Long-term oxygen therapy for chronic hypoxemic respiratory failure. LTOT is widely accepted as treatment to counterbalance chronic, significant hypoxemia in COPD although it is known to represent a considerable amount of still increasing health-care costs (Croxton et al 2006).
Full Answer
What are the 4 types of respiratory failure?
Pulmonary hygiene techniques are ways to treat your hypoxia symptoms without medication or oxygen. The techniques include: The techniques include: cough and deep breathe
How to prevent respiratory failure?
The patient’s Vital signs were as follows: temperature, 99.4 F (37.4°C); heart rate, 62 beats per minute; respiratory rate, 23 breaths per minute; blood pressure, 92/56 mmHg. The patient was well-nourished and in an acute on chronic hypoxic and hypercapnic respiratory distress (oxygen saturation of 96% on room air).
What are the signs and symptoms of acute respiratory failure?
May 02, 2022 · Use your oxygen as directed. You may need extra oxygen if your blood oxygen level is lower than it should be. Use pursed-lip breathing any time you feel short of breath. Take a deep breath in through your nose. Slowly breathe out through your mouth with your lips pursed for twice as long as you inhaled.
What are the causes of respiratory failure?
Nov 26, 2021 · Correction of Hypoxemia. The goal is to maintain adequate tissue oxygenation, generally achieved with an arterial oxygen tension (PaO2) of 60 mm Hg or arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2), about 90%. Un-controlled oxygen supplementation can result in oxygen toxicity and CO2 (carbon dioxide) narcosis.

How is hypoxic respiratory failure treated?
Is chronic respiratory failure with hypoxia curable?
What causes chronic respiratory failure with hypoxia?
What is the most appropriate treatment for a patient in respiratory failure?
How much oxygen should be given to a patient with chronic respiratory failure?
How is acute respiratory failure treated?
- Supplemental oxygen. For milder symptoms or as a temporary measure, oxygen may be delivered through a mask that fits tightly over your nose and mouth.
- Mechanical ventilation. Most people with ARDS will need the help of a machine to breathe.
Can you recover from acute respiratory failure?
Can acute respiratory failure be cured?
How is hypercapnic respiratory failure treated?
What is the best way to treat respiratory failure without medical help?
How do doctors treat lung failure?
What medications treat respiratory failure?
- Diuretics, Other.
- Nitrates.
- Opioid Analgesics.
- Inotropic Agents.
- Beta2 Agonists.
- Xanthine Derivatives.
- Anticholinergics, Respiratory.
- Corticosteroids.
What Is Chronic Respiratory Failure?
Chronic respiratory failure (CRF) is a long-term condition that happens when your lungs cannot get enough oxygen into your blood. Your heart, brain...
What Causes Chronic Respiratory Failure?
1. Heart conditions such as left-sided heart failure or mitral stenosis 2. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) 3. A problem with the nerve...
What Are The Symptoms of CRF?
1. Rapid breathing 2. Shortness of breath, especially with activity 3. Feeling like you cannot get enough air 4. A bluish color on your skin, finge...
When Should I Contact My Healthcare Provider?
1. Your have new symptoms. 2. Your symptoms get worse. 3. You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Does COPD cause shallow breathing?
In the chronic setting, patients with COPD often show a rapid shallow breathing. This presumably represents a key protective mechanism to prevent respiratory muscle fatigue, however at the price of an insufficient alveolar ventilation (Roussos et al 2003).
Is COPD a high risk for death?
Patients with advanced COPD and acute or chronic respiratory failure are at high risk for death . Beyond pharmacological treatment, supplemental oxygen and mechanical ventilation are major treatment options. This review describes the physiological concepts underlying respiratory failure and its therapy, as well as important treatment outcomes.
How to reverse hypoxia?
Reversing hypoxia involves increasing your oxygen intake. A common method for providing extra oxygen is oxygen therapy. Oxygen therapy is also called supplemental or prescribed oxygen. It involves using a mechanical device that supplies oxygen to your lungs.
Does COPD cause hypoxia?
COPD results in inflammation and swelling of your airways. It also causes destruction of the lung tissue called alveoli. COPD causes a restricted flow of oxygen in your body as well. Symptoms of hypoxia often include: COPD is a chronic condition, so you may experience any of these symptoms on an ongoing basis.
What are the best medications for COPD?
Besides oxygen treatments to treat hypoxia, and your regular medications for COPD, you may also need medications to control breathing problems caused by other conditions. These medications may include: 1 blood pressure medications that reduce swelling 2 heart medications that control heart failure 3 heart medications that control chest pain 4 medications that control indigestion or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) 5 allergy medications
What is the name of the condition that causes difficulty breathing?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a group of lung conditions that includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Restricted airflow characterizes all these conditions, and COPD causes difficulty when breathing. The inability to get enough oxygen into the lung raises the risk for developing hypoxia.
Why is breathing difficult with COPD?
Restricted airflow characterizes all these conditions , and COPD causes difficulty when breathing. The inability to get enough oxygen into the lung raises the risk for developing hypoxia. Hypoxia is a condition where not enough oxygen makes it to the cells and tissues in the body. This can happen even though blood flow is normal.
What is it called when you don't have enough oxygen?
Hypoxia is a condition where not enough oxygen makes it to the cells and tissues in the body. This can happen even though blood flow is normal. Hypoxia can lead to many serious, sometimes life-threatening complications. However, if you know what to look for you can manage the condition before it leads to dangerous complications.
How does COPD affect the body?
The only way for your body to get oxygen is through your lungs. COPD results in inflammation and swelling of your airways. It also causes destruction of the lung tissue called alveoli. COPD causes a restricted flow of oxygen in your body as well. Symptoms of hypoxia often include: shortness of breath while resting.
What causes respiratory failure?
Conditions that affect the way in which the brain, muscles, bones, or surrounding tissues support breathing can also cause chronic respiratory failure. Diseases and conditions that commonly lead to chronic respiratory failure include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) complicated pneumonia.
What is bipap therapy?
BiPAP therapy targets these dysfunctional breathing patterns. The nurses, especially the respiratory nurses, bedside nurses, and primary care physician play a big role in the management of the condition. It is responsible for the medical team to work together in managing the patient condition and to advocate for things when the condition worsens. On the other hand, the home physician plays a role in ensuring all the medications, exercises and deities are followed well to avoid further complications (Toshikuni et al., 2014).
What is M.J.'s medical history?
He has no past surgical history. Additional findings of M.J past medical history includes Cirrhosis of the Liver diagnosed within the past 3 years, hepatitis C, severe back and shoulder pain from a work-related injury, pressure headaches, depression, COPD, anxiety, abdominal distension, GERD and GOUT. M.J said he quit drinking and smoking 2 years ago. He reported smoking approximately 108 pack of cigarettes a year an average of 2 packs a day for the past 40 years. He also reported drinking 9 ounces of alcohol a day for 40 years. The patient was admitted to Metro Health Cleveland on June 7, 2019, for exacerbation of respiratory symptoms. The rest of M.J medical history is unremarkable. The patient upon arriving at the hospital did not use supplementary oxygen at home and at the time of his hospital assessment. He reported bowel incontinent which he stated started about 4 months ago and consistently occur once or twice a week. He gets about 4 loose liquid like stool per day.
What are the diagnoses of a nursing patient?
Nursing Diagnoses include possible ineffective airway clearance and breathing pattern; high risk for aspiration, infection, and/or altered respiratory function; Assessments include determining baseline respiratory status (assess patient’s ability to cough and deep breathe effectively, auscultate the chest, and note the breathing pattern); monitor chest x-rays, blood gas levels, CBC , sputum cultures , and pulmonary function tests. Nursing Interventions include frequent suctioning, intubation and ventilator support, as well as supplementary oxygen and consultation with pulmonologist, if necessary, and the respiratory regimen of chest percussion, and deep breathing due to the patients ventilator; assist with cough as needed; provide tracheostomy care every 4 hours, chest physical therapy and deep breathing exercises every 2 – 4 hours, IPPB every 4 hours, and use of incentive spirometer every 4 hours. This will reveal the level of decompensation as well as if interventions are effective Complete a full respiratory assessment to detect changes or further decompensation as early as possible and notify MD as indicate. Nursing Diagnoses include decreased cardiac output, altered tissue perfusion, the risk for peripheral neurovascular dysfunction, dysrhythmias, DVT, and hypovolemia. Assessments include monitoring vital signs, cardiac monitoring for arrhythmias, monitoring response to head elevation, observation for signs of thrombophlebitis, DVT, and PE, and EKG, electrolyte and coagulation tests. Nursing Interventions include treating life-threatening arrhythmias, heparin to prevent DVT, use of sequential compression boots, vasopressors and consultation with a cardiologist as needed. Provide supplemental oxygen as appropriate- Supplemental oxygen will ideally increase patient oxygen levels. (Use caution with COPD patients, as they cannot breathe out the CO2 adequately, so over-oxygenation is a concern, and they also may have a lower baseline SpO2 level). Ensure patient is in an optimal position to decrease work of breathing- Sitting up in bed to enable appropriate lung expansion allows for adequate inspiration and expiration, which facilitates better gas exchange (if clinically appropriate to be sitting up) Prepare for rapid sequence intubation, if necessary-Helpful to be prepared, as this can progress quickly. Know where the necessary meds and equipment are and how to get ahold of assistive personnel. Remove any negative/distracting stimuli: turn the TV off, encourage family members to be calm When patients are anxious or cannot focus it can increase their work of breathing and exacerbate the issue. Promote a calming environment so all the patient must worry about is breathing. Provide oral care- If a patient is intubated or receiving oxygen via nasal cannula/face mask or tent, or other methods of delivery, oral care is essential to protect the mucous membrane and prevent infection. Cluster care- Decreases oxygen demands if the patient’s rest can be maximized
What is oral care?
Provide oral care- If a patient is intubated or receiving oxygen via nasal cannula/face mask or tent, or other methods of delivery, oral care is essential to protect the mucous membrane and prevent infection. Cluster care- Decreases oxygen demands if the patient’s rest can be maximized.
Where is M.J. from?
The patient who I will refer to as M.J is a 55-year old single male Caucasian American living in Cleveland OH. He relocated to Cleveland 10 years ago from South Carolina where he has family. He has never been married. He has 4 siblings, a sister 20 years his junior who he claims he has never met and 3 brothers ages 22, 25 and 35 years respectively. His family according to M. J still reside in South Carolina. He has no family here in Cleveland. The assessment was done on June 10, 2019, at Metro Health Cleveland.
How to get oxygen out of your system?
Use pursed-lip breathing any time you feel short of breath. Take a deep breath in through your nose. Slowly breathe out through your mouth with your lips pursed for twice as long as you inhaled.
How to breathe out of your lungs?
Take a deep breath in through your nose. Slowly breathe out through your mouth with your lips pursed for twice as long as you inhaled. You can also practice this breathing pattern while you bend, lift, climb stairs, or exercise. It slows down your breathing and helps move more air in and out of your lungs.
What is CRF in medical terms?
What is chronic respiratory failure (CRF)? CRF is a long-term condition that happens when your lungs cannot get enough oxygen into your blood. CRF can also happen when your lungs cannot get the carbon dioxide out of your blood. A buildup of carbon dioxide in your blood can cause damage to your organs. The decrease in oxygen and the buildup of ...
What is a CRF?
CRF is a long-term condition that happens when your lungs cannot get enough oxygen into your blood. CRF can also happen when your lungs cannot get the carbon dioxide out of your blood. A buildup of carbon dioxide in your blood can cause damage to your organs. The decrease in oxygen and the buildup of carbon dioxide can happen at the same time.
How long does it take for a CRF to develop?
The decrease in oxygen and the buildup of carbon dioxide can happen at the same time. CRF may develop over a period of days to years.
What does ABG mean in blood work?
An arterial blood gas (ABG) test measures the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your blood. An ABG test also measures the pH of your blood. Pulse oximetry will show the decrease in blood oxygen without having to draw blood.
Why is ventilator important?
Ventilation helps get oxygen into your lungs and carbon dioxide out. Ventilation also makes the work of breathing easier. Some systems, such as a CPAP or BiPAP, may only be needed while you sleep. A mechanical ventilator may be needed some or all of the time. It is attached to a mask or breathing tube.
Is hypoxemia a respiratory failure?
Hypoxemia is common, and it is due to respiratory pump failure. Also, respiratory failure is classified according to its onset, course, and duration into acute, chronic, and acute on top of chronic respiratory failure. Etiology. Respiratory failure may be due to pulmonary or extra-pulmonary causes which include:
What is respiratory failure?
Respiratory failure happens when the respiratory system fails to maintain gas exchange and is classified into type 1 and type 2 according to blood gases abnormalities. In type 1 (hypoxemic) respiratory failure, the partial pressure of arterial oxygen (PaO2) is less than 60 millimeters of mercury ...
Is respiratory failure a disease?
The overall frequency of respiratory failure is not well known as respiratory failure is a syndrome rather than a single disease process. Pathophysiology. The main path physiologic mechanisms of respiratory failure are: Hypoventilation:in which PaCO2 and PaO2 and alveolar-arterial PO2 gradient are normal.
What are the symptoms of pneumonia?
Fever, cough, sputum production, chest pain in cases of pneumonia. History of sepsis, polytrauma, burn, or blood transfusions before the onset of acute respiratory failure may point to acute respiratory distress syndrome[2].
What Causes Hypoxia
Damage from COPD sometimes keeps the tiny air sacs in your lungs, called alveoli, from getting enough oxygen. That's called alveolar hypoxia.
Symptoms
With either hypoxia or hypoxemia, you'll probably feel short of breath. You might cough and wheeze.
Treatment
The treatment for serious hypoxia or hypoxemia is extra oxygen. You may get it through a tube called a nasal cannula or a face mask.
Complications
Many of the serious problems COPD causes happen because your lungs and bloodstream get too little oxygen. If not treated, alveolar hypoxia and hypoxemia can lead to high blood pressure in your lungs ( pulmonary hypertension) and raise your risk for heart problems.
What is respiratory failure?
Respiratory failure occurs when the breathing system fails to keep adequate blood oxygen levels. There may also be difficulties in removing waste gases, mainly blood carbon dioxide. Respiratory Failure.
What is the most common cause of respiratory failure?
There are various causes of respiratory failure, the most common being due to the lungs or heart.
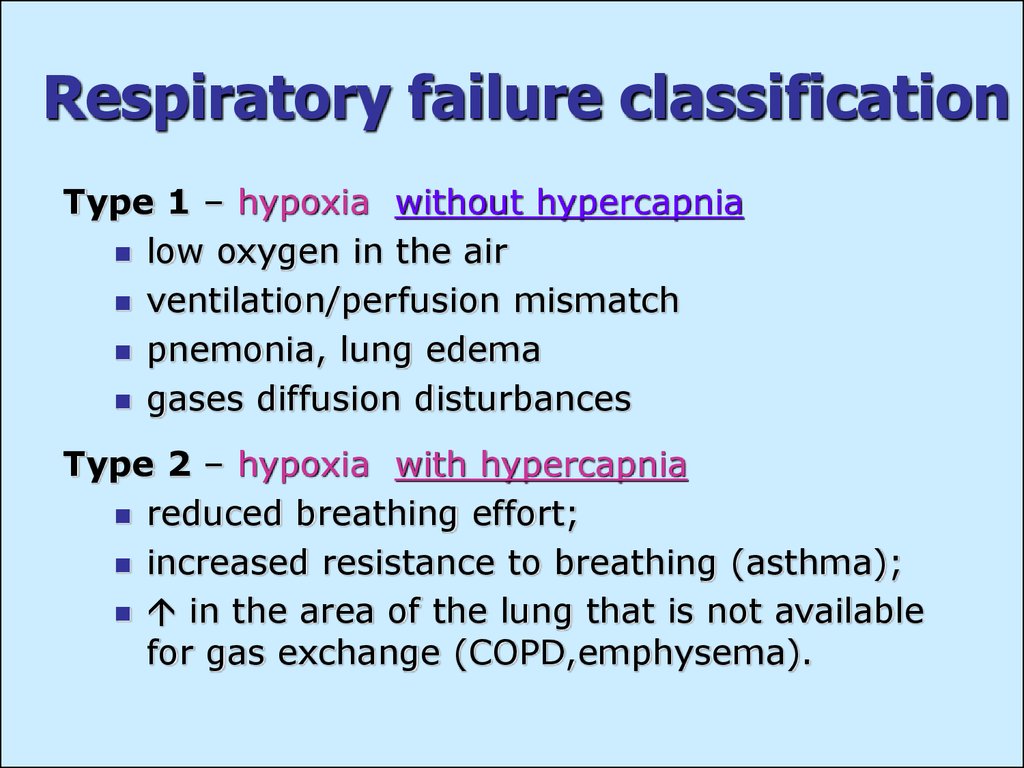
What is the difference between Type I and Type II respiratory failure?
Type I respiratory failure - the blood oxygen is low and the carbon dioxide is normal or low. Type II respiratory failure - the blood oxygen is low and the carbon dioxide is high. Respiratory failure can also be described according to the time it takes to develop: Acute - happens within minutes or hours; usually, ...
What is chronic lung disease?
Chronic - occurs over days and usually there is an underlying lung disease . Acute on chronic - this is usually a sudden or quick worsening of the respiratory function in someone who already has chronic respiratory failure.
What is the best way to measure lung volume?
Spirometry: this is used to measure the lung volumes and capacity and is useful in the evaluation of chronic cases. A heart ultrasound scan (echocardiography): this can look for cardiac causes, such as a leaking heart valve or heart failure.
Can you give oxygen through a mask?
Oxygen - high levels will be given through a mask (although lower levels may be needed in patients with chronic respiratory failure who have adapted to high carbon dioxide levels).
What is NIV in medical terms?
Non-invasive ventilation (NIV): This is an alternative to invasive ventilation and is increasingly being used, especially in cases where weaning from an artificial ventilator may prove difficult. It is used when there is a low blood oxygen level and high blood carbon dioxide level, ie type II respiratory failure.