What is the best home remedy for tooth pain?
“Prescribe non-opioid analgesics as the FIRST line of pain control for dental procedures. Prescribe combinations of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ( NSAIDs ) and acetaminophen following dental procedures where post-operative pain is anticipated, unless there are contraindications. If use of an opioid is warranted,
How to relieve denture pain?
Acute Dental Pain. The IHS Division of Oral Health offers approved clinical recommendations [PDF - 767 KB] to reinforce evidence-based acute pain management strategies, including optimizing non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as acetaminophen, as well as topical/local pain strategies to avoid or reduce opioid exposure.
How to stop tooth nerve pain naturally?
Sep 15, 2020 · Key Points Acute dental pain can affect the hard and soft tissues of the mouth, and can be due to underlying conditions or dental... Oral analgesics are used for the management of acute dental pain, and there are various medications and medication... Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) ...
What causes severe dental pain?
Safe and effective management of acute dental pain can be accomplished with nonopioid and opioid analgesics. To formulate regimens properly, it is essential to appreciate basic pharmacological principles and appropriate dosage strategies …

How long should I take opioids?
Follow the CDC guidelines: ‘Clinicians should prescribe the lowest effective dose of immediate-release opioids and should prescribe no greater quantity than needed for the expected duration of pain severe enough to require opioids. Three days or less will often be sufficient; more than seven days will rarely be needed.’.
Should dentists use anti-inflammatory analgesics?
“Dentists should consider nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory analgesics as the first-line therapy for acute pain management … [and]should recognize multimodal pain strategies for management for acute postoperative pain as a means for sparing the need for opioid analgesics.”
Can dental pain lead to opioids?
Dental Pain May Lead to First Encounter with Opioids. Dental pain may affect patients of all ages and notably may lead to the first encounter with opioids for adolescent and young adult populations.
What is the use of opioids in dentistry?
Concerns over what has been described as America’s opioid abuse epidemic have led to professional discussions on opioid prescriptions in dentistry. The American Dental Association’s Statement on the Use of Opioids in the Treatment of Dental Pain, 9 for example, offers recommendations for pain management. Among these, it suggests that clinicians consider a patient’s possible history of substance abuse as part of the medical/dental history, and “recognize multimodal pain strategies for management for acute postoperative pain as a means for sparing the need for opioid analgesics.” It also notes that NSAIDs should be considered as a “first-line therapy” for acute pain management.
Can acetaminophen be used with opioids?
Traditionally, oral health professionals have been taught that nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and acetaminophen should be used for mild-to-moderate pain, and opioids prescribed for severe pain. There is, however, no scientific evidence to support this recommendation. In fact, the evidence indicates that NSAIDs are more effective than opioids for severe pain. 5 An even better option may be the combination of acetaminophen and NSAIDs because the site of action of acetaminophen differs from that of NSAIDs. Therefore, the analgesic effect of acetamino phen is considered synergistic when combined with NSAIDs (Table 2).
What is pain experience?
Pain is a complex experience consisting of a specific sensation and the reactions evoked by that sensation. Conventional analgesics either interrupt ascending nociceptive impulses or depress their interpretation within the central nervous system (CNS).
Does aspirin cause gastric upset?
Although less likely to produce gastric upset, buffered aspirin carries similar risk for mucosal damage as regular aspirin.7. The ability of NSAIDs to inhibit cyclooxygenases in platelets reduces the synthesis of thromboxane A2, which normally contributes to platelet aggregation.
Is analgesic a non-opiod?
Analgesics are classified as opioids and nonopioids, but dated terms like narcoticand non-narcoticare used interchangeably. Formerly, it was believed that opioids acted only within the brain and spinal cord, but the action of nonopioids was confined to the periphery (ie, the site of injury).
Is NSAID contraindicated for GI mucosa?
In summary, NSAIDs are contraindicated for patients who have a current history of nephropathy, erosive or ulcerative conditions of the GI mucosa, anticoagulant therapy, hemorrhagic disorders, or intolerance or allergy to any NSAID.
How to stop toothache?
If your toothache isn’t caused by a serious underlying issue or you are waiting for an upcoming dental appointment, you can reduce pain using the following strategies: 1. Apply a cold compress. In general, there are two ways to stop or blunt toothache pain.
What are the symptoms of tooth pain?
Blood or pus. Throbbing pain. Unpleasant or salty taste in the mouth. Swollen face or jaw. If you’re experiencing any of the above symptoms, call one of our experienced dentists immediately. Whatever the cause of your dental pain, it’s important to visit your local dentist for an evaluation.
How to use garlic for toothache?
To use garlic for toothaches, crush a clove to create a sticky paste and apply it to the affected area. Alternatively, you can chew a clove of fresh garlic and spit it out afterword. 8. Rinse with a guava mouthwash.
What to do if your tooth is infected?
If the area has become infected, the dentist may prescribe antibiotic medication to kill bacteria. Occasionally, dentists will use phototherapy with a cold laser, along with other treatments to reduce inflammation and pain.
How to reduce swelling and blunt pain signals?
You can also reduce swelling and blunt pain signals by taking an anti-inflammatory medication, such as ibuprofen. If you do take ibuprofen, try to continue taking the medication every few hours, according to the product label. Avoid taking the medication once and then stopping when you feel relief, or the pain and inflammation is likely to return. If you don’t have ibuprofen, you can take acetaminophen instead; however, while this will help with the pain, it isn’t an anti-inflammatory medication.
What to expect at a dentist?
What to Expect at the Dentist. To treat your tooth pain, a dentist will first review your medical history and conduct an exam. He or she will ask specific questions about your toothache, including when it started, where it is located, how severe it is, what makes it feel worse and what makes it feel better.
How to get rid of jaw pain?
If you don’t have a hot pack, you can make one by filling a clean sock with rice and tying one end. Then, place the rice-filled sock in the microwave and heat it for a couple of minutes.
What structures need to be examined carefully in order to be sure that the pain is of dental origin?
Associated pathology and referred pain should also be considered. The following structures need to be examined carefully in order to be sure that the pain is of dental origin: tongue. buccal mucosa.
Why does my dentine hurt?
The pain may be due to fluid movement through open tubules in the dentine or there may be some initial inflammatory changes in the dental pulp. It can be caused by caries, dentine exposure on root surfaces, split cusp, lost or fractured restoration or a fractured tooth.
What is the best way to diagnose tooth pain?
Radiographic examination. If it is possible to obtain a screening radiograph, such as an orthopantomograph (OPG), this may assist in the diagnosis and localisation of the cause of the pain. The radiograph should show clearly the apical and periapical structures of teeth and associated tissues.
How deep is the gingival sulcus?
Bleeding and/or sulcus depths greater than 3-4 mm indicate gum disease.
What are the structures that cause pain?
The following structures need to be examined carefully in order to be sure that the pain is of dental origin: 1 tongue 2 buccal mucosa 3 floor of the mouth 4 hard palate 5 teeth and periodontal tissues (see Fig. 1) 6 tonsils 7 temporomandibular joints 8 airway 9 ears 10 salivary glands 11 lymph nodes.
Why do my teeth hurt so bad?
The most common dental cause of dull, throbbing persistent pain is caries. In many cases this is recurrent and associated with an existing restoration. Where the pulp is affected irreversibly, necrosis may follow with possible development of a periapical infection. A fractured cusp involving the pulp, or a large deep restoration may also be associated with this type of pain. Affected teeth may be tender to percussion in the later stages of periapical inflammation.
What causes stabbing pain?
At first the pain may be caused by a stimulus, but it then becomes spontaneous and remains for a considerable time after removal of the stimulus.
What is the most common oral pain?
By far the most common forms of oral pain are the acute form of pains that tend to last for short periods of time. These include toothache (dental pulpitis), gum pain (pericoronitis in 80% of the population), periapical periodontitis (owing to apical infection or postendodontic therapy of high occlusal contact).
What causes tooth pain in children?
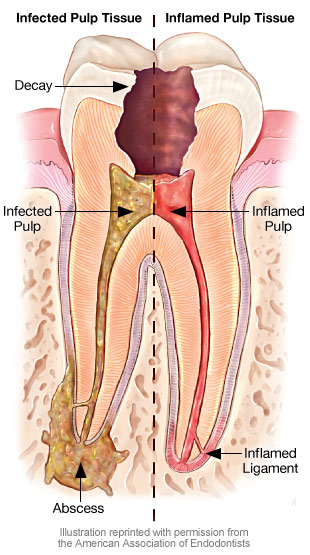
Toothache is caused by inflammation of the dental pulp (Figure 2), most commonly as a result of dental caries (tooth decay), the most common human infective disease worldwide, affecting 60–90% of school children worldwide. Open in a separate window. Figure 2.
What is the pain of a dry socket?
Dentine sensitivity affects 40% of the adult population; dry socket is an intense postsurgical pain that affects 10% of patients after extraction of their teeth. Other orofacial acute pain conditions include trauma or infection of the orofacial tissues. Odontogenic pain.
What is the most common cause of orofacial pain?
There are a wide range of causes of acute orofacial pain conditions, the most common being dental pain (toothache).
What test is used to diagnose tooth pain?
There are several simple tests that may assist in diagnosis of dental pain. Pulp sensitivity test. Dry ice on a cotton bud, or an ordinary ice stick (made in a plastic or glass tube), is placed on the cervical third (neck region) of the tooth crown.
What is the best treatment for sinus infection?
Inflammation of the maxillary sinuses is best treated using local and systemic decongestants and, if persistent, antibiotics may be prescribed10. Pain originating from the sinus arises mainly from pressure. Decongestants can help sinus drainage. Antibiotics probably have only a minor role in mild cases.
Can oral mucosal disease cause acute pain?
This article does not cover oral mucosal diseases (vesiculobullous disorders) that may cause acute pain. Dental pain is the most common in this group and it can present in several different ways. Of particular interest for is that dental pain can mimic both trigeminal neuralgia and other chronic trigeminal pain disorders.
What is the pain associated with dental treatment?
Pain concurrent with a headache. Pain triggered or exacerbated by palpation of trigger points or muscles of the head and neck. Pain associated with clicking or locking of the temporomandibular joints.
What is the management of tooth pain from biting?
3. When assessing the patient, consider the character and location of the pain. Sharp pain with short duration may be localised to a vital tooth with cracks or dislodged dental restorations. 11
What causes pain in the wisdom teeth?
bruxism (grinding of teeth) temporomandibular disorders. oral ulceration. periodontal issues with wisdom teeth ( pericoronitis) – this may present with continuous pain localised near a wisdom tooth which is exacerbated by eating or brushing.
What is an acute apical abscess?
Acute apical abscess – an inflammatory reaction to pulpal infection and necrosis characterised by rapid onset, spontaneous pain, tenderness of the tooth to pressure, pus formation and swelling of associated tissues.
What is the best antibiotic for spreading dental infection?
phenoxymethylpenicillin or amoxicillin. amoxicillin with metronidazole. amoxicillin with clavulanate or clindamycin. 29. If the patient presents with spreading dental infection, systemic sepsis or the risk of airway compromise, they will need immediate referral to the emergency department.
What is bilateral pain?
Bilateral pain or multiple teeth with pain. Pain that does not follow a neurological distribution. Pain described with unusual characteristics such as burning, stinging, electric, shooting, pins and needles. Pain that is chronic and unresponsive to dental treatment.
When to refer to dentist for abscess?
Urgent referral to a dentist is indicated when there is dental pain with swelling. A patient with an acute apical abscess will experience a rapid onset of spontaneous pain, which can sometimes be poorly localised and present with firm or fluctuating swelling in the overlying soft tissues. The tooth is extremely tender when palpated or tapped. 15

Consider Nonopioid Alternatives
Professional Concerns
- Rinse mouth with warm water
- Salt water rinse
- Hydrogen peroxide rinse
- Use dental floss to remove any food particles or plaque wedged between teeth
- If the toothache is caused by trauma to the tooth, apply a cold compress to the outside of cheek
- OTC pain relievers can also sometimes be beneficial
- You have toothache for more than one or two days
- Pain when you bite
- Abnormally red gums
See a doctor immediately if you notice:
- Fever
- Trouble breathing or swallowing
- Swelling
- Foul- tasting discharge, or pus
Key Takeaways
Conclusion
References
- Concerns over what has been described as America’s opioid abuse epidemic have led to professional discussions on opioid prescriptions in dentistry. The American Dental Association’s Statement on the Use of Opioids in the Treatment of Dental Pain,9for example, offers recommendations for pain management. Among these, it suggests that clinicians consider a pat…