What are the things to considered before designing a wastewater treatment plant?
- Locations of drinking water sources, surface water intakes and groundwater wells;
- Adequacy of isolation from residential areas and land use surrounding plant site;
- Prevailing wind directions;
- Susceptibility of site to flooding;
How do you size a wastewater treatment plant?
How do you create a treatment plant?
- Intake Screen Design.
- Coagulation Flash Mixer.
- Flocculators.
- Sedimentation / Clarification Design.
- Granular Active Carbon Filtration Design.
- Disinfection / Chlorination dosage.
- Sludge / Residual Management.
What are three critical things you would need to consider when designing a water treatment facility?
What is STP in layout?
How do you size a treatment plant?
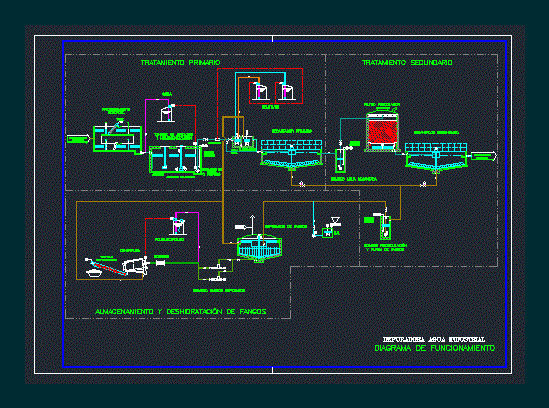
What are the steps of wastewater treatment?
- Stage One — Bar Screening. ...
- Stage Two — Screening. ...
- Stage Three — Primary Clarifier. ...
- Stage Four — Aeration. ...
- Stage Five — Secondary Clarifier. ...
- Stage Six — Chlorination (Disinfection) ...
- Stage Seven — Water Analysis & Testing. ...
- Stage Eight — Effluent Disposal.
How are water treatment plants built?
What is the process of wastewater treatment?
- Step 1: Screening and Pumping. ...
- Step 2: Grit Removal. ...
- Step 3: Primary Settling. ...
- Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ...
- Step 5: Secondary Settling. ...
- Step 6: Filtration. ...
- Step 7: Disinfection. ...
- Step 8: Oxygen Uptake.
What are two things that water treatment plants need to do?
- Coagulation. Coagulation is often the first step in water treatment. ...
- Flocculation. Flocculation follows the coagulation step. ...
- Sedimentation. Sedimentation is one of the steps water treatment plants use to separate out solids from the water. ...
- Filtration. ...
- Disinfection.
What are the components of water treatment plant?
- Raw water source, for example, and impounding reservoir, lake, or river canal.
- Intake well.
- Water pumping system.
- Cascade aerator.
- Alum mixer.
- Clarifier.
- Filter bed washing system.
- Sand filters.
What does a wastewater treatment plant do?
How to build a plant?
A good layout can often be helpful in public acceptance of the project. Consider the following: 1 Locate the plant downwind of residences and other concerned neighbors. 2 Keep some buffer between residences and the nearest plant facility (say 500 ft.). 3 Build odorous facilities farthest from residences (i.e. headworks). 4 Cover and/or house the odor causing facilities, provide necessary ventilation and air scrubbing.
Where is Tillman Water Reclamation Plant located?
A plant located in the Los Angeles area, owned and operated by the city of Los Angeles—the Tillman Water Reclamation Plant—houses a beautiful Japanese Garden on its property (below), which is regularly visited by tourists and has become a sought-after place for holding wedding ceremonies and receptions.
Is membrane bioreactor better than activated sludge?
For example, membrane bioreactors (MBR), by virtue of their smaller footprint, may be a better treatment process than conventional activated sludge. In small size plants, with MBRs, it may be possible to eliminate primary clarifiers, which often generate more odors than other processes at the plant.
How tall are chemical scrubbers?
The chemicals oxidize hydrogen sulfide and other odorous compounds producing innocuous byproducts. If the owners prefer chemical scrubbers, they usually will be tall (10 to 15 ft.), but can be hidden behind an architecturally designed wall facing the neighbors. In exceptional cases, the wall can have a nice mural painted on it to enhance appearance. [See Figure 1]
Can a plant degrade a neighborhood?
The plant should not degrade the neighborhood. This can be accomplished in a number of ways. The buildings associated with the project should match the buildings in the surrounding neighborhood—both architecturally and in materials selection. Sometimes, the fencing can be an eye sore.
Should treatment facilities be laid out in straight lines?
Too often, treatment facilities are laid out in straight lines and pushed together, resulting in the appearance of an industrial facility. This should be avoided. Structures, if possible, should be off-set, rotated, and separated to provide a more open appearance.
Should structures be off-set?
This should be avoided. Structures, if possible, should be off-set, rotated, and separated to provide a more open appearance. The bottom line is to be conscious and appreciative of the needs and concerns of the neighbors, and to build facilities that are compatible with their homes and businesses.
Is a coastal wastewater treatment plant a primary or secondary treatment plant?
The Coastal Wastewater treatment plant currently has a Primary Treatment Plant only. A design appraisal has been requested for a secondary treatment plant. This report is to design a draft based on the influent characteristics of the waste water and designed for the give effluent characteristics.
What is BNR in wastewater treatment?
BNR is a modification of Activated Sludge Treatment Process that incorporates an Anoxic and/or anerobic zones to enables removal of nitrogen and phosphorous from the wastewater. “Anerobic-anoxic-aerobic” is a type of BNR which has a 3 stage Phoredox Anerobic-Anoxic-Oxic (A 2 O) system.
What is BioWin used for?
BioWin is simulator used in designing of a wastewater treatment process, that bonds together the biological, chemical and the process models. BioWin is used all over the world to design, advancement and enhance wastewater treatment plants of all types.
When was the BNR process developed?
Biological Nutrient Removal Process was developed in the 1960s, it has been used since then due to is various advantages over other Chemical Process. BNR is a modification of Activated Sludge Treatment Process that incorporates an Anoxic and/or anerobic zones to enables removal of nitrogen and phosphorous from the wastewater.
Why is activated sludge wasted?
Because more activated sludge is produced than can be used in the process, some of it is wasted from the aeration basin or from the returned sludge line to the sludge – handling systems for treatment and disposal. Air is introduced into the aeration basin either by diffusers or by mechanical mixers.
What is the process of thickening sludge?
Centrifugations is a process by which solids are thickened or dewatered from the sludge under the influence of a ugal centrif field many times theforce of gravity. There are three basic types of centrifuges available for sludge thickening : (1) basket, (2) disc nozzle, and (3) solid bowl (or scroll – type decanter).
Is secondary sludge a single stream?
In some cases, secondary sludge is returned to the primary setting tank, ultimately giving a single stream consisting of combined sludge. Sludge contains large volume of water . the small fraction solids in the sludge is highly offensive. Thus, the problem involved with handling and disposal of sludge are complex.
What is the problem with sludge?
the small fraction solids in the sludge is highly offensive. Thus, the problem involved with handling and disposal of sludge are complex. Common sludge management processes include thickening, stabilization, dewatering , and disposal.
Is wastewater treated before it enters the water?
So, even though drinking water is treated before it enters our tap, wastewater must also be treated and cleaned before it is returned to a river.
What is wastewater engineering?
Environmental engineers design wastewater treatment plants to clean water before discharging into rivers, streams, lakes and seas. They use a variety of stages and processes to remove solids and contaminants from wastewater, including biological and mechanical processes.
What are the processes used to remove solids and contaminants from wastewater?
They use a variety of stages and processes to remove solids and contaminants from wastewater, including biological and mechanical processes . Filters and settling are common mechanical processes used to remove large particles from raw wastewater.
Where does water go after purification?
After purification, the water is distributed to homes, businesses and schools. Then, no longer clean, it flows to centralized wastewater treatment plants.
What is the RET grant for the Greenbush curriculum?
EEC 1301051—Shaping Inquiry from Feedstock to Tailpipe with Education Development (SHIFTED) through the Center for Environmentally Beneficial Catalysis, hosted by the University of Kansas Lawrence and the Southeast Kansas Education Service Center (referred to as Greenbush). Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
What is soil capable of treating?
The soil is capable of treating organic materials, inorganic substances, . and pathogens in wastewater by acting as a filter, exchanger, adsorber, and a surface on which many chemical and biochemical processes may occur. The combination of these processes acting on the wastewater as .
How long should a septic tank last?
designed and maintained concrete, fiberglass, or plastic tank should last for 50 years. Because of corrosion problems, steel tanks can be expected to last no more than 10 years. One cause of septic tank prob lems involves a failure to pump out the sludge solids when required. As.
