How is waste sludge calculated?
The equations used are as follows:Qr = (X - Xo)/(Xw - X)Qw = (8.34*V*X)/(8.34*SRT*Xw)VMG = V*7.48/1,000,000.F:M = (8.34*So*Qo)/(8.34*%Vol*X*VMG)Nov 19, 2010
How is sludge moisture calculated?
Final moisture = 10 %, 100 g moisture are associated with 900 g dry matter, Therefore (100 x 200)/900 g = 22.2 g moisture are associated with 200 g dry matter. 1kg of original matter must lose (800 – 22) g moisture = 778 g = 0.778 kg moisture.
What is sludge production rate?
Specific sludge production in wastewater treatment varies widely from 35 to 85 g dry solids per population equivalent per day (gTS PE-1 d-1).
How do you calculate sludge loading?
BOD (or COD) load: Units: kg/day The concentration of BOD (in mg/l) in the influent can be used to calculate the total BOD load per day being treated. This is simply done by multiplying the BOD in mg/l by the daily effluent volume in cubic metres (m3) and dividing the product by 1000.
What is the amount of sludge in wastewater in percentage?
The volume of sludge produced in a WWTP is only about 1% (dewatered sludge is 0.5‰) of the volume of influent wastewater to be treated.
What is SVI in wastewater treatment?
Sludge Volume Index (SVI) is used to describe the settling characteristics of sludge in the aeration tank in Activated Sludge Process. It is a process control parameter to determine the recycle rate of sludge.
How is MLSS calculated?
MLSS is measured by filtering a known volume of the mixed liquor sample, which is the same way that suspended solids are measured in wastewater. Some of the MLSS may be an inorganic material. Sometimes this may represent a large percentage of the solids present in the wastewater.
How do you calculate sludge age in wastewater?
The sludge age of an activated sludge process can be calculated by dividing the pounds of suspended solids or MLSS in the aeration tanks by the pounds of suspended solids that enter the aeration tanks (Equation I. 10).
How do you calculate wastewater flow rate?
2:549:50Calculation of Wastewater flow rate - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWastewater is done by this formula. Q wastewater equals a K factor multiplied by the square root ofMoreWastewater is done by this formula. Q wastewater equals a K factor multiplied by the square root of the sum of the discharged units.
What is formula A in wastewater treatment?
The maximum storm flow received at a treatment works is calculated by a formula known as Formula 'A'. This sets the minimum level at which the wastewater is sufficiently diluted by rainwater so as to avoid pollution of the receiving watercourse when overflowed from the sewer.
How do you calculate BOD and COD?
The COD test should be considered an independent measure of the organic matter in a wastewater sample rather than a substitute for the BOD test....Can I use my COD results to predict my BOD?Sample 1:COD = 2,150 mg/LBOD = 1,100 mg/LSample 3:COD = 1,850 mg/LBOD = 997 mg/LCOD ÷ BOD = 1,850 ÷ 997 = 1.867 more rows
How is BOD value calculated?
BOD is computed based on the difference between initial and final D.O. The test uses dilution water and a known amount of sample in a 250-300 ml incubation bottle. A small amount of seed is added to samples where microbial activity may not be present.Mar 22, 2008
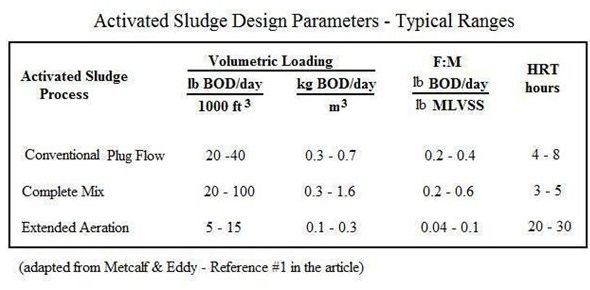
What are the three design parameters used for activated sludge aeration basins?
The table below shows typical values for three design parameters sometimes used for sizing activated sludge aeration basins: volumetric loading, food to microorganism ratio (F:M), and hydraulic residence time (HRT). Note that values for volumetric loading are given in both U.S. and S.I. units. The other two parameters are the same for either U.S. or S.I. units, since F:M will be the same as lb BOD/day/lb MLVSS or kg BOD/day/kg MLVSS, and HRT is simply in hours.
How long does it take for wastewater to aerate?
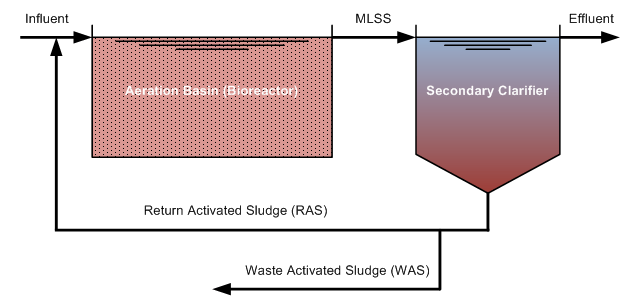
This is accomplished because the full wastewater flow is aerated for only 0.5 to 2 hours in an aerated contact tank. This is sufficient time for removal of the organic matter from the wastewater flow by the microorganism. If those microorganisms were recycled directly into the aeration tank after settling out in the secondary clarifier, however, they would not continue to take up organic matter, because they are “still full” from the 0.5 to 2 hour feast they recently had. If the recycle sludge is aerated for 3 to 8 hours to allow the microorganisms to “digest” the organic matter that they’ve taken up, then they go back into the aeration tank ready to go to work. Since the recycle activated sludge flow is less than the full wastewater flow, this results in less overall aeration tank volume for a given wastewater flow rate to be treated. The diagram below shows this process.
What is VMG in wastewater?
VMG is the tank volume in millions of gallons. It is introduced for convenience in calculations, since the primary effluent flow rate is given in MGD. The other parameters in the equations are as defined in the list above. The 8.34 factor in the equations above is used to convert mg/L to lb/MG, and the 7.48 is for conversion of ft3 to gallons. Also, note that the primary sludge flow rate is typically very small in comparison with the influent wastewater flow rate, so the primary effluent flow rate, Qo, is typically taken to be equal to the plant influent flow rate.
What is the BOD in water?
Biochemical oxygen demand ( BOD) is an indirect measure of the concentration of biodegradable organic matter in water or wastewater. Organic matter (as measured by BOD) is one of the major constituents
What is sludge volume index?
Sludge volume index, or SVI, is designed to provide an easy reference for wastewater treatment plant operators who want to gauge the health of their process.
How to calculate the SVI?
There is a tried and tested method of calculating the sludge volume index at your facility:
How to control the SVI?
The typical sludge volume index for a sludge wastewater system that is operating as it should will be between 50 and 150 mL/g. If your SVI is outside of this range, you may need to take steps to control the sludge levels in your system.
Activated Sludge Background
The activated sludge process is the most widely used method of biological wastewater treatment around the world. This process, only about 100 years old, was i nvented in England in 1914, and rapidly came into widespread use.
Activated Sludge Parameters
The diagram at the right below shows a typical flow pattern for a conventional activated sludge aeration tank and secondary clarifier, with some of parameters that will be used in the upcoming activated sludge wastewater treatment calculations shown for the primary effluent, secondary effluent, waste activated sludge, and recycle activated sludge.
Excel Formulas for Activated Sludge Design Calculations
The spreadsheet image at the left uses Excel formulas to calculate aeration tank volume requirement based on entered values for the input parameters shown: primary effluent flow rate, Q o; primary effluent biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), S o; Aeration tank MLSS, X; design volumetric loading, VL; and % volatile solids in the aeration tank, %Vol.
Excel Formulas for Activated Sludge Operational Calculations
The table at the left shows typical ranges for several operational activated sludge waste water treatment process parameters. Note that these values remain the same for U.S. or S.I. units. SRT will still have units of days. MLSS concentration will have the S.I. unit of g/m3, which is numerically equal to mg/L. F:M will have the S.I.
How much sludge is produced in a WWTP?
The volume of sludge produced in a WWTP is only about 1% (dewatered sludge is 0.5‰) of the volume of influent wastewater to be treated. To manage WWTPs effectively and efficiently, it is absolutely necessary to extract waste sludge, including inert solids and excess biomass, in order to prevent their accumulation within the system.
What are the consequences of sludge production?
As a consequence of the sludge production which is increasing, whereas disposal routes are narrowing, is a progressive further rising in costs. There are two aims with regard to sludge: the reduction of the amount of sludge produced, if sludge is considered waste.
What are the objectives of sludge solubilization?
Most of them are aimed at solids solubilisation and disintegration of bacterial cells in sludge, with the objectives of: reducing sludge production directly in the wastewater handling units; reducing sludge mass in the sludge handling units and simultaneously improving biogas production in anaerobic digestion or, in some cases, dewaterability;
What temperature does sludge need to be to be oxidized?
Once produced, the sludge can undergo hydrothermal oxidation processes to reduce the amount requiring disposal. The sludge mineralisation using oxygen can be achieved at high temperature (>850°C) in the gaseous phase (incineration) or at a relatively low temperature (in the range 150-320°C or >374°C) in the liquid phase: water (subcritical or supercritical) is used as a reaction medium. Two hydrothermal oxidation processes are available: (1) subcritical water oxidation, including wet air oxidation; (2) supercritical water oxidation.
Is sludge considered waste?
the reduction of the amount of sludge produced, if sludge is considered waste. For many producers, there are not enough economic advantages to make beneficial reuse of sludge an attractive investment. Even though a sludge-zero process remains the utopia in sludge management, a more realistic and feasible practice is to continue to reduce ...
Does biodegradability increase in inert solids?
Biodegradability increase in inert solids. A further mechanism, which is linked to biodegradability increase of inert solids, can be considered, even though it can not be considered a separate mechanism because it takes place in combination with other mechanisms.