What is the treatment for Wallenberg syndrome?
How is Wallenberg syndrome treated? No cure is available for this condition, but your doctor will probably focus treatment on relieving or eliminating your symptoms. They may prescribe speech and swallowing therapy to help you learn to swallow again. They may also recommend a feeding tube if your condition is severe.
What is the outlook for someone with Wallenberg’s syndrome?
Some doctors report that the anti-epileptic drug gabapentin appears to be an effective medication for individuals with chronic pain. The outlook for someone with Wallenberg’s syndrome depends upon the size and location of the area of the brain stem damaged by the stroke.
Do you need a CT scan for Wallenberg syndrome?
You may need to undergo a CT scan or MRI if your doctor suspects that you have Wallenberg syndrome. They can order these imaging studies to confirm whether or not there is a block in the artery near the lateral medulla.
What is the pathologic reappraisal of Wallenberg syndrome?
Pathologic reappraisal of wallenberg syndrome: a pathologic distribution study and analysis of literature. [Yonago Acta Med. 2014] Pathologic reappraisal of wallenberg syndrome: a pathologic distribution study and analysis of literature.

How is Wallenberg syndrome treated?
Treatment for Wallenberg's syndrome is symptomatic. A feeding tube may be necessary if swallowing is very difficult. Speech/swallowing therapy may be beneficial. In some cases, medication may be used to reduce or eliminate pain.
Can Wallenberg syndrome be cured?
The long-term outlook for people with Wallenberg syndrome is fairly positive. A successful recovery depends on where the stroke happened in the brainstem. It also depends on how much damage occurred. Some people can recover between a few weeks to six months after treatment.
Is Wallenberg syndrome a disability?
Complications of Wallenberg Syndrome Stroke syndromes can cause permanent disability and affect normal daily functioning, per StatPearls.
How is lateral medullary syndrome treated?
Lateral medullary syndrome patients require physical and occupational therapy until they gradually develop their physical strength. Patients should be aware of secondary stroke prevention strategies. Those with dysphagia should go through dysphagia rehabilitation. Severe dysphagia cases may require a gastrostomy tube.
What does Wallenberg syndrome affect?
Wallenberg syndrome is a condition that affects the nervous system. Signs and symptoms may include swallowing difficulties, dizziness, hoarseness, nausea and vomiting, nystagmus, and problems with balance.
Can you recover from medullary stroke?
As a result, dysphagia following a lateral medullary stroke (LMS) is often more severe and spontaneous recovery may not completely restore the swallowing function. It may persist for life time or may take months or years to resolve [2].
Can I claim benefits for FND?
It has been accepted FND causes real symptoms which can be debilitating. As long as a claimant is able to prove FND was caused by negligence it is possible to recover compensation for the full extent of their symptoms and financial losses.
What cranial nerves are affected in Wallenberg syndrome?
Cranial Nerves IX (Glossopharyngeal) and X (Vagus) The lateral medullary syndrome, also known as Wallenberg's syndrome, is the prototype lesion involving the nuclei of cranial nerves IX and X.
Where is the lesion in Wallenberg syndrome?
This neurological disorder is associated with a variety of symptoms that occur as a result of damage to the lateral segment of the medulla posterior to the inferior olivary nucleus.
How is lateral medullary syndrome diagnosed?
Since lateral medullary syndrome is often caused by a stroke, diagnosis is time dependent. Diagnosis is usually done by assessing vestibular-related symptoms in order to determine where in the medulla that the infarction has occurred.
Why does diplopia occur in lateral medullary syndrome?
Diplopia in Wallenberg's syndrome is considered to be caused by a lesion involving the otolith-ocular system. Vertical diplopia is simply explained by ocular skew deviation due to a lesion involving the vestibular nucleus; in which the affected eye becomes deviated inferiorly.
What is Wallenberg syndrome?
Wallenberg syndrome, also known as “lateral medullary syndrome” or “posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) syndrome”, is the most prevalent po...
What causes Wallenberg syndrome?
The most common cause of Wallenberg syndrome is an ischemic stroke of the brain stem, oftentimes a result from thrombus or embolism. Other less com...
What are common risk factors for Wallenberg syndrome?
The most common risk factors for Wallenberg syndrome include hypertension (high blood pressure), smoking, and diabetes. Other, less common, risk fa...
How is Wallenberg syndrome diagnosed?
Like most ischemic stroke syndromes, initial diagnosis is usually suspected from the patient’s clinical characteristics upon physical examination....
How is Wallenberg syndrome treated?
The management of Wallenberg syndrome is similar to the management of any acute stroke. Rapid evaluation is an essential component in improving the...
What is the prognosis of someone who has Wallenberg syndrome?
Like other ischemic strokes, the prognosis of a person with Wallenberg syndrome depends on the size and location of the area of the brain stem dama...
What is Wallenberg syndrome?
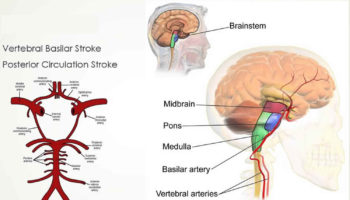
Wallenberg syndrome is also known as lateral medullary syndrome and posterior inferior cerebellar artery syndrome. This neurological disorder is associated with a variety of symptoms that occur as a result of damage to the lateral segment of the medulla posterior to the inferior olivary nucleus. It is the most common posterior circulation ischemic ...
What is the best test for infarct in the inferior cerebellar area?
The diagnosis is usually made or suspected from a clinical exam and history of presentation. MRI with diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is the best diagnostic test to confirm the infarct in the inferior cerebellar area or lateral medulla.[14] .
Is Wallenberg syndrome common?
A careful neurological examination is a key to the diagnosis. A complete Wallenberg syndrome is not common, yet partial syndromes are satisfactory for the diagnosis most of the time.
What is the long term outlook for people with Wallenberg syndrome?
What is the long-term outlook for people with Wallenberg syndrome? The long-term outlook for people with Wallenberg syndrome is fairly positive. A successful recovery depends on where the stroke happened in the brainstem. It also depends on how much damage occurred.
What are the symptoms of Wallenberg syndrome?
The most common symptom people with Wallenberg syndrome have is dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing. This can become very serious if it affects how much nutrition you’re getting. Other symptoms include: Sometimes, people with Wallenberg syndrome experience paralysis or numbness on one side of the body.
What is the best treatment for a blockage in the artery?
Pain medication can help treat chronic or long-lasting pain. Alternatively, they may prescribe a blood thinner, such as heparin or warfarin, to help reduce or dissolve the blockage in the artery. This can also help to prevent future blood clots from forming.
Can you remove a blood clot from the brain?
Surgery may be an option to remove the clot in extreme cases. This is not as common of a treatment due to the difficulty of getting to that area of the brain. Make sure to discuss your treatment options with your doctor and follow the plan carefully.
Can Wallenberg syndrome cause numbness?
Sometimes, people with Wallenberg syndrome experience paralysis or numbness on one side of the body. This can occur in the limbs, in the face, or even in a small area like the tongue. You can also experience a difference in how hot or cold something is on one side of the body.
How to prevent Wallenberg syndrome?
The following healthy lifestyle tips can help prevent a stroke, according to the Mayo Clinic: Control high blood pressure with healthy lifestyle changes and medications. Reduce the amount of cholesterol and saturated/trans fat in your diet, which may reduce buildup in your arteries.
What are the symptoms of Wallenberg syndrome?
According to GARD, the most common symptoms include: Trouble swallowing (dysphagia) Feeling hoarse. Dizziness.
What is the purpose of an ECG and CT?
An ECG to rule out any underlying atrial fibrillation ( irregular heartbeat) or acute coronary syndrome (blocked blood supply to the heart) Blood tests.
How to reduce buildup in arteries?
Reduce the amount of cholesterol and saturated/trans fat in your diet, which may reduce buildup in your arteries. If you use tobacco, quit. Smoking increases the risk of stroke for smokers as well as nonsmokers exposed to secondhand smoke. Manage diabetes with diet, exercise, and weight loss or medication if necessary.
What causes a swollen artery in the brain?
Less often, it can be caused by a stroke that occurs in the medullary arteries, notes StatPearls. Other causes include: Cerebral embolism (blood clot that travels to the brain) Vertebral artery dissection (which may be due to neck manipulation or injury) Marfan syndrome. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Is Wallenberg syndrome better than other strokes?
In general, however, people with Wallenberg syndrome have better outcomes than people who’ve had other stroke syndromes, per StatPearls. Most recover well; the most common lingering problems tend to be with balance and walking.
