Nutrition
Management and Treatment How is epiglottitis treated? Epiglottitis must be treated in the hospital as a medical emergency. The first step is to restore the airways to full capacity. An oxygen mask will be used to deliver air to the lungs.
How is epiglottitis treated?
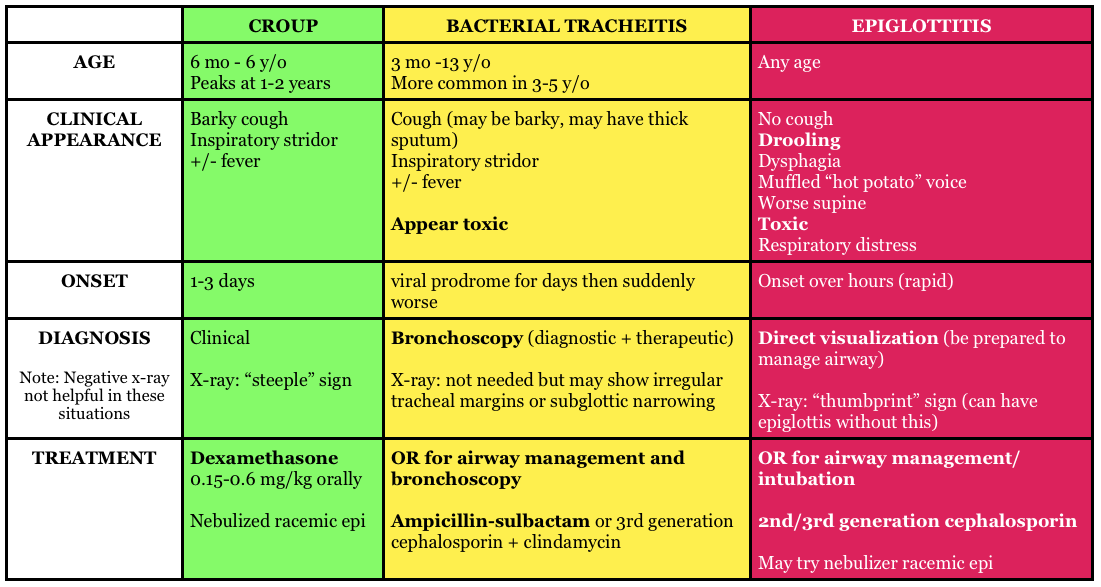
When we eat, the epiglottis covers the top of the windpipe, so that food goes into the swallowing tube (esophagus), and not into the lungs. Epiglottitis is a rare, but potentially life-threatening infection. It causes sudden swelling of the epiglottis, which often worsens rapidly, sometimes within hours.
What happens if the epiglottis is swollen?
An anesthesiologist and an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist or a general surgeon should be notified as soon as possible when epiglottitis is suspected. Early anesthesiologist and otolaryngologist consultation facilitates initial safe airway management, which is then followed by appropriate antibiotic treatment.
Which specialist consultations are beneficial to patients with epiglottitis?
Diagnosis. After doctors in the hospital confirm that the epiglottis is inflamed, the airway is kept open using a breathing tube. Blood tests and/or throat swabs are done to determine which organism is causing the infection.
How do you diagnose epiglottitis?
What is the best treatment for epiglottis?
TreatmentWearing a mask. The mask delivers oxygen to the lungs.Having a breathing tube placed into the windpipe through the nose or mouth (intubation). ... Inserting a needle into the trachea (needle cricothyroidotomy).
What is epiglottis EMT?
Epiglottitis is a more severe form of upper airway inflammation characterized by the swelling of the epiglottis. It is caused by a bacterial infection from the H. influenza type B bacteria (Hib). In recent decades, epiglottitis has become very rare due to immunization efforts.
Is epiglottis an emergency?
Epiglottitis is regarded as a medical emergency, as a swollen epiglottis can restrict the oxygen supply to your lungs. Call 999 for an ambulance if you think you or your child has epiglottitis.
Can you give epinephrine for epiglottitis?
Bronchodilators, such as racemic epinephrine, have not been shown to be effective in acute epiglottitis but may be considered in patients with impending airway obstruction while preparing for airway intervention. Racemic epinephrine should not be used in children because it may cause agitation and promote laryngospasm.
Is epiglottitis a droplet precaution?
Epiglottitis is spread via droplets, which harbors an infectious agent like bacteria. When is the HIB vaccine administered? It is part of the pediatric vaccination schedule and is given in 3-4 doses (depending on the brand used). It is administered at 2, 4, 6, and 12-15 months.
What drug is most effective in upper airway emergencies?
Nebulized epinephrine, via its alpha-1 effect of vasoconstriction, is a highly effective treatment for upper airway obstruction caused by croup. Asthma causes lower airway obstruction and is treated with albuterol whose beta-2 mechanism causes relaxation of the lower airways.
What are the 4 D's of epiglottitis?
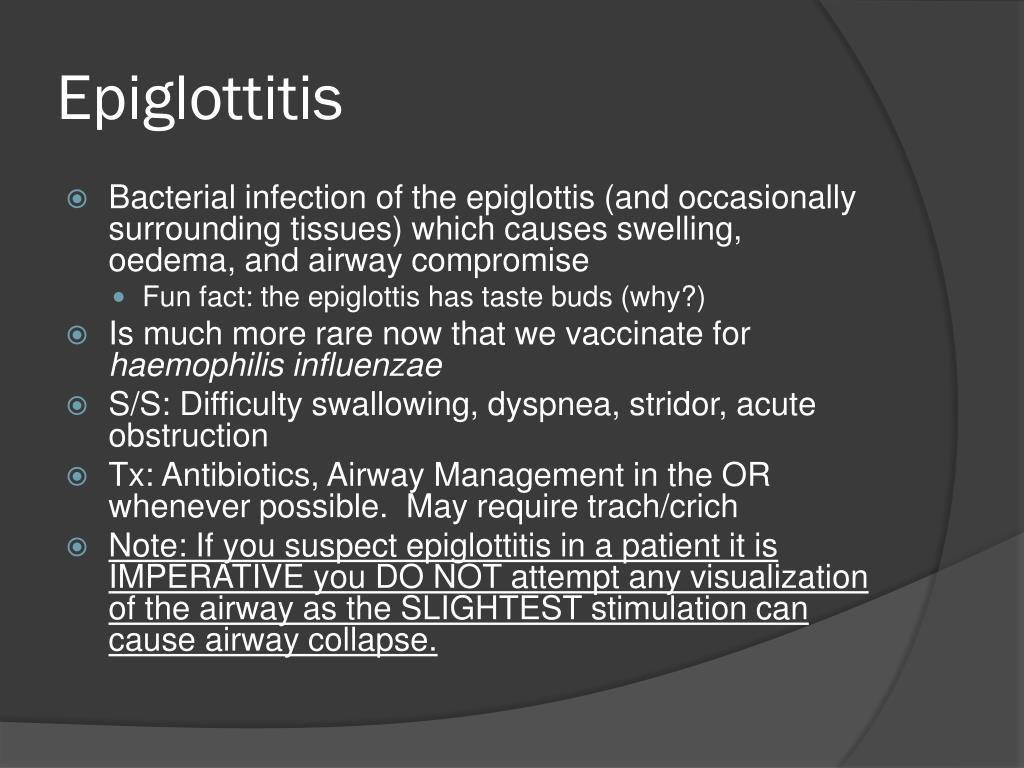
The throat is inflamed, and the epiglottis is swollen, stiff, and a beefy red color. The disease can progress rapidly resulting in toxicity, prostration, severe dyspnea, and cyanosis. The physician should be watchful for dysphagia, dysphonia, drooling, and distress—the four D's.
Why is epiglottis an emergency?
Epiglottitis can cause airway obstruction and inability to breathe, particularly in children. The epiglottis is a flap of cartilage that sits in the back of the throat and closes over the airway during swallowing so that food and liquids do not go into the lungs.
Which treatment is appropriate for the child with epiglottitis and severe respiratory distress?
Treatment involves emergency care and the opening the child's airway with a breathing tube. Your child may also get antibiotics or other medicines. The Hib vaccine can prevent most cases of epiglottitis.
Why is racemic epinephrine contraindicated in epiglottitis?
Racemic epinephrine should be avoided because of the rebound effect. Awareness of the possibility of epiglottitis in adults and close monitoring of the airway are the keys to management of this potentially life-threatening condition.
Do you intubate for epiglottitis?
Awake intubation is frequently described in the literature as the preferred method for securing the airway in adult patients with epiglottitis, whereas children with epiglottitis are usually intubated following an inhalational induction.
What is racemic epinephrine used for?
Epinephrine racemic is used for temporary relief of symptoms associated with bronchial asthma (e.g., shortness of breath, chest tightening, wheezing) and to treat croup in children. Epinephrine racemic is available under the following different brand names: AsthmaNefrin and S2.
How to treat epiglottitis in children?
Children with acute epiglottitis are in danger of full airway obstruction and respiratory arrest that comes on rapidly and may be caused by minor irritation of the throat. For this reason; gentle handling of a child suspected of having epiglottitis is essential. The following guidelines should be observed when dealing with the potentially fatal illness: 1 DO NOT try to lay the patient flat or dictate their position of comfort 2 DO NOT visualize the airway if the airway if the child is still adequately ventilating 3 Advise the receiving facility of your suspicion of epiglottitis 4 Administer 100% humidified oxygen by mask, if tolerated 5 DO NOT attempt vascular access (the added stress can be detrimental to the airway) 6 Have the proper advanced airway adjuncts ready and at hand 7 Intercostal retractions with decreasing stridor is an ominous sign of impending respiratory failure 8 Transport the child in position of comfort with parent nearby 9 Decreasing mental status means decreasing respiratory drive; TREAT AGGRESSIVELY! 10 If respiratory arrest occurs before arrival at the ED, intubation should be attempted once, rapidly 11 If respiratory arrest occurs then IV/IO access is appropriate after airway control is initiated
Why is epiglottitis dangerous?
Children with acute epiglottitis are in danger of full airway obstruction and respiratory arrest that comes on rapidly and may be caused by minor irritation of the throat. For this reason; gentle handling of a child suspected of having epiglottitis is essential.
What is the best prehospital care for croup?
Good prehospital management of croup includes airway maintenance with the administration of humidified, or nebulized oxygen and rapid transport in the position of comfort to an appropriate medical facility. Symptoms may improve dramatically in patients with croup after the child is treated with O2 therapy.
Is 104 F dangerous?
A serious fever above 104F (40C) often accompanies the illness and can be dangerous if the patient isn't treated promptly.
Can a patient be ventilated with a BVM?
Sometimes a patient may be ventilated effectively with a BVM and a tight facial seal. This method requires two skilled rescuers to deliver the ventilations. If the patient can not be intubated; medical command may order a needle cricothyroidotomy.
Is epiglottitis a disease?
Epiglottitis although rare, is inflammation of the epiglottis. The epiglottis is located in the upper airway. It's that little flap that covers the trachea during swallowing. If this "flap" becomes inflamed, it swells and this swelling could cause a partial or even complete airway occlusion, thus compromising ventilation and if intubation is needed. The inflammation may involve other structures such as the arytenoid, false cords and the posterior tongue. Epiglottitis affects children 2-5 years of age; however, the median age has been steadily increasing over the past decade and may be seen in children of all ages. The associated inflammation common with epiglottitis presents acutely in these otherwise healthy children. Epiglottic inflammation occurs quickly and can be deadly if not recognized and dealt with rapidly. A serious fever above 104F (40C) often accompanies the illness and can be dangerous if the patient isn't treated promptly.#N#These children will often be found sitting on the edge of their chair; leaning forward and using accessory muscles in an attempt to help move air in and out of their lungs more effectively. Many children with epiglottitis will complain of a severe sore throat especially when they swallow. It is common to witness excessive salivation in children experiencing a sore throat and/or difficulty swallowing (dysphagia). A cough is usually not associated with epiglottitis, mainly due to upper airway component of the illness. Epiglottitis is a true medical emergency that requires prompt, expert airway management!
What is epiglottitis inpatient?
SUMMARY. Epiglottitis is defined as inflammation of the epiglottis and/or neighboring supraglottic structures and is generally caused by a bacterial infection.
What are the clinical manifestations of epiglottitis?
Clinical presentation of epiglottitis can include odynophagia, dysphagia, use of the tripod position, and stridor once the resulting edema begins to cause substantial airway obstruction.
What is epiglottitis in the lungs?
Epiglottitis is defined as inflammation of the epiglottic or adjacent supraglottic structures including the hypopharynx. If left untreated, the progression of epiglottitis and the resulting edema can be devastating leading to complete or partial airway obstruction.
What is a high pitched wheezing sound?
Stridor is a high-pitched wheezing sound that results from disrupted airflow, a key sign of partial airway obstruction that can be associated with several different disease states. Stridor itself is caused by restrictions to airflow most commonly resulting from inflammation in the tissues surrounding the airway.
How to secure airway in a patient?
Immediate steps should be taken to secure the patient's airway either by intubation or placement of a tracheostomy.12If intubation is deemed necessary, pressing down on the patient's chest may allow for an air bubble to form in the glottic opening, which may aid in the placement of the endotracheal tube.
What is the cause of epiglottitis?
Epiglottitis is typically caused by a bacterial infection. Historically, epiglottitis has been an infection mostly prevalent in children ages 2 to 6 years old. However, since the introduction of the Haemophilus influenzae B(HiB) vaccine, there has been a shift with increasing incidence within the adult population.
Can a radiograph show epiglottitis?
Radiographs can be helpful in diagnosing epiglottitis; however, they should not supersede or postpone securing the airway.
What is the cause of epiglottitis?
Epiglottitis is usually caused by an infection from Haemophilus influenza type b (Hib) bacteria, the same bacteria that cause pneumonia and meningitis. Transmission of the bacteria is the same as with the common cold: Droplets of saliva or mucus are spread into the air when a carrier of the bacteria coughs or sneezes.
What is the inflammation of the epiglottis?
Epiglottitis. Epiglottitis is an inflammation and swelling of the epiglottis. Usually caused by a bacterial infection, it can cause pain when swallowing, severe sore throat and difficulty breathing. Appointments & Access. Contact Us. Overview. Symptoms and Causes. Diagnosis and Tests.
What are the symptoms of swallowing pain?
Difficulty and pain when swallowing (a main symptom in older children and adults) Difficulty breathing (a main symptom in children), which may be helped by sitting up and leaning forward, or breathing with an open mouth and protruding tongue.
How to restore airways to full capacity?
The first step is to restore the airways to full capacity. An oxygen mask will be used to deliver air to the lungs. If air passages have already been blocked, a tube is placed in the throat and is pushed past the swelling to deliver oxygen into the lungs.
Can you lay on your back with epiglottitis?
At no time should a person suspected of having epiglottitis be laid on their back, have anything inside their mouth, or have anyone but a doctor examine their throat. Remaining calm and under control is also important so that additional stress-induced tightening of the throat does not occur.
How long does it take to extubate a patient after intubation?
If intubated, patients can be extubated once the initial insult and airway obstruction have resolved. This usually occurs after two to three days of antibiotics if the pathogen is HiB.
What is the purpose of the BC Emergency Medicine Summary?
The purpose of this document is to provide health care professionals with key facts and recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of patients in the emergency department. This summary was produced by the BC Emergency Medicine Network and uses the best available knowledge at the time of publication. However, healthcare professionals should continue to use their own judgment and take into consideration context, resources and other relevant factors. The BC Emergency Medicine Network is not liable for any damages, claims, liabilities, costs or obligations arising from the use of this document including loss or damages arising from any claims made by a third party. The BC Emergency Medicine Network also assumes no responsibility or liability for changes made to this document without its consent.
When did epiglottitis occur?
Epiglottitis can occur at any age. Until 1985, epiglottitis occurred most commonly in children aged 3 to 7, but with the development of a vaccine against Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib), epiglottitis is now increasingly rare in vaccinated children.
What happens if you press on your tongue to look down your throat?
N ever try to look down the throat of a person who is suspected of having epiglottitis. Pressing on the tongue to look down the throat may cause the epiglottis to swell even more and further block the airway.
Can you have a tube inserted in your throat for epiglottitis?
Epiglottitis needs to be treated in the hospital so the person's breathing can be monitored. If the person is having trouble breathing, he or she may need to have a breathing tube inserted in his or her throat.
Can an X-ray show an enlarged epiglottis?
X-rays of the neck sometimes can show an enlarged epiglottis, but the time needed to take the X-rays may delay other important tests and treatment. After doctors in the hospital confirm that the epiglottis is inflamed, the airway is kept open using a breathing tube.
Can epiglottis cause death?
It causes sudden swelling of the epiglottis, which often worsens rapidly, sometimes within hours. Without timely treatment, the epiglottis can become so large that it blocks the windpipe, making it hard to breathe. This can cause death. Epiglottitis can occur at any age.