Natural Remedies to Treat Esophagitis
- Aloe Vera Juice. First of all, aloe vera gel contains vitamin B, mucilage, and essential amino acids. These help to...
- Licorice Infusion. Liquorice is a natural antacid. Therefore, it can control the main discomfort of oesophagitis. Its...
- Baking Soda. Baking soda is one of the best products to treat esophagitis. It’s an...
- Endoscopic mucosal resection: Using a special instrument to access your esophagus (endoscope), we trap your tumor and remove it. ...
- Endoscopic submucosal dissection: This procedures starts by creating a cushion between healthy tissue and your tumor with a small amount of fluid.
What are the stages of esophageal cancer?
Esophageal cancer stages include: Stage I - Cancer is found only in the top layer of cells that line your esophagus. Stage II - Cancer has invaded deeper layers of the lining of your esophagus and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes. Stage III – Cancer has spread to the deepest layers of the wall of the esophagus and to nearby tissues or ...
What diseases affect the esophagus?
Symptoms of the Most Significant Esophagus Diseases
- Achalasia. Achalasia is a disease that is sometimes hereditary where the esophagus (formed by a type of ring) stops contracting and stops transporting food to the stomach normally.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. We know that the stomach separates acid and pepsin, which are fundamental for the digestion of food.
- Esophageal Varices. ...
How treatable is esophageal cancer?
Esophageal or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) cancer is the seventh most common cancer worldwide, causing an estimated 509,000 deaths in 2018 (1). Multimodal treatment consisting of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (NCRT) and surgical resection has been the ...
What are the main causes of esophageal cancer?
- Obesity
- Increasing age (45-70 years)
- Male gender
- Physical inactivity
- Poor oral hygiene
- History of lung cancer, mouth cancer or throat cancer
- Prior surgery on the stomach (gastrectomy)
- Human papillomavirus ( HPV) infection (rare cause)
- Rare conditions
- Tylosis (a hereditary disorder that causes extra growth on the esophagus)
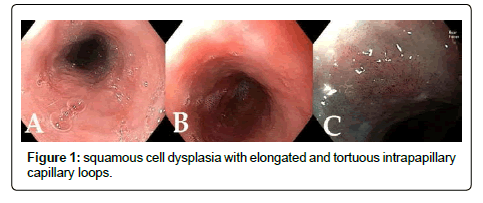
How do you remove nodules from the esophagus?
If a small polyp-like nodule is seen in the esophagus, an endoscopic mucosal resection can be done to try to remove it. This procedure is performed using a small cap with a small wire loop that fits on the end of the endoscope.
What is a nodule in esophagus?
Abstract. Xanthomas are localized nonneoplastic lesions within tissues that may manifest as papules, plaques, or nodules. These lesions can be found anywhere along the gastrointestinal tract, commonly in the stomach and colon, and rarely in the small intestine and esophagus.
Are esophageal nodules usually cancerous?
Esophageal webs and esophageal rings They do not usually develop into cancer.
How often are esophageal nodules benign?
Benign esophageal tumors are rare, with a prevalence ≤ 0.5%[1], while benign tumors represent 20% of esophageal neoplasms on autopsy[2].
What causes nodule on esophagus?
Esophageal duplication happens when the middle layer of the esophagus forms an extra layer, creating a “bump” or growth. Both types of cysts can develop anywhere along the esophagus. As esophageal tumors grow, you may experience these effects: Bleeding.
Is a nodule the same thing as a tumor?
Tumors that are generally larger than three centimeters (1.2 inches) are called masses. If your tumor is three centimeters or less in diameter, it's commonly called a nodule. If the nodule forms in your lungs, it's called a pulmonary nodule. Hamartomas are the most common type of benign lung nodule.
How often are esophageal nodules cancerous?
The lifetime risk of esophageal cancer in the United States is about 1 in 125 in men and about 1 in 417 in women.
Should esophageal polyps be removed?
In conclusion, an esophageal polyp is a kind of benign neoplasm that rarely occurs in the esophagus. An esophageal polyp should be removed immediately by surgery or endoscopy, preferably via endoscopy as the technique causes less damage to the patient.
What are nodules?
A nodule is a growth of abnormal tissue. Nodules can develop just below the skin. They can also develop in deeper skin tissues or internal organs. Dermatologists use nodules as a general term to describe any lump underneath the skin that's at least 1 centimeter in size.
Do you need chemo for a benign tumor?
Chemotherapy is less frequently used to treat non-cancerous brain tumours. It's a powerful medicine that kills tumour cells, and can be given as a tablet, injection or drip. Side effects of these treatments can include tiredness, hair loss, nausea, and reddening of your skin.
Can you feel an esophageal tumor?
Chest pain Someone with esophageal cancer may experience pain in the middle of the chest that feels like pressure or burning. This discomfort can often be confused with other problems, such as heartburn, so it is difficult to recognize it as a symptom.
Treating Stage 0 Esophagus Cancer
A stage 0 tumor is not true cancer. It contains abnormal cells called high-grade dysplasia and is a type of pre-cancer. The abnormal cells look lik...
Treating Stage I Esophagus Cancer
In this stage the cancer has grown into some of the deeper layers of the esophagus wall (past the innermost layer of cells) but has not reached the...
Treating Stages II and III Cancer of The Esophagus
Stage II includes cancers that have grown into the main muscle layer of the esophagus or into the connective tissue on the outside of the esophagus...
Treating Stage IV Cancer of The Esophagus
Stage IV esophageal cancer has spread to distant lymph nodes or to other distant organs.In general, these cancers are very hard to get rid of compl...
What is the treatment for Barrett's esophagus?
They have not grown into deeper layers of the esophagus. This stage is often diagnosed when someone with Barrett’s esophagus has a routine biopsy. Options for treatment typically include endoscopic treatments such as photodynamic therapy (PDT), radiofrequency ablation (RFA), or endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR).
What is the first treatment for gastroesophageal junction cancer?
If chemoradiation isn’t an option, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or a combination of the two might be used. For people with gastroesophageal junction cancers that are HER2 positive, immunotherapy with pembrolizumab, plus chemotherapy, plus the targeted drug, trastuzumab , might be used as the first treatment.
What is the treatment for cancer in the neck?
If the cancer is in the upper part of the esophagus (in the neck), chemoradiation may be recommended as the main treatment instead of surgery.
What is stage 0 esophagus cancer?
Treating stage 0 esophagus cancer. A stage 0 tumor contains abnormal cells called high-grade dysplasia and is a type of pre-cancer. The abnormal cells look like cancer cells, but they are only found in the inner layer of cells lining the esophagus (the epithelium). They have not grown into deeper layers of the esophagus.
What is the long term follow up after endoscopy?
Long-term follow-up with frequent upper endoscopy is very important after endoscopic treatment to continue to look for pre-cancer (or cancer) cells in the esophagus. Another option is to have the abnormal part of the esophagus removed with an esophagectomy. This is a major operation, but one advantage of this approach is ...
Is esophageal cancer stage IV?
Distant recurrence. Esophageal cancer that recurs in distant parts of the body is treated like a stage IV cancer. Your options depend on which, if any, drugs you received before the cancer came back and how long ago you received them, as well as on your health.
Can you give chemo after esophageal cancer?
Radiation may not be an option if it was already given as part of the initial treatment. If chemotherapy was given before, it is usually still possible to give more chemotherapy.
What tests are used to diagnose benign esophageal tumors?
Ulcers (sores) in the esophagus. To diagnose benign esophageal tumors, we may use several tests: Blood tests : Can tell us how well your organs are functioning. Barium swallow: After you drink a smooth chalky liquid of barium, which coats the inside of your organs, we do a series of X-rays.
What are the most common esophageal diseases?
Benign Esophageal Diseases. Achalasia. Acid Reflux Disorders. Paraesophageal Hernias. Benign Esophageal Tumors. Sometimes a tumor develops in your esophagus that is not cancerous (benign). The most common type—representing about 70 percent of benign tumors—is leiomyoma, which forms in the muscle. Doctors do not know what causes benign esophageal ...
What is the best way to see if a tumor has spread?
Endoscopic ultrasound: An imaging test that shows the location, size, and depth of the tumor. We can also tell if the tumor has spread to surrounding lymph nodes or tissues. Other imaging tests. Scans such as a positron emission tomography (PET) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can help us see your condition.
How long do you have to be in the hospital after esophagectomy?
We make an incision in your chest and remove part or all of your esophagus. You will be in the hospital for eight to ten days after the procedure. You may need to use a feeding tube for four to six weeks.
Can a cyst in the esophagus be a cyst?
It is also possible that you may develop a cyst in your esophagus. Simple cysts are sacs filled with fluid. Esophageal duplication happens when the middle layer of the esophagus forms an extra layer, creating a “bump” or growth. Both types of cysts can develop anywhere along the esophagus.
Can esophageal tumors grow in the esophagus?
Both types of cysts can develop anywhere along the esophagus. As esophageal tumors grow, you may experience these effects: Bleeding. Chest pain. Difficulty swallowing. Food getting stuck in the back of your throat. Sudden back-up of undigested food (regurgitation) Ulcers (sores) in the esophagus.
What to do if you have esophageal cancer?
You will want to weigh the benefits of each treatment option against the possible risks and side effects .
What is local treatment?
Local treatments treat the tumor in a specific location, without having major effects on the rest of the body. These treatments are more likely to be useful for earlier stage (less advanced) cancers, although they might also be used in some other situations.
Is treatment information given here official policy of the American Cancer Society?
The treatment information given here is not official policy of the American Cancer Society and is not intended as medical advice to replace the expertise and judgment of your cancer care team. It is intended to help you and your family make informed decisions, together with your doctor.
Does palliative care cure esophageal cancer?
Palliative treatment is meant to relieve symptoms, such as pain and trouble swallowing, but it is not expected to cure the cancer. Treating Esophageal Cancer by Stage. Supportive Therapy for Esophageal Cancer.
What is the procedure to expand the esophagus?
A gastroenterologist may perform a procedure to expand (dilate) the esophagus. This treatment is generally used only when the narrowing is very severe or food has become lodged in the esophagus. In esophageal dilation, your doctor uses one or more endoscopic devices — small narrow tubes inserted through the esophagus.
How to treat drug induced esophagitis?
Your doctor may recommend: Taking an alternative drug that is less likely to cause drug-induced esophagitis. Taking a liquid version of a medication if possible.
What is the term for inflammation of the lining of the esophagus?
Esophagitis is inflammation that damages the lining of the esophagus. An endoscope — a long, flexible tube equipped with a camera — may be used to see inside your esophagus. This endoscopic image of eosinophilic esophagitis shows rings of abnormal tissue (esophageal rings) resulting from chronic inflammation.
How does titanium help with acid reflux?
This strengthens the sphincter and prevents acid from backing up into the esophagus . A newer treatment involves minimally invasive surgery to place a ring of tiny magnetic titanium beads around the junction of the stomach and esophagus. In that position, the ring of beads strengthens the lower esophageal sphincter, preventing acid reflux.
Why is fundoplication used?
Fundoplication may be used to improve the condition of the esophagus if other interventions don't work. A portion of the stomach is wrapped around the valve separating the esophagus and stomach (lower esophageal sphincter). This strengthens the sphincter and prevents acid from backing up into the esophagus.
How to test for esophagitis?
Doctors guide a long, thin tube equipped with a tiny camera (endoscope) down your throat and into the esophagus. Using this instrument, your doctor can look for any unusual appearance of the esophagus and remove small tissue samples for testing. The esophagus may look different depending on the cause of the inflammation, such as drug-induced or reflux esophagitis. You'll be lightly sedated during this test.
What is the best medicine for heartburn?
Herbal remedies sometimes used for heartburn or reflux symptoms include licorice, slippery elm, chamomile, marshmallow and others. Herbal remedies can have serious side effects, and they may interfere with medications. Ask your doctor about a safe dosage before beginning any herbal remedy. Relaxation therapies.
How to treat esophageal sphincter pain?
Instead, it’s recommended that you consume a diet high in fiber, fruits, and vegetables. You should also avoid anything that that makes your symptoms worse. Symptoms are made worse by foods that relax the esophageal sphincter. Try keeping a food diary to track what foods trigger your symptoms.
Where is the esophagus?
An esophageal ulcer is a type of peptic ulcer. It’s a painful sore located in the lining of the lower part of the esophagus, at the junction of the esophagus and stomach. Your esophagus is the tube connecting your throat to your stomach. Esophageal ulcers usually form as a result of an infection with a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori.
Why does GERD cause acid reflux?
This can happen when the lower esophageal sphincter (the muscle that tightens to prevent food in the stomach from moving back up) is weakened or damaged so it doesn’t close properly.
Why do I have a painful esophageal ulcer?
Esophageal ulcers usually form as a result of an infection with a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori. It can also be caused by erosion from stomach acid moving up into the esophagus. In some cases, other infections from yeast and viruses can also in result in esophageal ulcers. An esophageal ulcer can be painful.
How do you know if you have an esophageal ulcer?
Symptoms. The most common symptom of an esophageal ulcer is burning pain in the chest. The pain can be mild or severe. Other symptoms of an esophageal ulcer include: nausea. indigestion. acid reflux ( heartburn) bloating. vomiting.
Can GERD cause ulcers in the esophagus?
A chronic condition known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) may also eventually lead to an esophageal ulcer. People with GERD have frequent acid reflux.
Can Helicobacter pylori cause an esophageal ulcer?
It’s now known that this is not the case, though these factors may aggravate an existing ulcer. Most often, an esophageal ulcer is caused by a bacterium known as Helicobacter pylori, or H. pylori for short. The bacteria damage the mucosal lining of the esophagus.
What to do if you find a nodule?
If you do find a nodule, see your doctor to see what the diagnosis could be. Keep track of any other symptoms you’ve experienced, changes in size to the nodule, or any pain associated with the nodule. Share this information with your doctor. Last medically reviewed on September 30, 2019.
What are the symptoms of a nodule?
a pounding heart. an intolerance to heat. muscle weakness. neck pain. sudden, unexplained weight loss. difficulty sleeping. nervousness. irritability. Even if you don’t think your nodule is harmful, it’s best to contact your doctor for an accurate diagnosis.
What causes thyroid nodules?
Thyroid nodules have a variety of causes. The following are common types of thyroid nodules: 1 Colloid nodules develop from a lack of iodine, which is a mineral essential to the production of thyroid hormones. These growths are noncancerous, but they may be large. 2 Hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules produce thyroid hormone, which may cause hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid). 3 Multinodular goiter occurs when the thyroid gland forms multiple nodules, which grow over time. It can occur due to a lack of iodine in your diet, but most people with goiters have a thyroid gland that functions normally. 4 Thyroid cancer is another cause of thyroid nodules, but most thyroid nodules aren’t cancerous. Research estimates 5 percent of biopsied thyroid nodules are cancerous.
What happens if you don't get enough iodine?
Iodine is a mineral necessary for the production of thyroid hormones. When your body doesn’t get enough iodine, thyroid nodules may develop. This can also lead to decreased functioning of the thyroid gland.
What is a nodule in skin?
A nodule is a growth of abnormal tissue. Nodules can develop just below the skin. They can also develop in deeper skin tissues or internal organs. Dermatologists use nodules as a general term to describe any lump underneath the skin that’s at least 1 centimeter in size. It’s not a specific diagnosis. Rather, it’s used to communicate ...
Why do thyroid nodules grow?
Thyroid nodules. Thyroid nodules have a variety of causes. The following are common types of thyroid nodules: Colloid nodules develop from a lack of iodine, which is a mineral essential to the production of thyroid hormones. These growths are noncancerous, but they may be large.
What is the size of a lung nodule?
Lung nodules typically range from 0.2 to 1.2 inches in size, but they can be larger. They may represent swollen lymph nodes in some instances. There are several reasons why a nodule forms in the lungs, such as infection.
How to get rid of esophageal spasms?
Choose food that is warm or cool. Let foods and drinks that are very hot or very cold sit for a bit before eating or drinking them. Suck a peppermint lozenge. Peppermint oil is a smooth muscle relaxant and might help ease esophageal spasms. Place the peppermint lozenge under your tongue.
What to do if your esophageal spasms are frequent?
If your spasms are occasional, your doctor might first recommend avoiding extremely hot or cold foods to see if that relieves your symptoms. If your spasms make it difficult to eat or drink, your doctor might recommend: Managing any underlying conditions. Esophageal spasms are sometimes associated with conditions such as heartburn ...
What is the test for swallowing?
Your doctor might recommend: Esophageal manometry. This test measures the rhythmic muscle contractions in your esophagus when you swallow, the coordination and force exerted by the esophagus muscles, and how well your lower esophageal sphincter relaxes or opens during a swallow.
What is the purpose of an upper endoscopy?
Your doctor inserts a thin, flexible tube equipped with a light and camera (endoscope) down your throat to examine the inside of your esophagus and stomach. Endoscopy can also be used to collect a sample of tissue (biopsy) to be tested for other esophageal diseases.
What is the procedure to insert a tube down your throat and into your esophagus?
Endoscopy . An endoscopy procedure involves inserting a long, flexible tube (endoscope) down your throat and into your esophagus. A tiny camera on the end of the endoscope lets your doctor examine your esophagus, stomach and the beginning of your small intestine (duodenum). Your doctor might recommend: Esophageal manometry.
What is the best medicine for GERD?
Your doctor might recommend a proton pump inhibitor to treat GERD, or an antidepressant, such as imipramine (Tofranil), which may help reduce the sensation of pain in the esophagus. Medications to relax your swallowing muscles.
Where is the endoscope inserted?
In this new minimally invasive technique, an endoscope inserted through your mouth and down your throat allows a surgeon to make an incision in the inside lining of your esophagus. Then, as in standard myotomy, the surgeon cuts the muscle at the lower end of the esophagus.
What is esophageal stricture?
What is an esophageal stricture? An esophageal stricture is an abnormal tightening or narrowing of the esophagus. Your esophagus is a muscular tube that connects the throat to the stomach, carrying food and liquid. A stricture narrows the esophagus, making it more difficult for food to travel down the tube. In severe cases, even drinking liquid can ...
How does endoscope work for GERD?
Your provider will also numb your throat. If you have GERD, you may receive medication that makes your body produce less acid . Then your provider inserts an endoscope down your throat and into your esophagus.
What is a stricture in the neck called?
This type of stricture is called a peptic stricture. Radiation therapy: Treatment for cancer in the head, neck or chest can cause strictures up to a year and a half later. Surgery: A procedure in the esophagus can leave inflammation and scarring, causing a stricture. Other causes: Ulcers, some medications (for example, ...
What is the most common treatment for strictures?
Esophageal dilation is the most common treatment for strictures. Your provider uses a balloon or dilator (a long plastic or rubber cylinder) to widen the narrow area of the esophagus.
What is the name of the test that examines the esophageal muscles and sphincter
If needed, your provider can take a small piece of tissue to be tested for cancer ( biopsy ). Esophageal manometry: This test examines the esophageal muscles and sphincter. A small catheter tube is inserted into the nose and into the esophagus.
What is an endoscope?
Endoscopy: A healthcare provider inserts an endoscope into your mouth and down your throat. The tool is a thin and flexible tube with a light and camera at the end. The healthcare provider can examine your esophagus. If needed, your provider can take a small piece of tissue to be tested for cancer ( biopsy ).
Can strictures cause perforations?
In rare cases, severe and untreated esophageal strictures can cause perforations (small rips), which can be life-threatening.