
Considerations When Designing a Wastewater Treatment Plant
- Choosing a Plant Name. ...
- Designing the Layout. ...
- Selecting the Appropriate Wastewater Treatment Processes. ...
- Controlling & Mitigating Odors. ...
- Public Relations for Wastewater Treatment Plants. ...
- Build a 3D Model of the Plant. ...
- Assess the Aesthetics & Neighborhood Compatibility. ...
- Review Landscaping & Area Lighting. ...
- Noise & Decibel Ratings. ...
- Conclusions. ...
Full Answer
How to make a waste water treatment plant model?
Concepts of Sustainable Water Treatment / 2.9. Treatment and Sustainability Goals / 2.10. Water Supply / 2.10. Water Treatment Plant Design / 2.11. Integrated Design Process / 2.14. Project Specifications / 2.16. Infrastructure Construction / 2.17. Water Treatment Plant Operation / 2.18. Transmission and Distribution of Water / 2.19
What are the steps of a water treatment plant?
planned to design an efficient water treatment plant which makes the water useful for drinking purpose. This project deals with the design of various components of water treatment plant at Peelarmozhi , Chalakudy. The water from Kappathodu canal is directed to the pond near the site by constructing a weir across the canal and the water undergoes proper treatment before it is …
How to improve water treatment plant efficiency?
Optimal Design of the Water Treatment Plants 15 12 22 12 2 40 0 0 1 min. s.t. , xx xx x x (1) As shown in Fig. 1, the feasible region is an arc. If the initial point is X 4=(2, 0), then it needs to move through the arc −X 5 6−X 6−X 6 6+4=0, and finally converges at the optimal point X∗=(2/√2,2/√2).
How to build a water plant?
Jun 06, 2018 · Design a drinking water treatment plant to treat 40 million gallons per day. The design includes one conventional surface water treatment plant that complies with current regulations, and two alternative treatment plants that comply with future regulations. The treatment plant is designed to treat water with the characteristics shown in Table 1. A jar test …
How do you make a water treatment plant?
3.1 WTP layout and flow rate capacityIntake Screen Design.Coagulation Flash Mixer.Flocculators.Sedimentation / Clarification Design.Granular Active Carbon Filtration Design.Disinfection / Chlorination dosage.Sludge / Residual Management.Sep 28, 2021
How do I make a water treatment facility?
0:242:16Learn Water Treatment Facility Design Criteria - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAll equipment must be sized to handle this hydraulic capacity an average flow rate should also beMoreAll equipment must be sized to handle this hydraulic capacity an average flow rate should also be determined which will be used to estimate operating costs costs such as chemical.
What is design of water treatment?
Typically, a water treatment plant (WTP) comprises intake, pumping, pre-sedimentation (in some cases), coagulation, flocculation, clarification, adsorption, filtration, disinfection, storage, and pumping to treat water for consumption [1-4]. The designs of a unit or some units for WTPs are available [5-10].
How do you calculate the capacity of water treatment plant?
Assuming density of water is 995 kg/m3 so, demin water demand is 10.35 m3/h or 45.57 USgpm....From water balance above we can see that :Capacity of utility water package (using filtration & reverse osmosis) = 252.06 USgpm.Capacity of potable water package = 25.2 USgpm.Capacity of demineralized water package = 45.57 USgpm.Jan 28, 2017
Is code for STP design?
Indian standard code of practice for installation of septic tanks (IS: 2470) - Bureau of Indian Standards (1986) | India Water Portal.Apr 11, 2011
Which of the following software is used for design in water treatment plant?
WAVE is an integrated expert modeling software for water-treatment plant design, including wastewater-treatment plant design, offering: Flexible design using three technologies, with multiple-unit operation combinations, plus the option to specify system-feed or net-product flow rate.
What is the purpose of design the water treatment plant?
Wastewater usually contains toxic chemicals, bacteria, and other harmful resins. The treatment unit aims at reducing the contaminants to acceptable levels so that it can be discharged back into environment.Oct 31, 2018
What are three critical things you would need to consider when designing a water treatment facility?
Major factors to be considered are: (1) type of the water source, (2) desired finished water quality, (3) skill of facility operators, and (4) the relative size of available funds.
What are the things to consider before designing a wastewater treatment plant?
Some of the factors which should be taken into consideration in this evaluation include:Locations of drinking water sources, surface water intakes and groundwater wells;Adequacy of isolation from residential areas and land use surrounding plant site;Prevailing wind directions;Susceptibility of site to flooding;More items...
How do you design a STP?
2:085:43Sewage Treatment Plant Design Calculation / Capacity - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe size of the symmetry plant or B is equal to the STP. So you say STP. So capacity of a surfaceMoreThe size of the symmetry plant or B is equal to the STP. So you say STP. So capacity of a surface treatment plant.
What is STP in layout?
Sewage Treatment Plants (STP) and their Maintenance in Apartment Complexes.Jun 10, 2020
What are the types of STP?
Following are few STP process & System commonly used in India.Activated Sludge Process.Moving Bio Bed Reactor (MBBR)Membrane Bio Reactor (MBR)Electro Coagulation System.Sequential Bio Reactor (SBR)Rotating Bio Reactor (RBC)Aug 16, 2021
What is the process of bringing water and air into close contact?
Aeration is the process of bringing water and air into close contact in order to remove dissolved gases, such as CO2, and to oxidise dissolved metals such as iron. It can also be used to remove volatile organic chemicals in the water. Aeration is often the first major process at the treatment plant. During aeration , constituents are removed or modified before they can interfere with the treatment processes.
What is the process of separating solids from fluids?
Filtration is an operation used for the separation of solids from fluids by interposing a medium through which the fluid can pass, where the solids in the fluid are retained . It depends on the pore size and the thickness of the medium as well as the mechanism that occur during filtration. In filtration other mechanisms like direct diffusion and centrifugal action also take place where in those particles, which are unable to follow the tortuous channels of the filter will also , adhere to the structure of the medium and are retained.
What is water treatment system design?
The design of a water treatment system represents a decision about how limited resources should be used to achieve specific objective, and the final design is selected from various proposals that would accomplish the same objectives [1].
What is flexible tolerance?
proposed the concept of flexible tolerance, in which the tolerance is gradually reduced in the process of calculations, and approaches zero when the optimal solution is reached. Using this method, many pull-in operations are not needed [7], and thus intuitively this is a feasible approach.
How to solve NLP problems?
One of the ways to solve an NLP problems is the use of a combined technique, which the objective function and constraints are combined by using a special algorithm to become an unconstrained NLP. While the solution remains the same as for the original problem, the unconstrained NLP is much easier to solve than the constrained one. Therefore, this method of functional conversion is favored by most researchers, and many methods have been proposed to convert functions, using the interior penalty value, exterior penalty value, and multipliers, with this last one being considered the best [9,10].
Is input water quality always constant?
The input water quality is not always at a constant level, and thus the model will generate a probability problem. Due to space limitation, this work will only consider the chance-constrained stochastic model.
What is presentation in business?
Presentation is the organization of the final results in a way that makes sense to the client, as the client needs to see why the proposed plan is preferable to alternative, to the appreciates, and that the trade-offs between objectives are reasonable.
What is sensitivity analysis?
Sensitivity analysis is the process of investigating the dependence of an optimal solution to changes in the way a problem is formulated. Doing a sensitivity analysis is a key part of the design process, equal in importance to the optimization of the process itself.
What is opportunity cost?
Opportunity costs, in the context of sensitivity analysis, are related to the coefficients of the decision variables in the objective function. In general terms they define the “cost” of using decision variables that are not part of the optimal design.
What is WTP water?
In a conventional water treatment plant (WTP), raw water undergoes a series of processes which include the units below. In addition, Australian drinking water is treated with fluoride and the pH is adjusted. Intake and screening. Coagulation (rapid mix)
Why is it important to treat water?
While the main role for treating drinking water is to make it safe, it’s also important to treat water for aesthetic purposes. No one wants to drink discolored, odorous water no matter how safe it is.
How does nanofiltration work?
Membrane separation such as in nanofiltration forces water through a membrane, effectively straining the water and leaving behind the contaminants. The water is forced through the membrane that is less than 1 mm thick using by applying pressure to push it through in a process called Reverse Osmosis (AWWA 2011)
What is adsorption in water?
According to Crittenden (2012), adsorption is predominantly the transfer of mass in which organic and inorganic toxic substances are adsorbed or collected onto a solid compound and subsequently removed. In the case for drinking water, adsorption is commonly used to remove compounds with foul taste and odor, artificial organic chemicals, compounds which adds color to water, residual by product of disinfectants and inorganic chemicals such as heavy metals and arsenic. Granular or powdered active carb (GAC) is mostly used as adsorbents to remove toxic chemicals which are dissolved in water (Crittenden, 2012)
What is the process of oxidation?
Ozonation is a conventional oxidation process using the chemical ozone or O 3 through which organic compounds can be removed by converting them into CO 2, H 2 O and mineral acids (Pham 2017, (Eckenfelder, 2000 and Tchobanoglous, Burton and Stensel, 2004). O 3 being an oxidizing agent is used when chlorination isn’t sufficient to remove various organic compounds like dieldrin, leading to a higher TOC (Ross, Leeuwen and Grabow, 1976).
What is Table 1?
Table 1 is a comparison of the existing raw water quality of the river of interest compared to the Australian Drinking Water Guidelines (ADWG) recommendations. If ADWG recommendations were not listed for a parameter, then recommendations from the U.S Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) or other government agencies were used. Both Health-based and Aesthetic-based requirements are outlined.

Table of Contents
Introduction
- While the main role for treating drinking water is to make it safe, it’s also important to treat water for aesthetic purposes. No one wants to drink discolored, odorous water no matter how safe it is. People like water to taste clear, look clear and smell clear; and it’s the quality of the water source that will determine what kind of treatment it will need. For instance, mountain spring water fres…
Overview of WTP Unit Processes
- 2.1 Intake and screening
First, large floating objects like leaves and sticks are separated with bar rack screens so the mechanical equipment and pumps in the subsequent processes are safe. Smaller macro particles are removed with finer mesh screens and grit removers. Additionally, the more effective the scre… - 2.2 Coagulation
Water then reaches the coagulation stage. At this stage, the water still has fine light particles that cannot be physically removed. The tiny particles are called colloids. To remove these colloids a chemical coagulant is added in a series of tanks and mixed vigorously in a flash mixer through …
Water Treatment Plant (WTP) Design
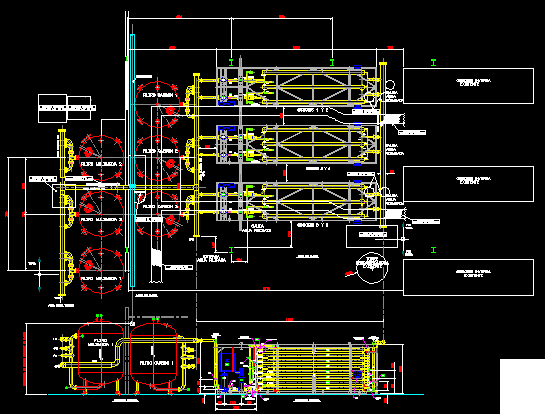
- Figure 3.0 Unit Operation in a Conventional WTP
Figure 3.0 Unit Operation in a Conventional WTP (Pham, 2017) - 3.1 WTP layout and flow rate capacity
Figure 3.0 displays the WTP Unit processes which include: 1. Intake Screen Design 2. Coagulation Flash Mixer 3. Flocculators 4. Sedimentation / Clarification Design 5. Granular Active Carbon Filtration Design 6. Disinfection / Chlorination dosage 7. Sludge / Residual Management Annual …
Environmental Impacts
- Two major environmental impact parameters were assessed across each unit of the WTP. According standard environmental impact categories of a Life Cycle Assessment (ISO14040), the production of GHG emissions (Global Warming Potential., GWP) affects Ecosystem Quality and Climate Change. Chemical toxicity (such as Aluminum) and eutrophication factors, namely high …