
- Low Cholesterol Diet: A cholesterol lowering diet should be followed by those who have atherosclerosis. They should avoid food containing saturated fats. ...
- Water: You should drink plenty of water and stay hydrated at all times.
- Dietary Supplements: It has been proved that certain natural supplements can help dissolve plaque. Garlic tablets, vitamin E and vitamin K supplements, fish oil supplements, etc. ...
- Atherosclerosis and cholesterol.
- Artichoke extract.
- Garlic.
- Niacin.
- Policosanol.
- Hawthorn.
- Red yeast rice.
- Things to consider.
What is the best treatment for atherosclerosis?
Treatment Options for Atherosclerosis
- Lifestyle Changes for Atherosclerosis. Certain lifestyle changes can slow or even reverse the progression of atherosclerosis, and are generally the first-line treatment for people diagnosed with the condition.
- Medication for Atherosclerosis. ...
- Surgical Treatments for Atherosclerosis. ...
- Alternative Therapies for Atherosclerosis. ...
What does cholesterol reduce the risk of atherosclerosis?
Levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol are generally inversely associated with the risk for the development of atherosclerosis. The mechanism by which HDL imparts protection from the initiation and progression of occlusive vascular disease is complex and multifactorial. The major anti- …
Does atherosclerosis increase or decrease blood pressure?
The narrower your arteries the harder your heart has to work to pump blood through them. This further increases the pressure of the blood flow which causes your blood pressure to rise even more. The danger here is if an artery narrows to the extent that it becomes blocked which then prevents blood from flowing through.
What can lower risks of atherosclerosis?
Regular exercise improves blood flow, lowers blood pressure, and reduces your risk of conditions that increase the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease. Aim to exercise at least 30 minutes most days of the week. If you can't fit it all into one session, try breaking it up into 10-minute intervals.

What supplements reduce arterial plaque?
Niacin, or Vitamin B3, is the best agent known to raise blood levels of HDL, which helps remove cholesterol deposits from the artery walls.
Which vitamin prevents atherosclerosis?
Observational and experimental studies indicate that dietary vitamin E supplementation is associated with reduced risk of atherosclerosis.
How can I reduce atherosclerosis naturally?
A healthy diet rich in nutrient-dense foods may help reduce your risk of developing clogged arteries. Research has shown that adding foods like cruciferous vegetables, fish, berries, olive oil, oats, onions, greens, and beans to your diet may be an effective way to prevent atherosclerosis.
What herbs are good for atherosclerosis?
Table 2.Compounds/extractsHerbsTargets or indicatorPanax notoginseong saponinsPanax notoginsengICAM-1, VCAM-1CurcuminCurcuma longaMacrophagesProtocatechualdehydeSalvia miltiorrhizaFibronectin, NF-κBAqueous extract of Buddleja officinalisBuddleja officinalisVCAM-1, ICAM-1, NF-κB, ROS, IκB-α7 more rows
What supplements good for heart?
8 heart health supplements to take – and one to avoidMultivitamin & mineral. Vitamins and minerals taken in appropriate doses may aid in lowering heart disease risk. ... Coenzyme Q10 (Co Q10) Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a substance similar to a vitamin. ... Fiber. ... Omega-3 fatty acids. ... Magnesium. ... L-Carnitine. ... Green tea. ... Garlic.
Can vitamin K2 reverse atherosclerosis?
Conclusions: A 270-day course of vitamin K2 administration in patients with CKD stages 3-5 may reduce the progression of atherosclerosis, but does not significantly affect the progression of calcification. Vitamin K2 significantly changes the levels of calcification promoters and inhibitors: dp-ucMGP, OC, and OPG.
Can garlic clear clogged arteries?
Garlic is one of the most powerful superfoods available. Not only is it antimicrobial, antibacterial and antifungal, with antioxidant and anti-cancer properties, but it's also among the top foods that unclog your arteries. Many studies have proven raw garlic's ability to reduce cholesterol and blood pressure.
Can magnesium reverse atherosclerosis?
Moreover, oral magnesium therapy has been shown to improve endothelial function in patients with coronary artery disease. Magnesium, which is an inexpensive, natural and rather safe element, could be useful in preventing atherosclerosis and as an adjuvant therapy in patients with clinical manifestations of the disease.
Does Ginger clear your arteries?
Ginger has medicinal properties that help in preventing blood clots in the blood vessels of the heart. The antioxidants present in ginger help in reducing the formation of plaq in the arteries caused by high cholesterol. Consuming it in small amounts with your food or tea can be very beneficial for you.
Which fruit juice is good for arteries?
pomegranate juiceResearchers found that pomegranate juice not only appears to prevent hardening of the arteries by reducing blood vessel damage, but the antioxidant-rich juice may also reverse the progression of this disease.
Does magnesium dissolve arterial plaque?
Increased magnesium intake has been observed to lower the risk of adverse cardiac events including stroke, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and cardiac death, and it is thought that increased magnesium may slow or prevent arterial calcification and plaque formation.
How to reduce risk of atherosclerosis?
Lose extra pounds and maintain a healthy weight. If you're overweight, losing even just a few pounds can reduce your risk of high blood pressure and high cholesterol, two of the major risk factors for developing atherosclerosis. Ask your doctor what your target weight should be. Eat healthy foods.
How to tell if you have atherosclerosis?
This test can tell if you have atherosclerosis in the arteries in your legs and feet. During an ABI test, your doctor compares the blood pressure in your ankle with the blood pressure in your arm. An abnormal difference may be a sign of peripheral vascular disease, which is usually caused by atherosclerosis.
How to reduce the risk of heart disease?
Regular exercise improves blood flow, lowers blood pressure, and reduces your risk of conditions that increase the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease. Aim to exercise at least 30 minutes most days of the week. If you can't fit it all into one session, try breaking it up into 10-minute intervals.
How to control blood pressure and cholesterol?
Eat healthy foods. A heart-healthy diet full of fruits, vegetables and whole grains — and low in refined carbohydrates, sugars, saturated fat and sodium — can help you control your weight, blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar. Try substituting whole-grain bread in place of white bread.
What is the best test for atherosclerosis?
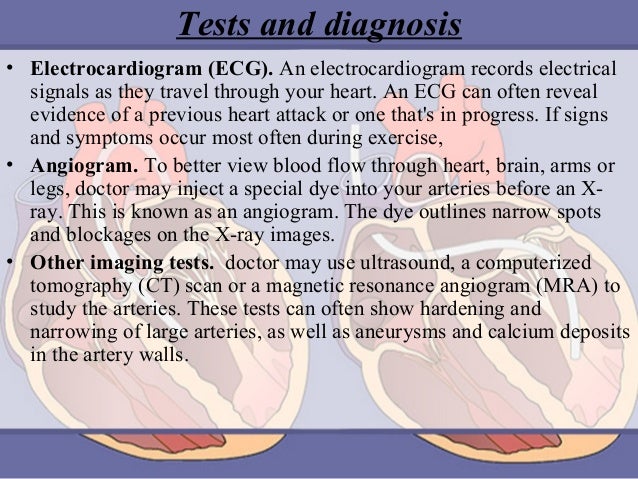
High levels of blood sugar and cholesterol raise your risk of atherosclerosis. A C-reactive protein (CRP) test also may be done to check for a protein linked to inflammation of the arteries. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This simple and painless test records the electrical signals in your heart. Exercise stress test.
Does herbal medicine help with high cholesterol?
It's thought that some foods and herbal supplements can help reduce your high cholesterol level and high blood pressure, two major risk factors for developing atherosclerosis. With your doctor's OK, you might consider these supplements and products:
Can statins slow down fatty deposits?
Statins and other cholesterol medications. Aggressively lowering your low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol — the bad cholesterol — can slow, stop or even rever se the buildup of fatty deposits in your arteries.
How to control atherosclerosis?
You can help control risk factors for atherosclerosis and heart disease — such as your weight, blood pressure, and blood cholesterol and glucose levels — by focusing on eating certain foods while avoiding others.
What are the treatments for atherosclerosis?
Medically Reviewed. Prescription drugs, surgery, and heart-healthy lifestyle changes are treatment options for atherosclerosis. Shutterstock (2) Atherosclerosis occurs when fat-containing deposits called plaque form in your arteries, causing them to harden and narrow. This can reduce blood flow to different areas of your body, ...
What are the medications that help reduce cholesterol?
Cholesterol Medication Drugs known as statins and fibrates can reduce your LDL (low-density lipoprotein, or "bad") cholesterol, which can help stop or even reverse the buildup of plaque in your arteries. In addition to regulating your cholesterol, statins can help stabilize the lining of your heart arteries and prevent atherosclerosis.
What is the best medicine for blood pressure?
Diuretics (Water Pills) Diuretics help lower your blood pressure by reducing fluid retention throughout your body. Other Drugs Your doctor may prescribe medication to control specific risk factors for atherosclerosis — like diabetes — or symptoms of atherosclerosis, like leg pain during exercise.
How does ACE inhibitor help with atherosclerosis?
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors ACE inhibitors may help slow the progression of atherosclerosis by lowering your blood pressure and relaxing your blood vessels. They also reduce your risk of having multiple heart attacks.
What is the best treatment for CAD?
Beta-Blockers Beta-blockers are widely used to treat CAD. They lower your heart rate and relax your blood vessels, which in turn lowers your blood pressure — along with your risk of a heart attack and certain heart rhythm problems.
What is a heart healthy diet?
A heart-healthy diet is widely understood to be high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and low in refined carbohydrates, saturated and trans fats, and sodium.
What supplements help with atherosclerosis?
are known to keep arteries in their top state of health. Plant Sterols and Stanols: Consumption of foods with plant sterols and stanols works great for atherosclerosis.
How long does it take to notice a reversal of atherosclerosis?
If the above instructions are religiously followed, the difference can be noticed within a few days itself. Atherosclerosis reversal is not that difficult, you just have to make a commitment to yourself.
How to reverse artery blockage?
Studies related to preventive medicine have proved that artery blockages can be reversed by changing your lifestyle and that too with no harmful side effects! In fact, these side effects are desirable ones, that result in a better quality of life. Cholesterol builds up the plaques inside the arteries, making the arteries clogged, leading to various cardiovascular diseases. Diet, exercise and stress management are the important keys used in reversing atherosclerosis.
What is the best vitamin for heart disease?
Vitamin B3 or Niacin: Niacin helps you avoid heart diseases. Vitamin E: Foods rich in Vitamin E like sunflower seeds or Swiss chard can reduce inflammation of the walls of the arteries. Low Cholesterol Diet: A cholesterol lowering diet should be followed by those who have atherosclerosis.
What is the term for the narrowing of blood vessels due to excess deposition of fats and cholesterol?
Narrowing of blood vessels due to excess deposition of fats and cholesterol is known as atherosclerosis. The plaque or cholesterol in the arteries results in narrowed lumen of the arteries. Atherosclerosis thus leads to restricted blood flow. Limited supply of blood and oxygen to the brain, heart and other organs can affect their functions badly. Reversing atherosclerosis is possible by undergoing a surgery or it is possible if a balanced diet is followed and exercises are performed regularly.
What happens when cholesterol hardens?
When this cholesterol hardens and settles down in the arteries, you notice the clogged artery symptoms, leading to various cardiovascular diseases or stroke or peripheral artery disease.
What foods lower cholesterol?
A high fiber diet can help you lower the cholesterol levels. Omega 3 Fatty Acids: Foods packed with omega 3 essential fatty acids such as salmon, tuna, flax seeds can prevent blood clotting and oxidation of cholesterol. The lycopene present in tomatoes also prevents the oxidation of cholesterol.
How do nutrients affect atherosclerosis?
At present, in nutrition science, the research on atherosclerosis focuses on which nutrients play an important role in its prevention strategy, and what are the possible mechanisms of its action. In the current study, the process of atherosclerosis can be affected by adjusting the proportion of nutrients in the diet. In this review, we pay attention to the effects of phytosterols, omega-3-polyunsaturated fatty acids, polyphenol, vitamin, and other nutrients on atherosclerosis, pay attention to their current epidemiological status, current nutritional research results, and prevention or a possible mechanism to reduce the risk of development of atherosclerosis. So that more personalized nutritional approaches may be more effective in terms of nutritional intervention responses to atherosclerosis.
What causes atherosclerosis?
The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis has not been elucidated. The injure of endothelial cells caused by various reasons leads to endothelial dysfunction, promotes the modification of lipoproteins and the infiltration of monocytes into inner subcutaneous space. The increased plasma lipoprotein is deposited on the arterial intima, causing connective tissue hyperplasia, thickening and hardening of the arterial wall, and then necrosis of the connective tissue to form atherosclerosis. Endothelial cells are damaged due to various reasons, so that plasma components include lipoprotein deposits on the inner membrane, causing platelets to adhere, aggregate, release various active substances [monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, interleukin (IL)-8, intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), vascular adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), E-selectin, and P-selectin], attract monocytes to aggregate, adhere to the endothelium, and migrate to the subendothelial tissue of the blood vessel, and combine with oxidized lipoproteins to form mononuclear cells. At the same time, the active substance activates the smooth muscle cells of the arterial media to migrate into the intima to form smooth muscle-derived foam cells. Finally, the proliferating smooth muscle cells synthesize extracellular matrix such as collagen and proteoglycan to thicken and harden the intima of the disease, promote plaque formation, and accelerate the development of atherosclerosis.
What is the role of lipoproteins in atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is defined as a chronic inflammatory disease. The infiltration and retention of lipoproteins in the arterial wall is a key initiation event that triggers an inflammatory response and promotes the development of atherosclerosis. Blood lipids are transported in the form of lipoproteins in the blood circulation. Studies have found that the increase in plasma low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels and the decrease in high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels are positively correlated with the incidence of atherosclerosis. After being oxidized and modified by arterial wall cells, LDL can promote the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. At present, oxidized LDL (ox-LDL) is considered to be an important atherosclerotic factor and a major factor that causes damage to endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells. Ox-LDL cannot be recognized by normal LDL receptors, but easily recognized by scavenger receptors of macrophages and quickly taken up, which promotes the formation of foam cells by macrophages. On the contrary, HDL remove cholesterol from the arterial wall through the cholesterol reverse transport mechanism, and prevent the occurrence of atherosclerosis. In addition, HDL also has antioxidant effects, can prevent the oxidation of LDL, and can competitively inhibit the receptors of LDL and endothelial cells.
How does vitamin D affect the body?
Vitamin D affects many cells involved in atherogenesis, such as immune cells, endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, and cardiomyocytes (Brewer et al., 2011). Vitamin D may influence the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis through decreasing the expression of TNFα, IL-6, IL-1, and IL-8 in isolated blood monocytes (Giulietti et al., 2007; Kassi et al., 2013). It may regulate the expression of thromboregulatory proteins and tissue factors in monocytes, thereby affecting platelet aggregation and thrombosis activity (Koyama et al., 1998). Thereby possibly preventing luminal rupture and thrombosis due to plaque instability (Oh et al., 2009). In addition, there is conclusive evidence that VDR and 1α-hydroxylase are expressed in the heart and blood vessels. Vitamin D has been shown to delay the development of porcine coronary artery disease by inhibiting NF-κB activation, supporting that vitamin D is considered an important factor in CVD (Chen et al., 2016).
Does vitamin C help with oxidation?
Previous studies have demonstrated that vitamin C being able to scavenge ROS. It may prevent the oxidation of LDL-c by reducing the α-tocopherol free radical. Inhibiting ROS-mediated direct damage to the vascular endothelium and oxidative stress-induced signaling pathways, which are involved in the occurrence and development of atherosclerosis (Haendeler et al., 1996). Therefore, vitamin C plays an important role in preventing atherosclerosis and delaying the progression of coronary heart disease. Vitamin C can also prevent activation of platelets and apoptosis. A study investigated the relationship between vitamin C in supplements and early atherosclerosis [detection of carotid intima-media thickness (IMT)] and found that vitamin C in food is associated with accelerated early atherosclerosis measured by carotid IMT (Meganathan and Fu, 2016). Many studies have shown that atherosclerosis is negatively related to the intake of antioxidants, in contrast, some clinical trials have found that vitamin C are not beneficial for supplementary treatment of CVD. However, these clinical trials are not without their limitations. Antioxidant therapy for a relatively short period of time or treatment of patients with advanced disease may not provide information related to disease.
Is resveratrol a flavonoid?
Resveratrol is a natural non-flavonoid polyphenol, which is found in wine, peanuts, red wine, etc. The current research has confirmed that it has anti-oxidant (da Silva et al., 2019), anti-platelet (Bertelli et al., 1995; Baur and Sinclair, 2006), and anti-inflammatory effects (Frémont, 2000), which play an important role in the process of atherosclerosis.
Does niacin lower cholesterol?
The mechanism of niacin to lower blood lipids and prevent atherosclerosis may have the following two aspects. Niacin can up-regulate PPARγ by stimulating the ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 in monocytes and macrophages, and ultimately lead to reverse cholesterol transport (Rubic et al., 2004). On the other hand, niacin can inhibit inflammation to prevent atherosclerosis. An animal study showed that niacin inhibits vascular inflammation by down-regulating the NF-κB signaling pathway (Si et al., 2014). Niacin lowers can reduce the level of CRP and lipoprotein-related phospholipase A2 (an independent risk factor for CVD) (Kuvin et al., 2006). Studies have shown that niacin has been shown to inhibit the expression and release of chemokine induced by TNF-α (Digby et al., 2010).
How to reverse atherosclerosis?
In addition to dietary changes, stop smoking, exercise regularly, limit your alcohol intake and maintain a healthy body weight to reverse atherosclerosis. If lifestyle changes alone aren't enough to lower your cholesterol levels, your doctor may recommend medication, such as statin drugs or niacin, to help.
What is the best way to lower cholesterol?
Eat foods high in omega-3 fatty acids. Found in wild salmon and other cold-water fatty fishes, omega-3s are a type of polyunsaturated fat that can reduce blood pressure, lower triglycerides -- another type of cholesterol that can cause atherosclerosis -- and increase "good" HDL cholesterol levels.
What causes arteries to be blocked?
View Work. Your arteries may be up to 70 percent blocked with no symptoms, allowing you to carry on as usual for a time. Excess cholesterol, fat and calcium can collect along the walls of your arteries, forming plaque and restricting blood flow. Called atherosclerosis, this narrowing and hardening of your arteries can lead to cardiovascular disease.
How to prevent heart disease?
Follow a low-fat diet. The first diet proven to reverse atherosclerosis and prevent heart disease was developed by Dr. Dean Ornish. It's a low-fat ovo-lacto vegetarian diet that limits simple carbohydrates and eliminates saturated fats. The Ornish program recommends that 70 percent of your calories come from whole grain, high-fiber carbohydrates, 20 percent of your calories come from protein and only 10 percent of your calories come from fat. By comparison, a typical American diet is up to 50 percent fat, according to AltMD. The American Heart Association recommends that no more than 30 percent of your diet come from fat.
What is the Ornish diet?
It's a low-fat ovo-lacto vegetarian diet that limits simple carbohydrates and eliminates saturated fats. The Ornish program recommends that 70 percent of your calories come from whole grain, high-fiber carbohydrates, 20 percent of your calories come from protein and only 10 percent of your calories come from fat.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Lifestyle changes can help you prevent or slow the progression of atherosclerosis. 1. Stop smoking.Smoking damages your arteries. Quitting smoking is the best thing you can do to keep your arteries healthy and prevent atherosclerosis complications. 2. Exercise most days of the week. Regular exercise improves blood flow, lowers blood pressure, and reduces your risk of co…
Alternative Medicine
- It's thought that some foods and herbal supplements can help reduce your high cholesterol level and high blood pressure, two major risk factors for developing atherosclerosis. With your doctor's OK, you might consider these supplements and products: 1. Alpha-linolenic acid 2. Barley 3. Beta-sitosterol (found in supplements and some margarines, such...
Preparing For Your Appointment
- If you think you may have atherosclerosis or are worried about having atherosclerosis because of a strong family history of heart disease, make an appointment with your doctor to have your cholesterol level checked. Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment and know what to expect from your doctor.