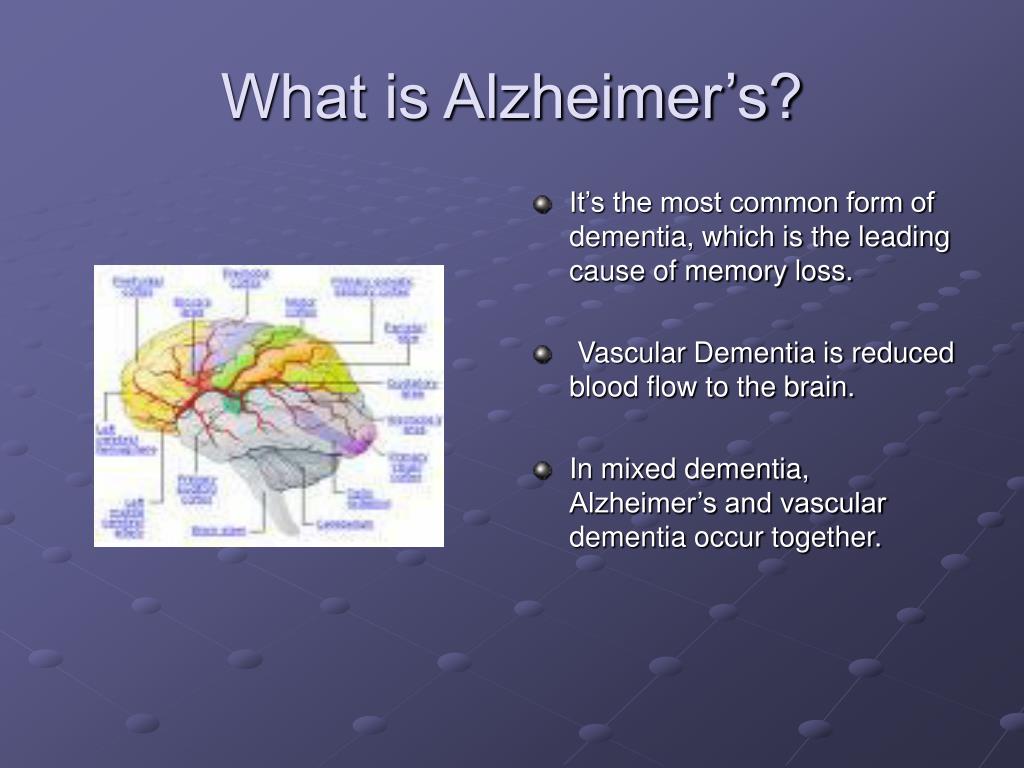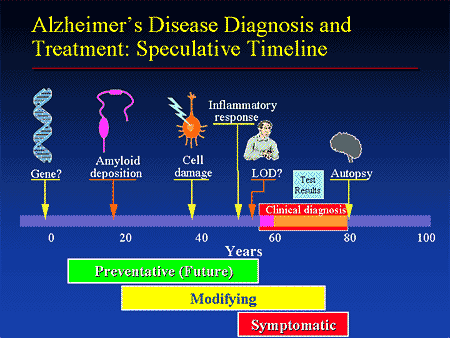
Medication
- Be sure to discuss the increased risk of stroke and death with the doctor and among family members. ...
- It’s best to start with the lowest dose possible.
- If there have been visual hallucinations or other signs of possible Lewy-Body dementia, quetiapine is usually the safest first choice.
Self-care
The drug company Biogen has received federal approval for a medicine to treat early Alzheimer's disease. The Food and Drug Administration approved the drug aducanumab to treat patients with Alzheimer's disease on Monday. It is the first new drug approved by the agency for Alzheimer's disease since 2003.
See more
As not everyone with Alzheimer’s will experience the disease the same way, treatment plans might look different as well. Although there is no cure right now, finding a cure for Alzheimer’s disease and a treatment that stops disease progression is an active area of biomedical research. Available treatments for Alzheimer's
What is the best medicine for Alzheimers?
That’s an important caveat because Medicare is expected to cover most of the patients who opt for Aduhelm, and the drug can cost as much as $28,000 annually, not counting expenses for brain scans and other care patients will need while taking it.
What is the new Alzheimer medicine?
Is there a cure for Alzheimer's?
Is aduhelm approved by Medicare?

How do drugs help Alzheimer's?
Donepezil, rivastigmine and galantamine all prevent an enzyme called acetylcholinesterase from breaking down acetylcholine. This means there is a higher concentration of acetylcholine in the brain, which leads to better communication between nerve cells. This may ease some symptoms of Alzheimer's disease for a while.
Are the drugs used to treat Alzheimer's symptoms effective?
Medications don't work for everyone, and they may lose effectiveness over time. They tend to be most effective for people with early to moderate Alzheimer's.
What are 3 treatments for Alzheimer's?
There are three drugs of this type: donepezil (Aricept), galantamine (Razadyne), and rivastigmine (Exelon). Aricept is the only treatment approved by the FDA for all stages of Alzheimer's disease: mild, moderate, and severe.
How is Alzheimer's treated early?
Although Alzheimer disease has no cure, you can make the best of a bad situation by keeping your mind and your body as healthy as possible. This can include eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, cutting down on alcohol, and using relaxation techniques to reduce stress.
How does dementia medication work?
These medicines prevent an enzyme from breaking down a substance called acetylcholine in the brain, which helps nerve cells communicate with each other. Donepezil (also known as Aricept), rivastigmine (Exelon) and galantamine (Reminyl) are used to treat the symptoms of mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease.
What is the best treatment for dementia?
Cognitive stimulation therapy It is currently the only psychological dementia treatment directly recommended by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) to help people with mild or moderate dementia.
How many Alzheimer's drugs are there?
There are four FDA-approved drugs available to treat symptoms due to Alzheimer's disease. While the drugs may modestly improve memory and reduce confusion, they are not curative and are unable to stop the disease from worsening over time.
What is the most effective treatment for Alzheimer's disease?
Aducanumab is the only disease-modifying medication currently approved to treat Alzheimer's. This medication is a human antibody, or immunotherapy, that targets the protein beta-amyloid and helps to reduce amyloid plaques, which are brain lesions associated with Alzheimer's.
What is the success rate of memantine?
Of the 318 patients randomized to and treated with memantine, 85% completed the study, compared with 91% of the 152 patients randomized to the placebo group.
How close is a cure for Alzheimer's?
With a growing understanding of how AD affects the neurons in the brain, finally, there has been an Alzheimer's cure breakthrough 2022. The majority of research has focused on the plaques in the brain of AD individuals.
Is there a cure for Alzheimer's 2021?
In June 2021, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved aducanumab for the treatment of some cases of Alzheimer's disease. This is the first drug approved in the United States to treat the underlying cause of Alzheimer's by targeting and removing amyloid plaques in the brain.
Role of Current Alzheimer's Drugs
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved two types of drugs specifically to treat symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. 1. Cholinesterase inh...
Cholinesterase Inhibitors
One way Alzheimer's disease harms the brain is by decreasing levels of a chemical messenger (acetylcholine) that's important for alertness, memory,...
Memantine For Later Stages
Memantine (Namenda) is approved by the FDA for treatment of moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. It works by regulating the activity of glutamat...
When to Discontinue Alzheimer's Drugs
Because Alzheimer's is a progressive disease, your symptoms and care plan will change over time. If you're taking an Alzheimer's drug, ongoing revi...
What is the drug used to treat Alzheimer's?
A medication known as memantine, an N-methyl D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonist, is prescribed to treat moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease. This drug’s main effect is to decrease symptoms, which could enable some people to maintain certain daily functions a little longer than they would without the medication.
What is the best treatment for Alzheimer's?
Aducanumab is the only disease-modifying medication currently approved to treat Alzheimer’s. This medication is a human antibody, or immunotherapy, that targets the protein beta-amyloid and helps to reduce amyloid plaques, which are brain lesions associated with Alzheimer’s.
Why was aducanumab approved?
The approval of aducanumab was based on the ability of the drug to reduce amyloid in the brain. When using the accelerated approval pathway, drug companies are required to conduct additional studies to determine whether there is in fact clinical benefit after the drug is approved.
How does memantine help Alzheimer's patients?
For example, memantine may help a person in the later stages of the disease maintain his or her ability to use the bathroom independently for several more months, a benefit for both the person with Alzheimer's and caregivers. Memantine is believed to work by regulating glutamate, an important brain chemical.
How does memantine work?
Memantine is believed to work by regulating glutamate, an important brain chemical. When produced in excessive amounts, glutamate may lead to brain cell death. Because NMDA antagonists work differently from cholinesterase inhibitors, the two types of drugs can be prescribed in combination.
What is the FDA's Accelerated Approval Program?
FDA’s Accelerated Approval Program. Aducanumab was approved through the FDA’s Accelerated Approval Program, which provides a path for earlier approval of drugs that treat certain serious conditions. This helps people living with the disease gain earlier access to the treatment.
What are the symptoms of Alzheimer's?
Common behavioral symptoms of Alzheimer’s include sleeplessness, wandering, agitation, anxiety, aggression, restlessness, and depression. Scientists are learning why these symptoms occur and are studying new treatments — drug and nondrug — to manage them.
How does Alzheimer's affect your life?
A person’s quality of life may be impacted by a variety of behavioral and psychological symptoms that accompany dementia, such as sleep disturbances, agitation, hallucinations and delusions. Some medications focus on treating these non-cognitive symptoms for a time, though it is important to try non-drug strategies to manage behaviors before adding medications.
What is the drug used for sleep wake?
Orexin receptor antagonist (Belsomra®) Prescribed to treat insomnia for individuals living with dementia, this drug is thought to inhibit the activity of orexin, a type of neurotransmitter involved in the sleep-wake cycle: Suvorexant (Belsomra®): approved for mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease.
What is aducanumab used for?
Aducanumab (Aduhelm™): anti-amyloid antibody intravenous (IV) infusion therapy approved for Alzheimer's disease. When considering any treatment, including aducanumab, it is important to have a conversation with your health care provider to determine if you are a candidate for the treatment.
How does Aducanumab work?
Aducanumab works by targeting beta-amyloid, a microscopic protein fragment that forms in the brain and accumulates into plaques . These plaques disrupt communication between nerve cells in the brain and may also activate immune system cells that trigger inflammation and devour disabled nerve cells. While scientists aren’t sure what causes cell death ...
What is cholinesterase inhibitor?
Cholinesterase (KOH-luh-NES-ter-ays) inhibitors are prescribed to treat symptoms related to memory, thinking, language, judgment and other thought processes. These medications prevent the breakdown of acetylcholine (a-SEA-til-KOHlean), a chemical messenger important for memory and learning.
What is the FDA approved medication for?
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved medications that fall into two categories: drugs that may change disease progression in people living with Alzheimer’s, and drugs that may temporarily mitigate some symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. When considering any treatment, it is important to have a conversation with a health care ...
What is the purpose of namenda?
Glutamate regulators (Namenda®) Glutamate regulators are prescribed to improve memory, attention, reason, language and the ability to perform simple tasks. This type of drug works by regulating the activity of glutamate, a different chemical messenger that helps the brain process information. This drug is known as:
How does memantine work?
However, when nerve cells are damaged by Alzheimer’s disease, too much glutamate is produced. This causes more damage to the nerve cells. Memantine protects nerve cells by blocking the ...
Why does acetylcholine get lost?
Acetylcholine helps to send messages between certain nerve cells. In Alzheimer’s disease some of the nerve cells that use acetylcholine are also lost. Because of these changes in the brain, symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease get worse over time.
Is cholinesterase inhibitor better than other drugs?
All three cholinesterase inhibitors work in a similar way. However, one drug might be better for someone than another. For instance, a person may have fewer side effects from one drug.
Why do people with Alzheimer's take medicine?
Some people with Alzheimer's take medicines to treat behavior problems such as restlessness, anxiety, depression, trouble sleeping, and aggression. Experts agree that medicines to treat behavior problems should be used only after other strategies ...
How to keep a list of medications for Alzheimer's?
Keep the list in a safe place at home, and make a copy to keep in your purse or wallet. Bring it with you when you visit the person's doctor or pharmacist. People with Alzheimer's should be monitored when they start taking a new drug. Follow the doctor's instructions and report any unusual symptoms right away.
How to make sure a medicine is taken safely?
Other ways to make sure medicines are taken safely: Keep all medications locked up. Check that the label on each prescription bottle has the drug name and dose, patient's name, dosage frequency, and expiration date.
How to treat Alzheimer's disease?
Some people with Alzheimer's take medicines to treat behavior problems such as restlessness, anxiety, depression, trouble sleeping, and aggression. Experts agree that medicines to treat behavior problems should be used only after other strategies that don't use medicine have been tried. Talk with the person's doctor about which medicines are safest and most effective. With these types of medicines, it is important to: 1 Use the lowest dose possible 2 Watch for side effects such as confusion and falls 3 Allow the medicine a few weeks to take effect
What are some examples of medications that can be swallowed?
Examples of these drugs include: Atrovent® (ipratropium) Dramamine® (dimenhydrinate) Diphenhydramine —includes brand names such as Benadryl® and Nytol®. Some people, especially those with late-stage Alzheimer's, may have trouble swallowing pills.
What are the other conditions that can be treated with Alzheimer's?
Medicines to Treat Other Medical Conditions. Many people with Alzheimer's disease also have other medical conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or heart disease. They may take different medicines for these conditions. It's important to track all the medicines they take and take the list with you to every visit to a doctor.
What is a pillbox?
A pillbox allows you to put pills for each day in one place. Some pillboxes come with alarms that remind a person to take the medicine. As Alzheimer's gets worse, you will need to keep track of the person's medicines. You also will need to make sure the person takes the medicines or give the medicines to him or her.
What is the chemical that helps Alzheimer's patients with memory loss?
Acetylcholine is a substance that occurs naturally in the brain and enables nerve cells in the brain to pass messages to each other. Research has shown that many people with Alzheimer’s disease have a reduced amount of acetylcholine in the brain, and it is thought that the loss of this chemical contributes to the memory loss of Alzheimer’s.
What is the main treatment for acetylcholine?
Cholinesterase inhibitors. The main treatments used are the cholinesterase inhibitors (also known as anti-cholinesterase drugs). Four have been licensed for use in many countries. These drugs work by reducing the breakdown of a chemical –acetylcholine – in the brain.
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat cholinesterase?
The cholinesterase inhibitors include donepezil (available with the brand name Aricept ®, Aricet® ), galantamine (Reminyl ®, Razadyne ®, Acumor ®, Gatalin ® ), and rivastigmine (Exelon ® ). An earlier drug of this type was tacrine (Cognex ® ), which has mostly been superseded by the newer compounds because of its significant side effects.
What is the purpose of antipsychotics?
Antipsychotic drugs (also known as ‘major tranquillisers’ or ‘neuroleptics’) are usually used to treat people with mental health conditions such as schizophrenia. In some people with dementia antipsychotics can help with certain symptoms such as aggression, agitation, hallucinations, and delusions (false beliefs).
Is glutamate toxic to nerve cells?
The drug modifies the function of a receptor in the brain which is involved with the chemical transmitter glutamate, and research has suggested that too much glutamate is damaging or toxic to the nerve cell.
Is there a cure for dementia?
There is a lot of research taking place into new drug treatments for Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias. The currently available medications are not a cure.
Does memantine slow the progression of Alzheimer's?
They do not slow the progression of the damage to the brain, but can stabilise some of the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease for a limited period of time. There are two types of medication currently available, cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine.
FDA-Approved Drugs to Help Control Symptoms
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the following medications that may help regulate or manage Alzheimer’s disease symptoms. They do so by regulating neurotransmitters, the brain chemicals that transmit messages between neurons.
How these Drugs Work
These drugs may work for some people but not others, and they do not stop the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Instead, the drugs may delay it or help with symptom control for a period of time, particularly in the earlier stages of the disease.
Side Effects
Always talk to a doctor about the pros and cons of trying a particular drug treatment, alone or in combination with other drugs or with behavioral approaches. Even if certain medicines are well tolerated by most patients, drugs may have side effects such as:
Treatments for Anxiety, Depression, and Psychosis
Often, as Alzheimer’s disease progresses, people experience depression, agitation, and psychotic symptoms such as paranoid thoughts or hallucinations. This may lead to behavior problems like:
Related Conditions
It’s important to see a physician to rule out any other medical conditions or drug interactions as the cause of these problems. Read more about medical conditions and medicines that can mimic dementia.
Environmental Factors that Affect Mood
Medications like anti-depressants may help reduce anxiety or depression. Before any drug therapies, however, physicians and family caregivers will want to review what may be triggering these symptoms to see whether any behavioral approaches may help.
What is the most common medication for dementia?
Commonly used drugs: Valproic acid (brand name Depakote) is the most commonly used medication of this type, in older adults with dementia. It is available in short- and long-acting formulations. Usual effects:The effect varies depending on the dose and the individual.
What are the different types of medications for dementia?
Most medications used to treat difficult behaviors fall into one of the following categories: 1.Antipsychotics. These are medications originally developed to treat schizophrenia and other illnesses featuring psychosis symptoms.
What is the name of the drug that calms agitation?
Olanzapine (brand name Zyprexa) Haloperidol (brand name Haldol) For a longer list of antipsychotics drugs, see this NIH page. Usual effects: Most antipsychotics are sedating, and will calm agitation or aggression through these sedating effects.
What is it called when you are acting crazy?
Sleep disturbances. These are technically called “neuropsychiatric” symptoms, but regular people might refer to them as “acting crazy” symptoms. Or even “crazy-making” symptoms, as they do tend to drive family caregivers a bit nuts.
What are the challenges of Alzheimer's?
These are symptoms beyond the chronic memory/thinking problems that are the hallmark of dementia. They include problems like: Delusions, paranoid behaviors, or irrational beliefs. Agitation (getting “amped up” ...
Does citalopram cause agitation?
Nausea and gastrointestinal distress, especially when first starting or increasing doses (SSRIs) SSRIs may be activating in some people, which can worsen agitation or insomnia. Citalopram (in doses higher than 20mg/day) can increase the risk of sudden cardiac arrest due to arrhythmia.
Should I taper down my dad's depakote?
You should certainly discuss your depakote concerns with your father’s doctors. It may be reasonable to further taper down his depakote and see how he is, both in terms of inappropriate behavior and in terms of the other symptoms you are concerned about. Good luck, I hope you find a better solution for your father.
What are the two types of dementia drugs?
There are two primary types of dementia drugs. One has been around for several decades and has been well studied—the cholinesterase inhibitors ( CI's) —which work by altering a brain chemical that may improve mental function temporarily. Most studies on these drugs have been done on Aricept (donepezil), one of the earliest versions, ...
What is dementia in psychology?
Rather, dementia is deterioration of the thought process. While people with memory loss may forget someone's name or not remember where they put their keys, people with dementia cannot follow a conversation and often become confused about simple tasks.
How many people improve with a placebo?
The most remarkable finding in dementia drug trials, and something rarely brought up, is that there is a tremendous placebo effect. In fact, of 1000 people who receive a placebo, approximately 300 of them will improve by 4 or more points on their ADAS-Cog.
How many people have reversible dementia?
There are also several conditions that mimic dementia and can potentially be treated, but these are rare; of 1000 people who are screened for a reversible cause of dementia, only 3 are found to have reversible disease, and most of those are discovered by a basic set of tests that can be done by a primary care doctor.
How many stages of dementia are there?
Most dementia also progresses through seven stages; the symptoms worsen with time at variable rates, and can often lead to total disability and dependency. While many forms of dementia exist, from Alzheimer's Disease to Pick's Disease, the deterioration in thinking and reasoning is similar in all of them.
How many people have dementia in 2015?
Written By: Andy Lazris, M.D. Published On December 16, 2015. Dementia is one of the most frightening diseases that inflicts my patients. Approximately 2 million Americans suffer from dementia, and that number is increasing as more people are aging. Dementia is not merely memory loss; in fact, ...
Can dementia make you agitated?
Some people with the disease hallucinate, some become agitated and violent, some become more passive and lethargic; there are probably many more forms of dementia than medical science has described, and most people have a combination of symptoms that change over time.