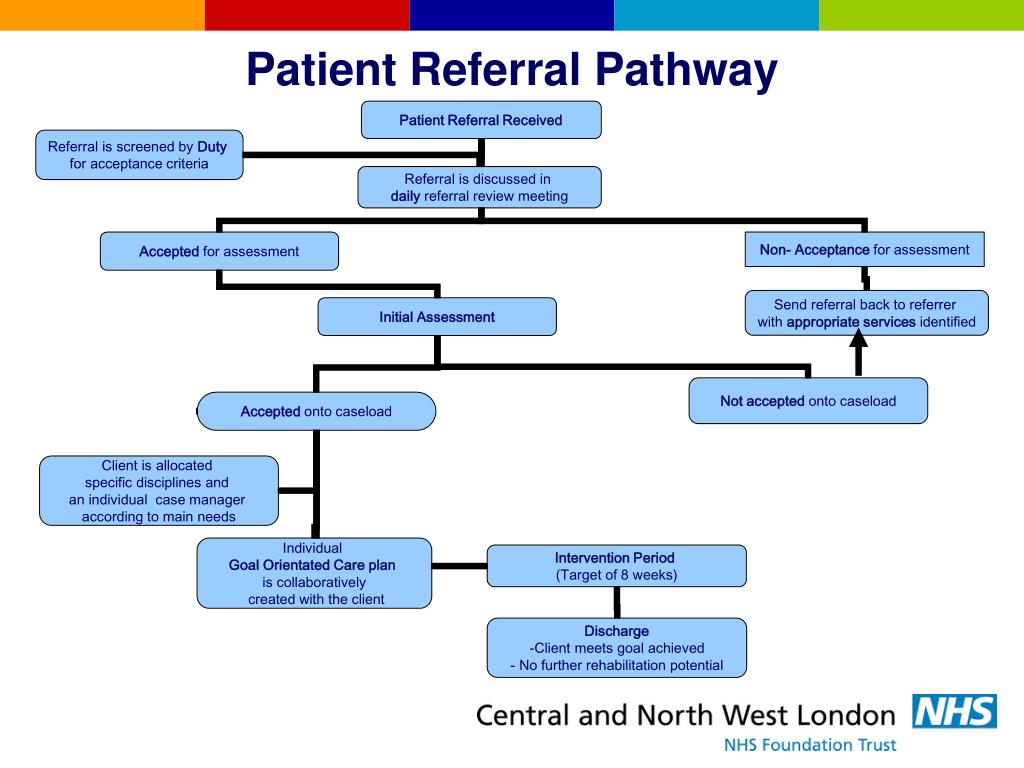
Some strategies to promote client participation in mental health interventions are:
- Making the treatment plan in collaboration with the client. Therapist and client can sit together to discuss what they...
- Engaging in active feedback sessions where both the therapist and the client can openly discuss what they like about the...
Full Answer
What is patient and client engagement in mental health?
Nov 25, 2021 · How to Engage Clients in Therapy: 6 Steps Make sure the focus is on the client. Introduce, maintain, and keep confidentiality. Incorporate client preferences into the treatment decision-making process. Structure the session. Use an eclectic approach. Practice questions. Blended care. Eliminate distractions.
How do you get clients to participate in mental health interventions?
Feb 01, 2016 · Within various treatment programs that treat comorbid substance and mental health conditions, factors identified to enhance engagement include shared goals, optimistic outlook that does not focus on medications, ongoing psychoeducation, collaborative team‐based care, and community outreach.
How do I get my client to engage with therapy?
As an organization of individuals with mental health conditions and their families, NAMI knows that the U.S. system of mental health care is failing to engage people who seek help. The facts say it all: many people who seek mental health care drop out. 70% that drop out do so after their first or second visit.1
How can interventions enhance engagement in mental health treatment?
Feb 10, 2022 · Some strategies to promote client participation in mental health interventions are: Making the treatment plan in collaboration with the client. Therapist and client can sit together to discuss what they... Engaging in active feedback sessions …
How to focus on client?
1. Make sure the focus is on the client. While this might sound obvious, it is perhaps the most important step, but one that can be easily overlooked. The spotlight needs to be kept on the client, with the beginning, middle, and end of each session focusing on the client’s thoughts, feelings, and actions.
Why is it important for therapists to keep focus on clients?
When therapists keep the focus on clients, this can help to build trust, an important aspect of the therapist–client relationship. Without it, clients may not feel comfortable opening up for therapists to listen.
Why is teletherapy important?
While teletherapy is convenient since clients can meet therapists while at home, removing distracting obstacles is crucial. Ask a client to move to a different part of their home, such as from the kitchen to a private room, and ask for devices to be turned off. This will ensure the client’s engagement can be achieved.
Why are clients resistant to change?
Clients may be resistant to change in part because therapists may not have the technique to manage what is going on in the moment or do not fully understand the client’s world to recognize why they are responding the way they are (Nienhuis et al., 2018). The keywords that stand out here are in the moment.
What is an eclectic form of therapy?
An eclectic or integrated form of therapy, which provides unique elements to therapy and can make clients feel more excited about the therapeutic process, can also make the therapist feel more engaged as well. 6. Practice questions.
Why is asking questions important?
Asking questions and maintaining an open-ended curiosity are very important when dealing with resistant clients. If resistant clients are asked closed-ended questions, they may feel more encouraged to give short, one-word answers where details are not explored. When details are not explored, change may not occur.
Do therapists respect what they say?
Respect may sound obvious, but resistant clients may feel therapists do not respect what they said in a session. If clients give closed answers, it is important for therapists to respect what the client is saying, even if it feels like clients are resisting change further.
What does it mean to meet patients and clients?
Meeting patients and clients where they are at means speaking their language, listening to their own explanatory model of the illness and, at least, attempting to address their most immediate concerns. Use their language, listen but do not judge, do not confront too early, educate when needed, but always ask permission first.
What are the barriers to engagement?
Research shows that barriers to engagement can be placed into three categories- structural, attitudinal, and cultural . Structural barriers to engagement include all those social determinants of health, which require attention for successful treatment outcomes. Attitudinal barriers encompass all attitudes your patients have about treatment, which at times, can be based on previous experiences. Having an idea of what these experiences have been for a particular patient can therefore be an important tool for the engagement process. Cultural barriers are not the least of these categories. Besides the broad cultural differences based on religion, language, race, or ethnicity, sub-cultures are equally as important and include family, neighborhood, peers, addiction, gang affiliation, and jail or prison subcultures.
What is engagement in a relationship?
Engagement is a process, and we can use engagement to establish concrete goals and achieve the best results. Some concrete goals may be to return to school, to obtain a job, to make new friends, or to start dating. Further, people can feel discouraged unless they have concrete ways to measure their progress.
Does engagement happen overnight?
As stated above, engagement is a process, it does not happen overnight, and it requires patience, flexibility, and a different mindset. As a result, to be successful you will need to see the importance of all that’s involved in the engagement process and decide to make them a priority.
What is engagement in mental health?
Engagement as participation or involvement is all about creating equality and making clients feel as powerful as the therapist (Dingle et al., 2008). Some strategies to promote client participation in mental health interventions are:
What is client engagement model?
The Client Engagement Model helps us in understanding the dynamics of therapeutic alliance and how it affects the upshot of therapy. Although it is mainly used in the corporate sectors, the principles of this model hold for therapeutic settings as well.
What is the outcome of psychotherapy?
The outcome of psychotherapy is mostly dependent on the quality of the relationship between the therapist and the client. Any form of therapy requires self-disclosure from the client’s end and an immense commitment to bringing about the desired change. Client engagement or treatment engagement in psychotherapy is one of ...
What is the importance of a treatment engagement plan?
A healthy treatment engagement plan in such cases can lead to better prognosis of the psychopathology and help the client address his issues with more reality orientation. While several factors influence the effectiveness of the engagement plan, one of the most critical factors is treatment entry.
Why is it important to discuss intervention strategies at the beginning and end?
Discussing the intervention strategy and techniques at the beginning and the end is a good step for ensuring client engagement. It helps the client to understand the road map and have something to look forward to.
Why is music important in therapy?
It bridges the gap between verbal and nonverbal communication (Slyter, 2012). Using music in therapy is, by far, one of the most reliable and effective strategies for sustaining client engagement in treatment (Veach & Gladding, 2006).
What are the positive aspects of therapeutic engagement?
There are multiple identifiers of positive therapeutic engagement, some of which are: Regular attendance to the sessions. Self-disclosure and emotional catharsis. Willingness to have awkward conversations. Diligent participation in the exercises and activities during therapy.