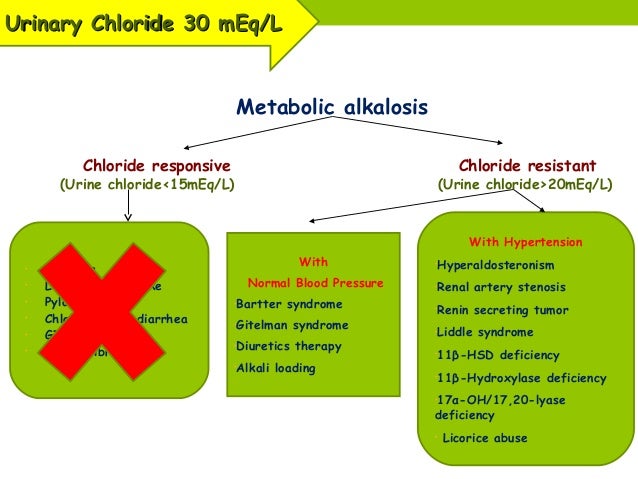
Metabolic alkalosis is diagnosed by measuring serum electrolytes and arterial blood gases. If the etiology of metabolic alkalosis is not clear from the clinical history and physical examination, including drug use and the presence of hypertension, then a urine chloride ion concentration can be obtained. Calculation of the serum anion gap may also help to differentiate between primary metabolic alkalosis and metabolic compensation for respiratory acidosis. (See Workup .)
What is metabolic alkalosis?
Metabolic alkalosis is defined as elevation of the body's pH above 7.45. [ 1] . Metabolic alkalosis involves a primary increase in serum bicarbonate (HCO 3-) concentration, due to a loss of H + from the body or a gain in HCO 3-. As a compensatory mechanism, metabolic alkalosis leads to alveolar hypoventilation with a rise in arterial carbon dioxide ...
Why does bicarbonate increase in concentration?
Because the original bicarbonate mass is now dissolved in a smaller volume of fluid, an increase in bicarbonate concentration occurs. This increase in bicarbonate causes, at most, a 2- to 4-mEq/L rise in bicarbonate concentration. Maintenance of metabolic alkalosis. Decreased perfusion to the kidneys, caused by either volume depletion ...
What is the name of the process that produces metabolic alkalosis?
Vomiting or nasogastric (NG) suction generates metabolic alkalosis by the loss of gastric secretions, which are rich in hydrochloric acid (HCl). Whenever a hydrogen ion is excreted, a bicarbonate ion is gained in the extracellular space.
What causes chloride-responsive alkalosis?
The principal causes of chloride-responsive alkalosis are the loss of gastric secretions, ingestion of large doses of nonabsorbable antacids, and use of thiazide or loop diuretics. [ 2] . Miscellaneous causes account for the remainder of cases. [ 3] Gastric secretions are rich in hydrochloric acid (HCl).
Why does refeeding with a carbohydrate rich diet after prolonged fasting result in mild metabolic alka?
Refeeding with a carbohydrate-rich diet after prolonged fasting results in mild metabolic alkalosis because of enhanced metabolism of ketoacids to bicarbonate. Massive blood transfusion results in mild metabolic alkalosis as the citrate in the transfused blood is converted to bicarbonate.
Why is cortisol in the reference range?
Serum cortisol is within the reference range because the negative feedback of cortisol on adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is intact. Active use of thiazides or loop diuretics in hypertension is the most common cause of metabolic alkalosis in hypertensive patients. The mechanism of alkalosis is discussed above.
What is the best treatment for metabolic alkalosis?
The choice of therapy in metabolic alkalosis varies with the underlying cause. Depending on the may be used in specific situation, the following may be used [ 19] : 1 Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (eg, acetazolamide) 2 Hydrochloric acid (HCl) 3 Potassium-sparing diuretics 4 Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors 5 Potassium supplements 6 Fluid replacement 7 Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
What is acidic IV?
Acidic IV solutions are used to treat severe metabolic alkalosis. Seek the advice of nephrologist in severe alkalosis when HCl therapy or dialysis is contemplated.
What is NH4Cl used for?
NH4Cl is converted to ammonia and HCl by the liver. By releasing HCl, NH4Cl may help correct metabolic alkalosis. This agent is available as 500-mg tablets and a 26.75% parenteral formulation for intravenous use.
What is the purpose of diuretics?
Diuretics may be used to treat severe metabolic alkalosis in edematous states (eg, from congestive heart failure (CHF), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or right heart failure). This agent inhibits carbonic anhydrase, the enzyme that catalyzes the hydration of CO2 and dehydration of carbonic acid.
What is the drug that inhibits binding to aldosterone receptors?
View full drug information. Spironolactone is an aldosterone antagonist that competitively inhibits binding to the aldosterone receptor. It competes for receptor sites in distal renal tubules and increases water excretion while retaining potassium and hydrogen ions needed to restore acid-base balance. Amiloride.
What is potassium essential for?
Potassium is essential for transmission of nerve impulses, contraction of cardiac muscle, maintenance of intracellular tonicity, skeletal and smooth muscles, and maintenance of normal renal function.
Is amiloride a diuretic?
Amiloride is a pyrazine-carbonyl-guanidine that is unrelated chemically to other known potassium-conserving (antikaliuretic) or diuretic agents. It is an antikaliuretic drug, which, compared with thiazide diuretics, possesses weak natriuretic, diuretic, and antihypertensive activity.
What is the treatment for metabolic alkalosis?
Correction of metabolic alkalosis in patients with renal failure may require hemodialysis or continuous renal replacement therapy with a dialysate that contains high levels of chloride and low levels of HCO 3. Note that use of the chelating agent sodium polystyrene sulfonate (SPS) for the treatment of hyperkalemia in children with chronic kidney disease may precipitate acute hypocalcemia and increased metabolic alkalosis. [ 19] Oral calcium supplementation and cessation of SPS therapy corrected the hypocalcemia in two affected children. [ 19]
How to avoid metabolic alkalosis?
Metabolic alkalosis may be avoided by judicious use of long-term diuretics with appropriate monitoring.
What is the role of a pediatric tertiary care center in the care of a child with metabolic?
The role of a pediatric tertiary care center where appropriate subspecialists are available in the care of a child with metabolic alkalosis cannot be overemphasized. If the patient requires dialysis or has a renal disease, such as Bartter syndrome, transfer the patient to a nephrologist. An endocrinologist should manage primary aldosteronism and mineralocorticoid excess states. Children who develop hypovolemic shock or those with persistent severe and symptomatic metabolic alkalosis are best monitored in a critical care setting.
What is the goal of alkalosis therapy?
As with correction of any electrolyte or acid-base imbalance, the goal is to prevent life-threatening complications with the least amount of correction. The initial target pH and bicarbonate levels in correcting severe ...
Is acetazolamide safe for cardiac patients?
Acetazolamide may help patients with chloride-resistant metabolic alkalosis. It has been safely used for treatment of diuretic- induced metabolic alkalosis in pediatric cardiac patients. [ 15, 16, 17] Acetazolamide also appears to be as effective as arginine hydrochloride in correcting metabolic alkalosis in critically ill pediatric patients. [ 18]
Can HCl be used for metabolic alkalosis?
For persistent severe metabolic alkalosis, administration of HCl or ammonium chloride (NH 4 Cl) may be considered, but each must be administered with care. [ 13] Although uncommon, fatality from extravasated HCl has been reported. [ 14]
Can metabolic alkalosis cause hypoventilation?
Other considerations. Respiratory status and oxygenation must be monitored. Failure to realize that severe metabolic alkalosis can lead to hypoventilation and consequent hypoxemia could delay treatment and result in hypoxic damage.
How to diagnose metabolic alkalosis?
Metabolic alkalosis is diagnosed by measuring serum electrolytes and arterial blood gases. If the etiology of metabolic alkalosis is not clear from the clinical history and physical examination, including drug use and the presence of hypertension, then a urine chloride ion concentration can be obtained. Metabolic alkalosis secondary to volume depletion is usually associated with a low urine chloride ion concentration (< 20 mEq/L).
Which approach is more accurate for diagnosing acid-base disorders?
In a study that compared the conventional Henderson-Hasselbalch equation with the strong ion approach, carried out in 100 patients with trauma who were admitted to a surgical intensive care unit, the investigators concluded that the strong ion approach provides a more accurate means of diagnosing acid-base disorders, including metabolic alkalosis and tertiary disorders. [ 13]
What is the purpose of measuring plasma renin activity and aldosterone level?
Measuring the plasma renin activity and aldosterone level may help in finding the etiology of metabolic alkalosis, especially in patients with hypertension, hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis, and renal potassium wasting without diuretic use.
How long to measure aldosterone levels in urine?
Measure aldosterone levels in a 24-hour urine collection after salt loading to diagnose primary hyperaldosteronism.
Does Henderson-Hasselbalch equation account for acid-base?
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation may fail to account for acid-base findings in critically ill patients. An alternative method of acid-base analysis, known as the quantitative, or strong ion, approach, [ 12] determines pH on the basis of the following 3 independent variables (see Metabolic Acidosis ):
Can bicarbonate be calculated?
Because pH and PaCO 2 are directly measured, bicarbonate can be calculated.
What is the best treatment for hypochloremic alkalosis?
Replacement of electrolytes with chloride salts is the most important mode of therapy for hypochloremic alkalosis. A full nutritional assessment should be obtained, energy intake calculated, and adequate energy intake ensured through oral or nasogastric methods. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs; eg, ...
Why should fluid intake be encouraged in patients with CLD?
In patients with CLD, fluid intake should be encouraged so as to prevent renal damage resulting from recurrent dehydration. Patients or caregivers should be instructed to avoid long periods of exposure to hot climates, which may exacerbate dehydration episodes.
What is the best treatment for Bartter syndrome?
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs; eg, indomethacin) are used in patients with Bartter syndrome. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (eg, acetazolamide) may be used in some acute situations. Potential complications of pharmacotherapy include the following:
What is preclinical lab workup?
The preclinic laboratory workup includes a biochemical profile and monitoring of urine electrolytes. The pharmacotherapeutic regimen should be reviewed at each visit. Medications should be refilled and dosages adjusted in accordance with the patient’s clinical status and laboratory results.
How long does it take for IV fluids to be discontinued?
Long-term management (after 72 hours) For long-term management, intravenous (IV) fluids can be discontinued. The physician should calculate the average daily amounts of chloride, sodium, and potassium that were required to correct the serum electrolyte levels.
What supplements should be given to patients with a trace element deficiency?
Multivitamins and hematinic agents should be provided as required. Supplemental trace elements (eg, zinc) should be provided to patients with a trace-element deficiency, such as some patients with chloride-losing diarrhea (CLD).
What is the treatment for shock?
If the patient is in shock, treatment should be directed toward aggressive resuscitation with isotonic fluid, preferably normal saline. Blood and urine samples for testing of electrolytes should always be obtained before any form of therapy is initiated; this is of great help in differentiating etiologic factors in new cases.
How to treat metabolic acidosis?
Metabolic acidosis in patients with CKD can also be treated with dietary modification. Dietary acid reduction can be accomplished by limiting the intake of acid-producing foods such as animal protein and emphasizing base-producing foods such as fruits and vegetables.
What is the best alkali for chronic metabolic acidosis?
Oral alkali administration is the preferred route of therapy in persons with chronic metabolic acidosis. The most common alkali forms for oral therapy include NaHCO 3 tablets. These are available in 325 and 650 mg strengths (1 g of NaHCO 3 is equal to 11.5 mEq of HCO 3- ).
What is the most commonly used agent to correct metabolic acidosis?
Sodium bicarbonate ( NaHCO 3) is the agent most commonly used to correct metabolic acidosis. The HCO 3- deficit can be calculated by using the following equation:
What happens to anions in high anion gap acidosis?
In high anion gap acidosis secondary to accumulation of organic acids, lactate, and ketones, these anions are eventually metabolized to HCO 3-. When the underlying disorder is treated, the serum pH corrects; thus, caution should be exercised in these patients when providing alkali to raise the pH much higher than 7.20, because an overshoot alkalosis may occur.
What happens when pH drops below 7.20?
When the serum pH is below 7.20, a continued fall in the serum HCO 3- level may result in a significant drop in pH. This is especially true when the PCO 2 is close to the lower limit of compensation, which in an otherwise healthy young individual is approximately 15 mm Hg. With increasing age and other complicating illnesses, the limit of compensation is likely to be less. A further small drop in HCO 3- at this point thus is not matched by a corresponding fall in PaCO 2, and rapid decompensation can occur. For example, in a patient with metabolic acidosis with a serum HCO 3- level of 9 mEq/L and a maximally compensated PCO 2 of 20 mm Hg, a drop in the serum HCO 3- level to 7 mEq/L results in a change in pH from 7.28 to 7.16.
How is insulin administered for diabetic ketoacidosis?
For diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), insulin is administered, usually intravenously, to facilitate cellular uptake of glucose, reduce gluconeogenesis, and halt lipolysis and production of ketone bodies. In addition, normal saline is administered to restore extracellular volume; potassium and phosphate replacement also may be necessary. The acidosis is corrected partly by the metabolism of ketones to HCO 3 -, partly by increased H + secretion by the collecting duct, and partly by H + excretion as NH 4 +.
How much alkali should I take for RTA?
Adult patients should be given the amount required to buffer the daily acid load from the diet. This is usually approximately 1-3 mEq/kg/d and can be administered in any form, although the preferred form is as potassium citrate. Correction of acidosis usually corrects the hypokalemia, but K + supplements may be necessary.
Why is respiratory alkalosis unsuccessful?
Because respiratory alkalosis usually occurs in response to some stimulus, treatment is usually unsuccessful unless the stimulus is controlled. If the PaCO 2 is corrected rapidly in patients with chronic respiratory alkalosis, metabolic acidosis may develop due to the renal compensatory drop in serum bicarbonate.
What is the best treatment for hyperventilation syndrome?
In hyperventilation syndrome, patients benefit from reassurance, rebreathing into a paper bag during acute episodes, and treatment for underlying psychological stress. Sedatives and/or antidepressants should be reserved for patients who have not responded to conservative treatment. Beta-adrenergic blockers may help control the manifestations of the hyperadrenergic state that can lead to hyperventilation syndrome in some patients. [ 4]
Can mechanical ventilation cause respiratory alkalosis?
In mechanically ventilated patients who have respiratory alkalosis, the tidal volume and/or respiratory rate may need to be decreased. Inadequa te sedation and pain control may contribute to respiratory alkalosis in patients breathing over the set ventilator rate.
Is respiratory alkalosis life threatening?
The treatment of respiratory alkalosis is primarily directed at correcting the underlying disorder. Respiratory alkalosis itself is rarely life threatening. Therefore, emergent treatment is usually not indicated unless the pH level is greater than 7.5. Because respiratory alkalosis usually occurs in response to some stimulus, treatment is usually unsuccessful unless the stimulus is controlled. If the PaCO 2 is corrected rapidly in patients with chronic respiratory alkalosis, metabolic acidosis may develop due to the renal compensatory drop in serum bicarbonate.
How to manage metabolic alkalosis?
Most cases of metabolic alkalosis can be managed with fluid and electrolyte therapy. When metabolic alkalosis needs to be resolved quickly or when conventional therapy cannot be tolerated, mineral acid administration should be instituted.
What is the role of buffering systems in the body?
Three buffering systems are used by the body to correct an arterial pH above 7.45--tissue, respiratory, and renal systems. The kidneys have the primary responsibility for correcting a severe metabolic alkalosis, but several conditions (e.g., severe volume contraction) can interfere with the renal mechanisms.
How to reverse metabolic alkalosis?
This can usually be reversed by treatment with a saline solution.
What is metabolic alkalosis?
Metabolic alkalosis is a condition that occurs when your blood becomes overly alkaline. Alkaline is the opposite of acidic. Our bodies function best when the acidic-alkaline balance of our blood is just slightly tilted toward the alkaline. Alkalosis occurs when your body has either:
What causes alkaline bicarbonate ions to deplete?
Heart, kidney, or liver failure. Metabolic alkalosis can be caused by failure of a major organ, such as your heart, kidney, or liver. This leads to potassium depletion.
How do kidneys help with alkalosis?
The kidneys can help combat alkalosis by increasing the excretion of bicarbonate ions through the urine. This is also an automatic process, but it’s slower than respiratory compensation.
How does the body compensate for alkalosis?
Your body compensates for both alkalosis and acidosis mainly through your lungs. The lungs change the alkalinity of your blood by allowing more or less carbon dioxide to escape as you breathe. The kidneys also play a role by controlling the elimination of bicarbonate ions.
What causes alkalosis in the body?
Loss of stomach acids. This is the most common cause of metabolic alkalosis. It’s usually brought on by vomiting or suction through a nose-feeding tube. The gastric juices have a high content of hydrochloric acid, a strong acid. Its loss causes an increase in the alkalinity of the blood.
What is the scale used to measure acidity?
The acidity or alkalinity of a liquid is measured on a scale called pH. In metabolic alkalosis, the pH of your blood is high.