Medication
Feb 24, 2021 · Dr. Russo had some advice on the matter. it’s all about taking good care of yourself to help ensure that the ECS doesn’t get out of balance. Here are some tips gleaned from his wisdom: 1. Clear your Gut; There is increasing evidence that the gut microbiome is a major regulator of the ECS. these include the levels of bacteria within it. People should avoid …
Procedures
Aug 31, 2021 · The distribution of the components of the ECS system throughout the body, and the physiological/pathophysiological role of the ECS-signalling pathways in many diseases (and the dysregulation thereof), all offer promising opportunities for the development of novel cannabinergic, cannabimimetic, and cannabinoid-based drugs that genetically or …
Therapy
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling system identified in the early 1990s by researchers exploring THC, a well-known cannabinoid. Cannabinoids are …
Self-care
Nov 11, 2015 · Treating Infection with Electrical Stimulation. Posted on November 11, 2015 by ECS. The electric current was able to kill almost all drug resistant bacterium within 24 hours. Image: Nature. A new alternative to traditional antibiotics is on the horizon. Through the application of electrical stimulation, researchers from Washington State ...
Nutrition
Jan 10, 2020 · ECS credit: When a bank makes credit to a bank account, like to pay salary, dividends, etc. it is called ECS credit. A single account is debited on regular intervals to credit multiple accounts. ECS debit: When aa single account is used to make payments like EMI, loans, premium, mutual funds, etc. Based on the geographical location of branches ...
How does ECS works?
At ECS CERRC our counselors work with you, addressing your unique situation and supporting you every step of the way. We use the evidenced-based Matrix Model for Young Adults which includes cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, relapse prevention and 12-step work.
How to apply for ECS scheme?
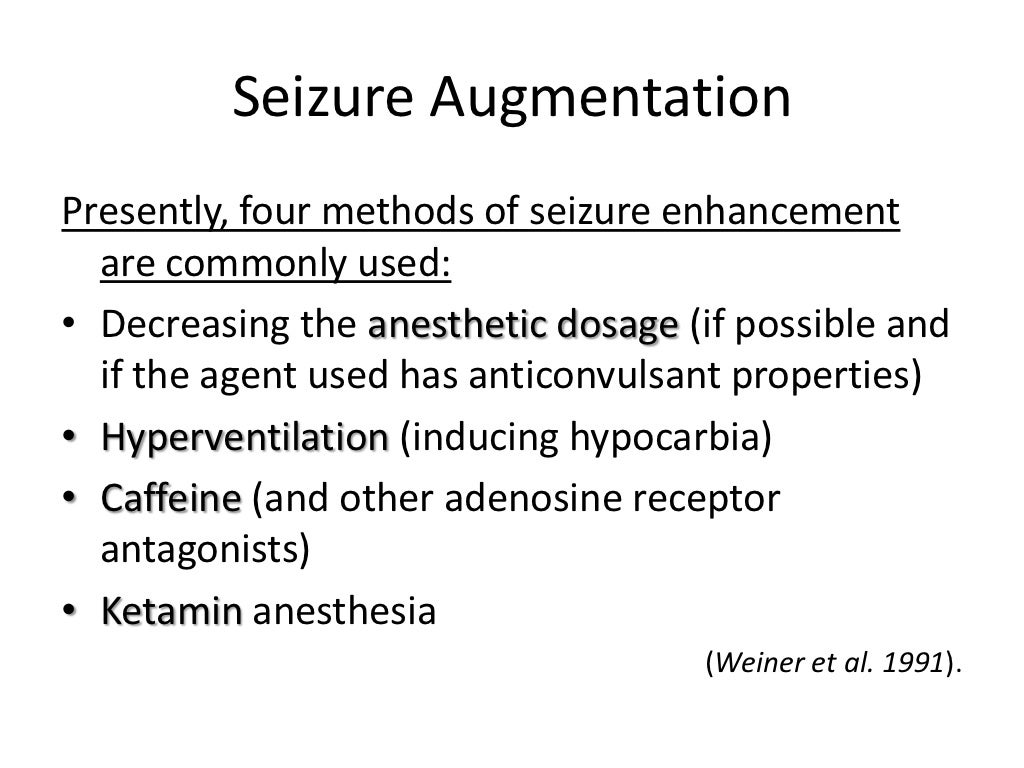
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a psychiatric treatment where a generalized seizure (without muscular convulsions) is electrically induced to manage refractory mental disorders. Typically, 70 to 120 volts are applied externally to the patient's head, resulting in approximately 800 milliamperes of direct current passing through the brain, for a duration of 100 milliseconds to 6 …
What is electronic clearing service (ECS)?
Oct 12, 2018 · Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure, done under general anesthesia, in which small electric currents are passed through the brain, intentionally triggering a brief seizure. ECT seems to cause changes in brain chemistry that can quickly reverse symptoms of certain mental health conditions. ECT often works when other treatments are unsuccessful and when …
How can i Improve my ECS tone?
Mar 02, 2022 · Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a treatment that sends a small electric current to your brain to cause a seizure. The seizure affects the chemicals in your brain, which may make your brain cells work better. ECT is used to treat certain conditions, such as depression, that do not get better after medicines or other therapies have been tried.

What is ECS treatment?
The over-riding purpose of cell membrane stimulation is repair of musculoskeletal damage, including: Improved overall circulation. Improved local blood circulation, oxygen and nutrient availability. Elimination of waste fluid, reduction of swelling and inflammation.
What does electrotherapy do to a cell?
What is ice and stim?
Can electrotherapy hurt you?
Is exercise good for ECS?
But, many fighters of chronic illness will experience an increase in symptoms if they push it. A low-impact aerobics program is best for many.
What does ECS love?
The ECS loves balance . But a body that’s stressed out and unrested is great at throwing all kinds of systems out-of-whack. So, get those eight hours and get real about managing stress.
Is the gut a regulator of ECS?
There is increasing evidence that the gut microbiome is a major regulator of the ECS. these include the levels of bacteria within it. People should avoid unnecessary antibiotics. they damage the natural microbiome balance in the gut. Also, try pro-and prebiotics to get that biome in shape.
Is ECS genetic?
ECS dysfunction isn’t genetic like eye color. But there are genetic tendencies. you should be extra careful if others in your family are fighters of chronic illness. Also, be mindful of the unhealthy habits you may share.
What is the endocannabinoid system?
All humans and mammals generally have an endocannabinoid system. It handles the balance and internal homeostasis in the body. The ES serves as a regulator in our body, it regulates sleep, mood, pain, immune response, memory, hunger, and so on. It does a great function of running the body well.
What is the role of ECS in the body?
But so far, we know it plays role in regulating a range of functions and processes, including: sleep. mood. appetite. memory . reproduction and fertility. The ECS exists and is active in your body even if you don’t use cannabis.
What is the ECS?
How it works. Functions. THC. CBD. Deficiency. Takeaway. The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling system identified in the early 1990s by researchers exploring TH C, a well-known cannabinoid. Cannabinoids are compounds found in cannabis.
What is the ECS in cannabis?
Deficiency. Takeaway. The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling system identified in the early 1990s by researchers exploring THC, a well-known cannabinoid. Cannabinoids are compounds found in cannabis. Experts are still trying to fully understand the ECS.
What is the endocannabinoid system?
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling system identified in the early 1990s by researchers exploring THC , a well-known cannabinoid. Cannabinoids are compounds found in cannabis. Experts are still trying to fully understand the ECS. But so far, we know it plays role in regulating a range of functions and processes, including:
What are the functions of cannabinoids?
But so far, we know it plays role in regulating a range of functions and processes, including: sleep. mood. appetite. memory. reproduction and fertility.
What are the receptors of endocannabinoids?
Endocannabinoids bind to them in order to signal that the ECS needs to take action. There are two main endocannabinoid receptors: CB1 receptors , which are mostly found in the central nervous system. CB2 receptor s, which are mostly found in your peripheral nervous system, especially immune cells.
Where are endocannabinoids found?
There are two main endocannabinoid receptors: CB1 receptors, which are mostly found in the central nervous system. CB2 receptors, which are mostly found in your peripheral nervous system, especially immune cells. Endocannabinoids can bind to either receptor.
What are the two types of ECS?
There are mainly two types of ECS, which are ECS credit and ECS debit. Read further to know what they are and how they are different from one another. ECS credit: When a bank makes credit to a bank account, like to pay salary, dividends, etc. it is called ECS credit.
What is ECS credit?
ECS credit: When a bank makes credit to a bank account, like to pay salary, dividends, etc. it is called ECS credit. A single account is debited on regular intervals to credit multiple accounts. Local ECS – It is operated at 81 centers across India by the RBI.
Do you have to notify the beneficiary of a change in the mandate?
Yes. If the information in the mandate undergoes any change, then the beneficiary must notify the changes to User Institution so that the correct information can be incorporated into its records.
Is Aditya Birla Capital Group liable for any decision arising out of this information?
Readers are advised to exercise discretion and should seek independent professional advice prior to making any investment decision in relation to any financial product. Aditya Birla Capital Group is not liable for any decision arising out of the use of this information.
What happens if you don't have enough funds in your bank account?
If at all you do not have adequate funds in your bank account and the ECS bounces, you will mostly be required to pay a penalty which can be as high as the penalty you pay for a bounced cheque. So, be a little cautious while using this facility for automating your EMI payments.
ECS Central East Regional Recovery Center
The ECS Central East Regional Recovery Center (CERRC), funded by San Diego County Behavioral Health Services, provides outpatient treatment services to adults with substance use disorders.
Transition Age Youth Services at CERRC
CERRC also offers specialized substance use disorder services for young adults age 18 to 25. The needs of young adults are different and we know that. At ECS CERRC our counselors work with you, addressing your unique situation and supporting you every step of the way.
How often is ECT given?
In the United States, ECT is usually given three times a week; in the United Kingdom, it is usually given twice a week. Occasionally it is given on a daily basis.
Is ECT a second line treatment?
ECT is generally a second-line treatment for people with catatonia who do not respond to other treatments, but is a first-line treatment for severe or life-threatening catatonia. There is a plethora of evidence for its efficacy, notwithstanding a lack of randomised controlled trials, such that "the excellent efficacy of ECT in catatonia is generally acknowledged". For people with autism spectrum disorders who have catatonia, there is little published evidence about the efficacy of ECT; as of 2014 there were twelve case reports.
When was the ECT procedure first used?
The ECT procedure was first conducted in 1938 by Italian psychiatrist Ugo Cerletti and rapidly replaced less safe and effective forms of biological treatments in use at the time. ECT is often used with informed consent as a safe and effective intervention for major depressive disorder, mania, and catatonia.
How long does it take for a person to relapse from ECT?
There is little agreement on the most appropriate follow-up to ECT for people with major depressive disorder. When ECT is followed by treatment with antidepressants, about 50% of people relapsed by 12 months following successful initial treatment with ECT, with about 37% relapsing within the first 6 months.
What is ECT used for?
ECT is used to treat people who have severe or prolonged mania; NICE recommends it only in life-threatening situations or when other treatments have failed and as a second-line treatment for bipolar mania.
Is ECT used for schizophrenia?
ECT is widely used worldwide in the treatment of schizophrenia, but in North America and Western Europe it is invariably used only in treatment resistant schizophrenia when symptoms show little response to antipsychotics; there is comprehensive research evidence for such practice. It is useful in the case of severe exacerbations of catatonic schizophrenia, whether excited or stuporous. There are also case reports of ECT improving persistent psychotic symptoms associated with Stimulant-induced psychosis.
What are the effects of ECT?
Immediately following treatment, the most common adverse effects are confusion and memory loss. Some patients experience muscle soreness after ECT. The death rate during ECT is around 4 per 100,000 procedures. There is evidence and rationale to support giving low doses of benzodiazepines or otherwise low doses of general anesthetics, which induce sedation but not anesthesia, to patients to reduce adverse effects of ECT.
How to get ready for ECT?
To get ready for the ECT procedure: You'll have general anesthesia. So you can expect dietary restrictions before the procedure. Typically, this means no food or water after midnight and only a sip of water to take any morning medications. Your health care team will give you specific instructions before your procedure.
What is ECT used for?
ECT is used to treat: Severe depression, particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. Treatment-resistant depression, a severe depression that doesn't improve with medications or other treatments. Severe mania, a state of intense euphoria, agitation or hyperactivity ...
Is ECT good for dementia?
Agitation and aggression in people with dementia, which can be difficult to treat and negatively affect quality of life. ECT may be a good treatment option when medications aren't tolerated or other forms of therapy haven't worked.
Can ECT cause headaches?
On the days of an ECT treatment, some people experience nausea, headache, jaw pain or muscle ache. These generally can be treated with medications. Medical complications. As with any type of medical procedure, especially one that involves anesthesia, there are risks of medical complications.
How long does it take for ECT to work?
Full improvement may take longer, though ECT may not work for everyone. Response to antidepressant medications, in comparison, can take several weeks or more. No one knows for certain how ECT helps treat severe depression and other mental illnesses.
Is anesthesia a risky procedure?
As with any type of medical procedure, especially one that involves anesthesia, there are risks of medical complications. During ECT, heart rate and blood pressure increase, and in rare cases, that can lead to serious heart problems. If you have heart problems, ECT may be more risky.
Does ECT work for everyone?
ECT seems to cause changes in brain chemistry that can quickly reverse symptoms of certain mental health conditions. ECT often works when other treatments are unsuccessful and when the full course of treatment is completed, but it may not work for everyone. Much of the stigma attached to ECT is based on early treatments in which high doses ...
What is ECT therapy?
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW: Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a treatment that sends a small electric current to your brain to cause a seizure. The seizure affects the chemicals in your brain, which may make your brain cells work better.
How long does it take for ECT to go away?
ECT may cause memory loss and confusion. Your confusion may go away in a short time, such as 1 hour after your treatment. You may lose your memory for 1 to 3 weeks, and some memories may be lost forever.
What does it mean when you have a fever?
You have a fever. You have a severe headache that does not get better, even after you take medicine to treat it. You have a stiff neck or trouble thinking clearly. You have feelings of guilt or hopelessness, or thoughts of hurting or killing yourself or others.
