Common tests & procedures
DO NOT SCRATCH! Q: Can I use a Band-aid if it bleeds? A: NO. Band-aids increase allergies. Use a dry cotton ball to dab away any blood. You must return within 48-72 hours to have your arm looked at or you will have to repeat the skin test. HHSA:DC-466 (6/02) Taking care of your arm after the
What not to do after a TB test?
- If concern exists regarding persistence of infection despite treatment
- If symptoms of infection persist
- If lack of adherence to the treatment regimen is suspected
- After treatment of chlamydia during pregnancy
Why do I need to retest after treatment?
Uncommon side effects of Tubersol include:
- injection site reactions (redness, ulceration of the skin, skin rash, pain, discomfort, or itching),
- fever,
- shortness of breath,
- generalized rash, and
- lightheadedness or fainting.
- Rarely, an allergic reaction may occur.
What causes a sick feeling after a TB test?
- Bad cough lasting longer than 3 weeks
- Pain in the chest
- Coughing up blood
- Weakness
- Lack of appetite
- Chills
- Fever
- Night sweats
What happens if I test positive for TB?
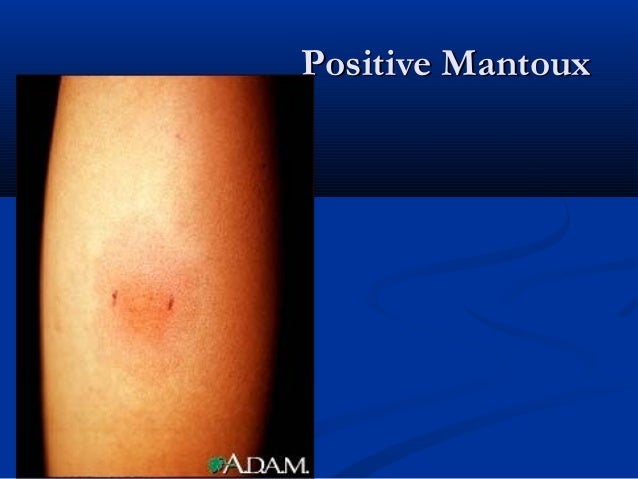
Do you retest for TB after treatment?
If someone was treated for LTBI in the past, they do not need treatment again, even if their tuberculosis test (skin test or IGRA) is “positive” or “reactive”. The exception is if they are re- exposed to someone with tuberculosis and someone from the Department of Health decides that re-treatment is indicated.
How do you know if TB is cured?
After taking TB medicine for several weeks, a doctor will be able to tell TB patients when they are no longer able to spread TB germs to others. Most people with TB disease will need to take TB medicine for at least 6 months to be cured. Who is at risk for developing TB Disease?
What happens after finishing TB treatment?
Once your course of treatment is finished, you may have tests to make sure you are clear of TB. You might need more treatment if tests show there is still TB bacteria in your body, but most people will get the all-clear. Your treatment will not be stopped until you are cured.
Will I always test positive for TB?
Did you know? Once you have a positive TB skin test you will always have a positive TB skin test, even if you complete treatment. Ask your doctor for a written record of your positive skin test result. This will be helpful if you are asked to have another TB skin test in the future.
Is TB 100% curable?
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) that most often affect the lungs. Tuberculosis is curable and preventable.
Does TB stay with you forever?
Many people who have latent TB infection never develop TB disease. In these people, the TB bacteria remain inactive for a lifetime without causing disease. But in other people, especially people who have a weak immune system, the bacteria become active, multiply, and cause TB disease.
Can TB patient live normal life after treatment?
While tuberculosis (TB) is a highly contagious disease, it's also very treatable. The best way to avoid complications from the disease is to take medications regularly and complete the full course as prescribed. In the United States, people with TB can live a normal life, both during and after treatment.
What are the symptoms of TB relapse?
Signs and symptoms of active TB include:Coughing for three or more weeks.Coughing up blood or mucus.Chest pain, or pain with breathing or coughing.Unintentional weight loss.Fatigue.Fever.Night sweats.Chills.More items...•
Do lungs heal after tuberculosis?
Researchers have found that more than one-third of patients who are successfully cured of TB with antibiotics developed permanent lung damage which, in the worst cases, results in large holes in the lungs called cavities and widening of the airways called bronchiectasis.
How long is a TB test good for?
California State law requires that current tuberculosis (TB) clearance test results are on file and must be renewed every four years.
Is latent TB gone after treatment?
Patients with latent tuberculosis do not show symptoms and are not contagious. However, they are still treated to prevent the bacteria from developing into active TB.
Does chest xray show latent TB?
TB chest x-rays can only detect active TB in the lungs. This means that you may have latent TB bacteria in your body, even if you have had a clear chest x-ray.
What test is used to determine if a person has been infected with TB?
There are two kinds of tests that are used to determine if a person has been infected with TB bacteria: the tuberculin skin test and TB blood tests.
What is TB testing?
Testing for Tuberculosis (TB) Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease that is spread through the air from one person to another. When someone who is sick with TB coughs, speaks, laughs, sings, or sneezes, people nearby may breathe TB bacteria into their lungs. TB usually attacks the lungs, but can also attack other parts of the body, such as the brain, ...
What does a positive TST mean?
Positive TST: This means the person’s body was infected with TB bacteria. Additional tests are needed to determine if the person has latent TB infection or TB disease. A health care worker will then provide treatment as needed.
What happens if you don't have TB?
If a person does not have TB disease, but has TB bacteria in the body, then latent TB infection is diagnosed. The decision about taking treatment for latent TB infection will be based on a person’s chances of developing TB disease.
How long does it take for a TST to return?
The person given the TST must return within 2 or 3 days to have a trained health care worker look for a reaction on the arm where the liquid was injected. The health care worker will look for a raised, hard area or swelling, and if present, measure its size using a ruler.
How is blood collected?
Blood is collected into special tubes using a needle. The blood is delivered to a laboratory as directed by the IGRA test instructions. The laboratory runs the test and reports the results to the health care provider.
Where is TB common?
People who have symptoms of TB disease (fever, night sweats, cough, and weight loss) People from a country where TB disease is common (most countries in Latin America, the Caribbean, Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, and Russia)
What does a positive TB test mean?
Positive TB blood test: This means that the person has been infected with TB bacteria. Additional tests are needed to determine if the person has latent TB infection or TB disease.
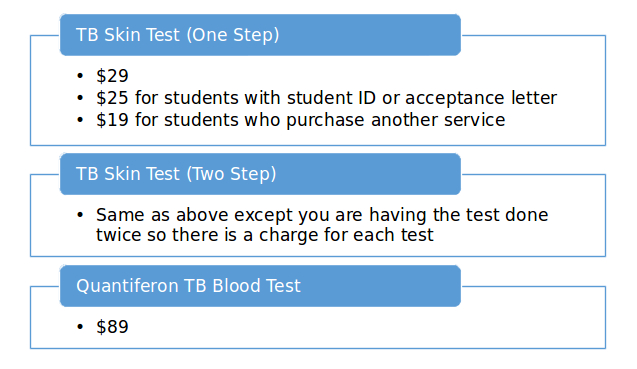
How many visits to get a TB test?
A TB skin test requires two visits with a health care provider. On the first visit the test is placed; on the second visit the health care provider reads the test. The TB skin test is performed by injecting a small amount of fluid (called tuberculin) into the skin on the lower part of the arm.
What does negative TB mean?
Negative TB blood test: This means that the person’s blood did not react to the test and that latent TB infection or TB disease is not likely. TB blood tests are the preferred TB test for: People who have received the TB vaccine bacille Calmette–Guérin (BCG).
What are the two types of TB tests?
There are two types of tests for TB infection: the TB skin test and the TB blood test. A person’s health care provider should choose which TB test to use. Factors in selecting which test to use include the reason for testing, test availability, and cost.
Can TB be delayed?
Testing for TB Infection. The COVID-19 vaccine should not be delayed because of testing for TB infection. TB skin tests and TB blood tests are not expected to affect the safety or the effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccine. Visit Interim Clinical Considerations for Use of COVID-19 Vaccines Currently Authorized in the United States ...
Can you have a TB test and a blood test?
Generally, it is not recommended to test a person with both a TB skin test and a TB blood test. The TB skin test is also called the Mantoux tuberculin skin test (TST). A TB skin test requires two visits with a health care provider. On the first visit the test is placed; on the second visit the health care provider reads the test.
What is the test for TB?
Sputum tests. If your chest X-ray shows signs of tuberculosis, your doctor might take samples of your sputum — the mucus that comes up when you cough. The samples are tested for TB bacteria. Sputum samples can also be used to test for drug-resistant strains of TB.
What test is used to test for tuberculosis?
The most commonly used diagnostic tool for tuberculosis is a skin test, though blood tests are becoming more commonplace. A small amount of a substance called tuberculin is injected just ...
How long does ethambutol last?
If you have drug-resistant TB, a combination of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones and injectable medications, such as amikacin or capreomycin (Capastat), are generally used for 20 to 30 months. Some types of TB are developing resistance to these medications as well.
What to do if you have a positive skin test?
If you've had a positive skin test, your doctor is likely to order a chest X-ray or a CT scan. This might show white spots in your lungs where your immune system has walled off TB bacteria, or it might reveal changes in your lungs caused by active tuberculosis.
How long do you have to take antibiotics for tuberculosis?
For active tuberculosis, you must take antibiotics for at least six to nine months. The exact drugs and length of treatment depend on your age, overall health, possible drug resistance and where the infection is in your body.
Can a TB test be wrong?
Results can be wrong. The TB skin test isn't perfect. Sometimes, it suggests that people have TB when they don't. It can also indicate that people don't have TB when they do. You can have a false-positive result if you've been vaccinated recently with the bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine.
Can TB drugs cause liver damage?
Serious side effects of TB drugs aren't common but can be dangerous when they do occur. All tuberculosis medications can be toxic to your liver. When taking these medications, call your doctor immediately if you have any of the following:
Can you stop TB treatment?
You might need more treatment if tests show there is still TB bacteria in your body, but most people will get the all-clear. Your treatment will not be stopped until you are cured.
Can you catch TB more than once?
It is possible to catch T B more than once, if you are unlucky enough to breathe in TB bacteria at another time. Always take new TB symptoms seriously and get them checked out by a doctor. After finishing treatment you might feel like looking at your life with new eyes. You have achieved a lot!
What is a TB blood test?
TB blood tests (sometimes called IGRAs) use a blood sample to find TB infection. The tests measure the response of TB proteins when they are mixed with a small amount of blood. Only one visit is required to draw blood for the test.
Should TB be tested?
Testing for TB infection should be a routine and integralpart of health care for patients with increased risk for TB. Health care providers are encouraged to use newer TB blood tests to screen for TB infection .
How to get rid of TB?
Throw the used tissue away. If possible, flush used tissues down a toilet. Avoid close contact with others. Babies and elderly people are at increased risk for TB. Tell family, friends, and coworkers that you have TB. They may have latent TB and need to take medicine to prevent it from becoming active.
What is TB in the body?
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW: Tuberculosis (TB) is a severe infection caused by bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. TB usually starts in the lungs. The bacteria are easily spread from one person to another through the air. They can live in your body a long time without making you sick. This is called latent TB.
How to take medicine if you are allergic to it?
Take your medicine as directed. Call your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell him if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them.
What to do if you forget to take a pill?
Write down that you missed a dose and tell your healthcare provider at your next visit. Wash your hands often. Use soap and water . Wash your hands after you use the bathroom, change a child's diapers, or sneeze.
How to tell if you have a symtom?
Contact your healthcare provider if: 1 You have a fever. 2 You have a rash, nausea, or vomiting. 3 The whites of your eyes or your skin look yellow. 4 Your urine looks like dark tea or coffee. 5 Your symptoms do not go away or get worse, even after you take medicine. 6 You have a cough that does not go away after 3 or 4 weeks. 7 You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
How to make sure you take your medicine?
Healthcare providers help make sure you take your medicines correctly. Take your medicine at the same time every day. Each night, put out the pills for the next day. Mark a calendar each day you take your pills. Create reminders. Ask a family member or friend to remind you to take your pills.
How long do you need to take antibiotics for a syphilis infection?
Antibiotic medicine will help fight the infection. You will need to take 3 to 4 types of antibiotics for up to 8 weeks. Then you will need to take at least 2 types of antibiotics for another 18 to 31 weeks. Take your medicine as directed.
What should a clinic decide on TB treatment?
Clinicians should choose the appropriate treatment regimen based on drug susceptibility results of the presumed source case (if known), coexisting medical conditions (e.g., HIV ), and potential for drug-drug interactions. Consultation with a TB expert is advised if the known source of TB infection has drug-resistant TB.
What is a latent TB test?
A diagnosis of latent TB infection is made if a person has a positive tuberculin skin test (TST) or TB blood test (interferon-gamma release assays, or IGRA) result and a medical evaluation does not indicate TB disease.
How long does rifamycin last?
Four months of daily rifampin (4R) Three months of daily isoniazid plus rifampin (3HR) Shorter, rifamycin-based treatment regimens generally have a lower risk of hepatotoxicity than longer 6 to 9 months of isoniazid monotherapy (6H/9H, respectively).
What is the best treatment for latent TB?
Rifampin (RIF) In 2020, CDC and the National Tuberculosis Controllers Association (NTCA) published new guidelines for the treatment of latent TB infection. CDC and NTCA preferentially recommend short-course, rifamycin-based, 3- or 4-month latent TB infection treatment regimens over 6- or 9-month isoniazid monotherapy.
Why is latent TB important?
Why is treatment of latent TB infection important? Treatment of latent TB infection is essential to controlling TB in the United States because it substantially reduces the risk that latent TB infection will progress to TB disease.
How long does it take for TB to develop?
Some people develop TB disease soon after becoming infected (within weeks) before their immune system can fight the TB bacteria. Other people may get sick with TB disease when their immune system becomes weak for another reason. Latent TB infection can be treated to prevent the development of TB disease.
What age can you get latent TB?
Treating latent TB infection is especially important for people with a higher risk of developing TB disease once infected, including children under age five and people with medical conditions, like HIV, diabetes, or other conditions that weaken the immune system.
