- Add garlic to your diet. Garlic is a known blood-thinner, so try adding more to your food. You could also take supplements for a more concentrated dose.
- Take curcumin supplements. Curcumin is a compound in turmeric, and it's effective for thinning blood.
- Spice your food with turmeric. Turmeric naturally contains curcumin, so you can also include this Asian spice in your food to get a curcumin dose and thin your blood.
- Try ginkgo biloba. Ginkgo can stop your blood from coagulating too much and prevent blood clots. A a concentration of 25 mg/ml, ginkgo had a strong blood-thinning effect.
- Improve blood flow with grape seed extract. Grape seed extract is a popular natural remedy that could thin blood and improve blood flow.
What foods can help Thin blood?
List of Foods That Thin Blood
- Fish. The omega-3 fatty acid found in fish and fish oil exerts a mild influence on platelets, preventing them from sticking and reducing the ability of blood to clot.
- Ginger. ...
- Turmeric. ...
- Other Foods Containing Salicylates. ...
- Green Tea and Other Beverages. ...
- Other Foods. ...
- Reference. ...
What are some natural ways to thin blood?
Top 8 Natural Blood Thinners
- Turmeric. Turmeric acts as a natural anticoagulant, and it has anti-platelet effects. ...
- Cayenne Pepper. Cayenne contains salicylate, a natural blood-thinning agent that’s valued for its anti-thrombosis effects.
- Cinnamon. ...
- Ginger. ...
- Garlic. ...
- Vitamin E. ...
- Exercise. ...
- Helichrysum Essential Oil. ...
What are the best foods to thin your blood?
Foods that contain vitamin E include:
- almonds
- safflower oil
- sunflower oil
- sunflower seeds
- wheat germ oil
- whole grains
How do you thin blood naturally?
You can thin your blood naturally by making changes to your diet and taking supplements. Try to incorporate more fatty fish into your diet. Fish contains omega 3 fatty acids that can help thin blood. You should also try to use olive oil in your cooking, since it contains anti-inflammatory and anti-coagulant properties.

What is the treatment for thrombocytopenia?
Treating thrombocytopenia often means treating the condition causing thin blood. For example, if the drug heparin is causing your platelet count to drop too low, your doctor may recommend you switch to a different anti-platelet drug. If alcohol use is a factor, you may be advised to reduce or avoid alcohol consumption entirely.
What causes low platelet levels?
A number of things can lead to low platelet levels. For example, your bone marrow may not make enough platelets. Or, your bone marrow may manufacture plenty of platelets, but they don’t survive in the body.
How do you know if you have thrombocytopenia?
The more obvious signs of thrombocytopenia are changes in external bleeding. Platelets help blood clot by clumping together to stop an injury from bleeding too much. If you’ve ever cut your finger and noticed that it stops bleeding soon and begins to heal, that’s healthy blood clotting.
How to check platelet levels?
Your doctor will measure your platelet levels with a blood test. They may also recommend a bone marrow test to see if and why your bone marrow isn’t making enough platelets.
What diseases affect platelets?
Lupus and rheumatoid arthritis are two common autoimmune diseases that affect platelet levels. Surgery. When blood passes through tubes for a blood transfusion or a heart-lung machine during heart surgery, platelets can be lost along the way. Cancer.
How long does it take to recover from a platelet resuscitation?
If you take a drug to restore your platelet levels, it could be a few months or a year before your levels are healthy again. Take your medications and follow the advice of your doctor. It’s the surest way to recover completely and as quickly as possible. Last medically reviewed on October 13, 2017.
What percentage of women develop thrombocytopenia while pregnant?
Pregnancy. According to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, approximately 5 percent of women develop temporary thrombocytopenia while pregnant.
How to thin blood?
Take curcumin supplements. Curcumin is a compound in turmeric, and it's effective for thinning blood. Try including a daily curcumin supplement in your routine to see if it helps you. [2]
How to thin blood naturally?
You can thin your blood naturally by making changes to your diet and taking supplements. Try to incorporate more fatty fish into your diet. Fish contains omega 3 fatty acids that can help thin blood. You should also try to use olive oil in your cooking, since it contains anti-inflammatory and anti-coagulant properties.
How to stop blood clots from forming?
Get more vitamin E in your diet. Vitamin E prevents your platelets from clumping together and can stop blood clots from forming. Try to get at least 15 mg per day from your daily diet to avoid clotting problems.
What spices can thin blood?
Spice your food with turmeric. Turmeric naturally contains curcumin, so you can also include this Asian spice in your food to get a curcumin dose and thin your blood. As an added bonus, it adds a nice, earthy flavor to your food.
How to prevent blood clots?
This is definitely not safe for everyone, though, so only try it if your doctor tells you it's necessary. Doctors usually recommend blood-thinning medications like warfarin to prevent clots. However, some natural compounds could also thin your blood. If you’d like to try these for yourself, then first ask your doctor to make sure this is safe. After that, take some dietary and lifestyle steps to reduce your risk of forming clots.
What does it mean when your blood is too thin?
If you’re trying to thin your blood, always monitor yourself for easy bruising or excessive bleeding. This could mean your blood is too thin and isn't clotting properly.
Can natural compounds help with blood clots?
While doctors usually recommend medications to prevent blood clots, some natural compounds might help as well. They probably aren’t as effective as medications but could complement other medical treatments. As long as your doctor says it’s safe, then you can try these for yourself to see if any of them work. If not, then talk to your doctor for further treatment options.
What is a natural blood thinner?
Natural blood thinners are substances that reduce the blood’s ability to form clots. Blood clotting is a necessary process, but sometimes the blood can clot too much, leading to complications that can be potentially dangerous. People who have certain medical conditions, such as congenital heart defects, may require blood-thinning medications ...
Why do people need blood thinners?
People who have certain medical conditions, such as congenital heart defects, may require blood-thinning medications to reduce their risk of heart attack or stroke. It is essential to speak with a doctor before trying these remedies, as they may not work as well as medication and may interfere with some prescription drugs.
What is the best pepper to use for blood thinners?
3. Cayenne peppers. Share on Pinterest. Cayenne peppers are also high in salicylates and can act as powerful blood-thinning agents. Cayenne pepper is quite spicy, however, and many people can only tolerate it in small amounts. Capsules containing cayenne pepper are available in health food stores and online.
Does turmeric help with blood clotting?
A study published in 2012 suggests that taking a daily dose of turmeric spice may help people maintain the anticoagulant status of their blood.
Is ginger a blood thinner?
It contains a natural acid called salicylate. Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is a synthetic derivative of salicylate and a potent blood thinner. To get the anticoagulant effects of natural salicylates, people may want to use fresh or dried ginger regularly in baking, cooking, and juices.
Can salicylates be used as blood thinners?
It is unlikely, however, that natural salicylates are as effective as blood-thinning medications.
How to treat a blood thinner?
If you have suffered from any condition or ailment that requires a blood thinner, your doctor will likely prescribe you an anticoagulant, which are medications that target clotting factors. Your doctor may prescribe you a coumarin-based medication, such as coumadin or warfarin. These work to reduce the formation of vitamin K dependent clotting factors in the blood. It is generally taken by mouth once a day, at the same time every day, with or without food.
How to thin blood?
Drink more water. Water is a great natural blood thinner. Dehydration makes your blood thicker, which causes clumps that turn to clots. Drink more water each day to help thin your blood and keep yourself healthier overall.
How to reduce the risk of blood clots?
1. Take baby aspirin carefully. If you have had a heart attack or stroke, or have certain risk factors, your doctor may recommend a daily, 81mg tablet of aspirin. Aspirin thins your blood by preventing blood cells from sticking together, thus decreasing the risk of clots. [7]
What are the side effects of Plavix?
There are some common side effects of Plavix: head pain, muscle and joint pain. You may experience some less frequent side effects of Plavix including danger of bleeding, hemorrhage, nosebleeds, etc.
What to take for blood thinners?
2. Take coumarin-based medications. If you have suffered from any condition or ailment that requires a blood thinner, your doctor will likely prescribe you an anticoagulant, which are medications that target clotting factors. Your doctor may prescribe you a coumarin-based medication, such as coumadin or warfarin.
How to prevent heart disease early?
Diet and exercise will only help prevent heart disease early on. Once you have heart disease or have had an episode where your blood needs to be thinned, diet and exercise will not be enough to prevent a stroke or heart attack. Always follow your doctor's advice on diet and medication.
What happens if you don't treat a blood clot?
Talk to your doctor. Conditions such as blood clots, pulmonary embolisms, heart attacks, atrial fibrillation, and strokes are life threatening and serious. If they are not treated properly, you are at risk for recurrence. These conditions require regular check ups and care from a doctor. Under your doctor's care, you may be prescribed a medication to help with thinning your blood as well as a special diet.
What Are Blood Thinners?
Blood thinners are medications that treat and prevent blood clots. Blood clots are semi-solid clumps of red blood cells, platelets, fibrin (a type of protein), and other proteins.
Why Are Blood Thinners Prescribed?
In a broad sense, blood thinners are used to treat blood clots or prevent blood clots from forming when they are dangerous to the body. The following are some specific conditions that could require blood thinners: 1 2
How Do Blood Thinners Work?
In general, all blood thinners work by either blocking or inactivating part of the system that forms blood clots. These medications work by binding to proteins that are involved in either the coagulation cascade or to proteins on platelet surfaces.
Types of Blood Thinners
Anticoagulant blood thinners target various proteins in the coagulation cascade. These medications are used for treating red clots, like deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, as well as preventing strokes in atrial fibrillation and mechanical heart valves.
Side Effects
Unsurprisingly, the main side effect of blood thinners is bleeding. People who take blood thinners will notice that a cut or nick takes longer to stop bleeding and that they bruise more easily. But serious bleeding, such as bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract or brain, can occur. These bleeds can be life-threatening.
Natural Blood Thinners
Some foods and supplements are believed to have some blood thinning properties. However, they are not regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and the concentration of active compounds in supplements is not consistent.
Summary
Blood thinners are important medications used for treating and preventing blood clots. These include anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications. The benefit of taking blood-thinning medications must always be weighed against their risk of serious bleeding.
What are the inflammatory mediators that cause inflammation which thickens the blood?
At your next medical examination, ask your doctor to test your C-reactive protein (CRP), homocysteine, Lp (a), and fibrinogen. These are the inflammatory mediators that cause inflammation which thickens the blood.
What happens when you have too many clotting factors?
When you have too many clotting factors, your red blood cells get caught up in a “fibrin web” that bogs them down. The artery walls get injured and vulnerable, and your blood becomes sticky, which leads to clumps and clots. These fibrin webs are a major contributor to hyperviscosity, sludging, plaque formation, and eventual blood vessel closure (thrombus).
What is the name of the strands of blood cells that are in spider webs?
Your red blood cells are intermingled inside spider web-like configurations. These strands are called fibrin. Without fibrin, you’d bleed to death from any cut or scrape. Your body’s job is to produce just enough fibrin to help your blood to clot when it needs to, but not so much that you end up with thick blood.
Why do people have high hematocrit?
Some people also have a high hematocrit count, meaning there are too many red blood cells in the body, which can thicken the blood. Or, they have red blood cell deformability, which occurs when red blood cells are misshapen and more prone to clotting. Plus, there are disorders like lupus and certain cancers can cause thick blood.
Is blood thicker than water?
"Blood is thicker than water" is an old saying about the importance of family ties. But in the medical world, you don’t want thick blood. Thick blood, formally known as hyperviscosity syndrome, spells trouble for your health.
Can you take garlic with Coumadin?
As a note of caution: If you have been prescribed to take Coumadin for a blood-thinning effect, do not take garlic, nattokinase or lumbrokinase, as they may accelerate the effect. Up to 2 grams daily of omega-3s is okay. Also, do not sleep grounded when you are on Coumadin.
How to treat blood clots?
Treatment for blood clots depends on where the clot is in the body, and the severity of the condition. Blood-thinning medications are commonly used to prevent blood clots from forming or getting bigger. Thrombolytic medications can break up existing clots.
What is the best treatment for a clot in the leg?
For patients who are at high risk of developing clots in the deep veins of the legs—also known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT)—preventive measures should be considered. In addition to or instead of blood thinners, intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC) devices can be very effective. A cuff is placed around the leg, where it periodically fills with air and squeezes, helping move blood toward the heart.
Where is a thrombectomy tube used?
Surgical thrombectomy, in which the clot is surgically removed from the vein or artery, is often used in arms or legs, but can be used elsewhere in the body.
Can blood clots cause shortness of breath?
Blood clots can be very serious, so symptoms of blood clots should be evaluated by a doctor immediately. If not treated, a clot can break free and cause a pulmonary embolism—where the clot gets stuck in a blood vessel in the lung, causing severe shortness of breath and even sudden death.
What causes blood to be thicker?
Following is small sample of the many conditions that can cause thick blood: lupus, which causes your body to produce extra antiphospholipid antibodies, which can cause clotting. polycythemia vera, which causes your body to make too many red blood cells, resulting in thicker blood.
Why is my blood thick?
If an imbalance in the proteins and cells responsible for blood and blood clotting develops, your blood can become too thick. This is known as hypercoagulability. A number of factors can cause thick blood, such as: excess blood cells in circulation. diseases that affect blood clotting.
Why do people get blood clots?
For example, a person may experience a heart attack because their blood came in contact with plaque in their arteries, which causes a clot to form. Those with poor circulation also are more prone to blood clots because their blood doesn’t move through their bodies as well. This isn’t due to the blood’s thickness. Instead, the arteries and veins of these people are damaged, so blood can’t move as fast as normal.
What blood test shows if you have thick blood?
An example of some of the blood tests used if your doctor thinks you may have thick blood include: Complete blood count: This test screens for the presence of red blood cells and platelets in the blood. High hemoglobin and hematocrit levels could indicate the presence of a condition like polycythemia vera.
What are the symptoms of a blood clot?
lack of energy. shortness of breath. If you experience any of these symptoms, you should see your doctor to test for thick blood: having a blood clot of unknown origin. having repeated blood clots for no known reason.
How long after a blood clot can you test for thick blood?
The Cleveland Clinic recommends that testing for thick blood occur at least four to six weeks after you have a blood clot. Testing sooner could lead to a false-positive result due to the presence of inflammatory components in the blood from the clot.
What is blood made of?
While a person’s blood may look uniform, it’s made of a combination of different cells, proteins, and clotting factors, or substances that aid clotting . As with many things in the body, blood relies on a balance to maintain a normal consistency. If an imbalance in the proteins and cells responsible for blood and blood clotting develops, ...
How to protect thin skin from cuts?
Measures to protect thin skin from cuts and tears include: Wearing long sleeves and long pants to protect the skin from the sun. Wearing double layers to protect the skin from tearing when working outside. Applying rolled gauze bandages under clothing for skin that is very fragile to protect it from tearing.
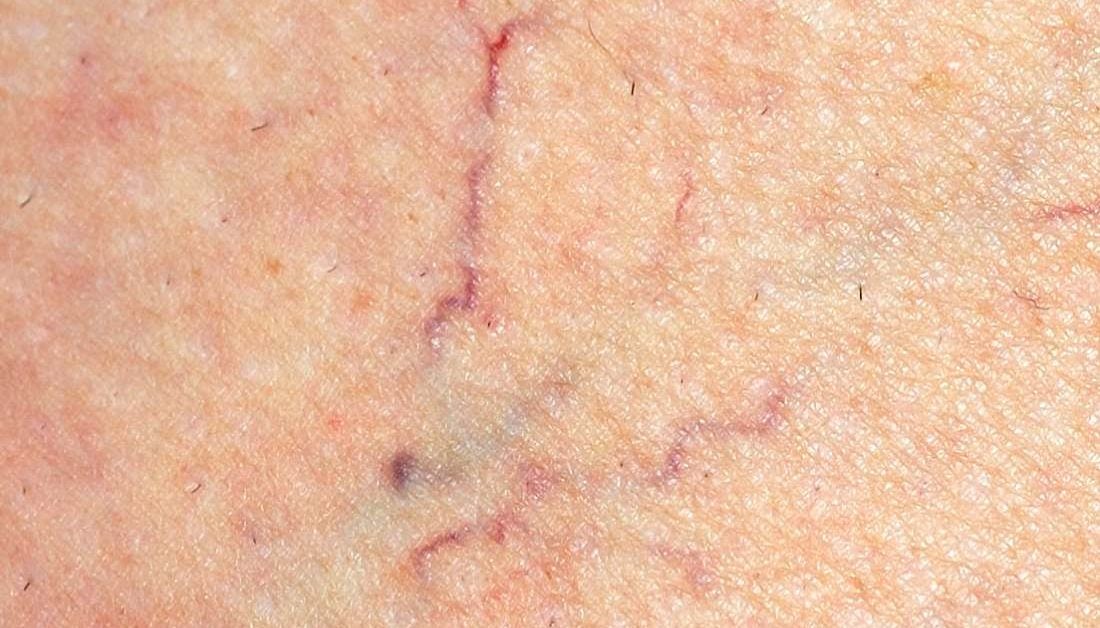
What is thin skin?
Thin skin is a result of thinning of the outermost layer of the skin, called the epidermis. It is most common in older adults and is most visible on the face, arms, and hands. A person with thin skin may find that they are able to see the veins, tendons, bones, and capillaries under the skin of their hands and arms.
Why is my skin thin?
The primary cause of thin skin (due to aging) is changes of the skin that occur as part of the aging process, these include: 2 . The breakdown of collagen and elastin fibers (often caused by ultraviolet sunlight) Damage to the small capillaries near the surface of the skin, causing the skin to bruise easily .
Why does my skin bruise so easily?
Damage to the small capillaries near the surface of the skin, causing the skin to bruise easily. Shrinkage of the cells that make up the layers of the skin. Thinning of the fatty layer of tissue under the skin. Menopause (resulting in the decrease in estrogen levels) Factors that increase the risk of thin skin include:
How do you know if you have thin skin?
Symptoms of Thin Skin. Common symptoms of thin skin include: 1 . Skin that appears thin, dry, or transparent. Skin that tears or bleeds easily. Atrophic (thinning) of the top layers of the skin. Bruising—commonly found on the forearms—after very minor trauma.
What are the risk factors for thin skin?
These risk factors can include environmental factors (such as sun exposure) as well as internal changes in the body, like hormone level fluctuations. Risk factors include:
What causes thin skin?
Menopause (resulting in the decrease in estrogen levels) Factors that increase the risk of thin skin include: Genetics. Long-term exposure to sunlight. Dehydration. Malnutrition. Mobility impairment. Long term use of certain medications, such as topical or oral cortisone creams.