
How do you treat V tach with a pulse?
- Attempt vagal maneuvers.
- If unsuccessful, administer adenosine 6 mg IV bolus followed by a rapid normal saline flush.
- If unsuccessful, administer adenosine 12 mg IV bolus followed by a rapid normal saline flush.
How dangerous is ventricular tachycardia?
When it lasts only a few seconds, ventricular tachycardia may cause no problems. But when sustained, ventricular tachycardia can lower the blood pressure, resulting in syncope (fainting) or lightheadedness. Ventricular tachycardia can also lead to ventricular fibrillation (a life-threatening arrhythmia) and cardiac arrest.
What to do for V tach?
This may include:
- Taking medicines for heart failure
- Treating heart artery disease
- Having surgery to fix heart valve problems
- Following a heart-healthy diet and exercise plan, to help reduce your risk for some of these conditions
What is Vtach and risk?
Ventricular tachycardia (v tach) is a sudden, rapid, potentially very dangerous cardiac arrhythmia originating in the heart's ventricles. While it occasionally causes only minimal symptoms, it more typically causes immediate problems.
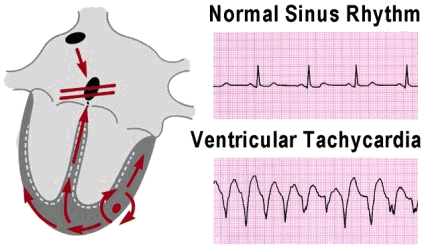
How is Vtach treated?
If you have ventricular tachycardia, you may be given medications called anti-arrhythmics by mouth or IV to slow the fast heart rate. Other heart medications, such as calcium channel blockers and beta blockers, may be prescribed with anti-arrhythmic drugs.
What is the initial treatment for V tach?
VT associated with loss of consciousness or hypotension is a medical emergency necessitating immediate cardioversion. In a normal-sized adult, this is typically accomplished with a 100- to 200-J biphasic cardioversion shock administered according to standard Advanced cardiovascular life support (ACLS) protocols.
What is the best medication for ventricular tachycardia?
Amiodarone is the drug of choice for the treatment of hemodynamically unstable VT that is refractory to other antiarrhythmic agents. Prehospital studies currently suggest that amiodarone is safe and efficacious for use in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
Is Vtach an emergency?
Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is a fast, abnormal heart rate. It starts in your heart's lower chambers, called the ventricles. VT is defined as 3 or more heartbeats in a row, at a rate of more than 100 beats a minute. If VT lasts for more than a few seconds at a time, it can become life-threatening.
How do you treat Vtach with a pulse?
Treatment for ventricular tachycardia may include medication, a shock to the heart (cardioversion), catheter procedures or surgery to slow the fast heart rate and reset the heart rhythm.
Do you give epinephrine in v tach?
Currently, the ACLS protocol for v fib and pulseless v tach recommends that epinephrine be given after the second defibrillation. Many hospitals and EMS systems, however, have been giving it earlier.
Is V tach a shockable rhythm?
Ventricular tachycardia (v-tach) is the other shockable rhythm that can cause cardiac arrest.
Can you give adenosine for Vtach?
Adenosine is safe and effective for differentiating wide-complex supraventricular tachycardia from ventricular tachycardia.
Does metoprolol help V tach?
Metoprolol (200 mg/day) resulted in suppression of 60% of total premature ventricular beats, with couplets (pairs) and ventricular tachycardia decreased 84% and 94%, respectively (all p less than 0.01). Exercise-induced premature ventricular beats, especially ventricular tachycardia, were effectively suppressed.
Does ventricular tachycardia always require immediate cardioversion?
In those who have normal blood pressure and strong pulse, the antiarrhythmic medication procainamide may be used. Otherwise, immediate cardioversion is recommended, preferably with a biphasic DC shock of 200 joules....Ventricular tachycardiaFrequency~7% of people in cardiac arrest12 more rows
Do patients in V-tach have a pulse?
But sometimes, a fast heartbeat can signal an underlying medical issue called ventricular tachycardia, also called “VT” or “V-tach.” V-tach occurs when your pulse rate is more than 100 beats per minute, and you have at least three irregular heartbeats, or arrhythmias, in a row.
What triggers V-tach?
Ventricular tachycardia most often occurs when the heart muscle has been damaged and scar tissue creates abnormal electrical pathways in the ventricles. Causes include: Heart attack. Cardiomyopathy or heart failure.
What is the initial treatment response for a patient in either pulseless ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation?
Ventricular Fibrillation/Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia. The most critical interventions during the first minutes of VF or pulseless VT are immediate bystander CPR (Box 1) with minimal interruption in chest compressions and defibrillation as soon as it can be accomplished (Class I).
Do you Cardiovert or defibrillate v tach?
Ventricular tachycardia (v-tach) typically responds well to defibrillation. This rhythm usually appears on the monitor as a wide, regular, and very rapid rhythm. Ventricular tachycardia is a poorly perfusing rhythm; patients may present with or without a pulse.
What immediate steps must be taken if the patient has pulseless ventricular tachycardia?
Pulseless VT is a medical emergency that requires immediate defibrillation. The energy of 150-200 J on biphasic and 360 J on monophasic defibrillator should be used. Delaying defibrillation of pulseless VT dramatically decreases the survival rate.
How do you treat v tach ACLS?
Apply defibrillator pads (or paddles) and shock the patient with 120-200 Joules on a biphasic defibrillator or 360 Joules using a monophasic. Continue High Quality CPR for 2 minutes (while others are attempting to establish IV or IO access).
What causes ventricular tachycardia?
Your heart rate is regulated by electrical signals sent to your heart muscle. Certain conditions can interfere with normal electrical signals and cause ventricular tachycardia:
What are the signs and symptoms of ventricular tachycardia?
Ventricular tachycardia goes away on its own in 30 seconds. However, sustained ventricular tachycardia can last more than 30 seconds and requires emergency treatment.
How is ventricular tachycardia diagnosed?
Your doctor will ask you about your symptoms and take a complete medical history. They may order tests that include:
What can you do to prevent ventricular tachycardia?
Following your doctor’s treatment recommendations can help you prevent or manage episodes of the disease. In some cases, the causative factor (cardiovascular disorder, tumor, drugs, electrolyte imbalance, etc.) may need to be addressed and treated. It is also advised to adopt a healthy lifestyle that includes:
Top Best Treatment of Ventricular Tachycardia Related Articles
This procedure is used to treat abnormal heart rhythms. Depending on the type of arrhythmia and the presence of other heart disease, a nonsurgical ablation or a surgical ablation, may be performed. During a catheter ablation, catheters are advanced to the heart via blood vessels in the groin, neck, and arm.
What is the heart rate of ventricular tachycardia?
Ventricular tachycardia starts in the heart’s lower chambers. Most patients who have ventricular tachycardia have a heart rate that is 170 beats per minute or more. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission.
What causes tachycardia in the heart?
When something goes wrong and signals are sent too quickly, it can cause tachycardia. Most patients with ventricular tachycardia have another heart problem, such as coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, an enlarged heart (cardiomyopathy) or heart valve disease.
How long do you have to wear a Holter monitor?
Your doctor may also want to track your heart rhythm at home. If so, you will wear a Holter monitor at home for 24 to 48 hours. Normal Heart Rhythm recorded on EKG. Ventricular Tachycardia recorded on EKG. Your doctor may refer you to a specialist to electrophysiology testing.
Does ablation help with ventricular tachycardia?
Ablation of ventricular tachycardia has a long history of safety and success. For some patients, ablation completely cures the abnormal rhythm, and no other treatment is needed. Ablation can also improve treatment with an implantable cardioverter defibrillator.
What is NSVT in a sinus?
NSVT is defined as 3 consecutive PVCs, but <30 seconds. Sustained ventricular tachycardia is recognized as follows: The QRS is wide, the rate is fast (>100 bpm). It interrupts sinus rhythm, with the first beat of VT occurring before the next sinus P wave or after the P wave but with a shorter P–R than when in sinus.
What supplements can help with torsades?
Magnesium supplement is often used and can be helpful in terminating or preventing torsades episodes. The cause of the torsades must be determined-acquired, long Q–T drugs (the list is quite long and includes sotalol, dofetilide, methadone, or a congenital condition), long Q–T 1-3 being most common.
What is PVC in a ventricular beat?
A PVC is recognized as a premature ventricular beat and must not be preceded by a P wave that may have been conducted with aberrancy (distortion of the QRS). PVCs can be uniform or multiform. They can occur singly or in short runs. The origin of the PVC could be identified by the morphology (RBBB or LBBB) in lead V1. The axis (leads 1, AVF) will determine the site such as the apex or outflow tract. If there is a need to quantify the PVC count, a Holter recording is justified.
Can beta blockers suppress PVCs?
With respect to therapies, for example, beta-blockers are not very good for suppressing PVCs, but the patient may feel less of a burden. Ventricular arrhythmias may or may not be associated with heart disease. However, sustained monomorphic VT offers a clue to the presence of coronary heart disease.
Can antiarrhythmics be missed?
Drugs are very difficult to take on a regular basis. Antiarrhythmic agents, if successful, must not be missed. Keep in mind that antiarrhythmic agents can be proarrhythmic in that they can worsen the arrhythmia.
Is ARVC genetic or autosomal?
ARVC is genetic and inherited as an autosomal dominant trait with variable penetrance. Torsades de pointes is associated with long Q–T and maybe acquired (e.g., drugs) or inherited. In acquired long Q–T syndrome, women are at a higher risk of developing torsades. Short Q–T syndrome is genetic.
What are the symptoms of tachycardia?
Unstable patients have signs or symptoms of insufficient oxygen delivery to vital organs as a result of the tachycardia. Such manifestations may include the following: 1 Dyspnea 2 Hypotension 3 Altered level of consciousness
Does polymorphic VT recur?
Polymorphic VT in stable patients typically terminates on its own. However, it tends to recur. After sinus rhythm returns, the ECG should be analyzed to determine whether the QT interval is normal or prolonged. Polymorphic VT in patients with a normal QT interval is treated in the same manner as monomorphic VT.
Can tachycardia cause cardiomyopathy?
Prolonged exposure to this (or any other) tachycardia may cause a tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy, which typically improves with medical or ablative treatment of the VT. [ 19] Pulseless VT. Pulseless VT, in contrast to other unstable VT rhythms, is treated with immediate defibrillation.
Can antiarrhythmics be used for VT?
Combinations of these therapies are often used when structural heart disease is present. Antiarrhythmic drugs have traditionally been the mainstays of treatment for clinically stable patients with VT. However, some patients experience unacceptable side effects or frequent recurrence of VT with drug therapy.
Can VT cause hemodynamic collapse?
Sustained ventricular tachycardia (VT) may lead to hemodynamic collapse. Consequently, these patients require urgent conversion to sinus rhythm. The strategy for conversion depends on whether the patient is hemodynamically stable or unstable.

Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
- Regular exercise for body fitness and weight management
- Avoid excessive consumption of stimulant substances e.g. tea, coffee, soda, drugs
- Avoid or control stress
- Quit smoking
- Avoid alcohol consumption
- Quit recreational drug abuse e.g. cocaine
- The symptoms worsen even after treatment
See a doctor immediately if you notice:
- Difficulty in breathing, dizziness, fainting or chest pain for more than few minutes
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment