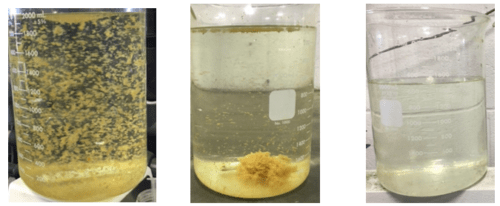
Jar Test enables the correct choice and dosage of chemical coagulants aimed at removing suspended matter and pollutants in water treated in wastewater treatment plants. The choice and dosing of the chemical coagulants derive in fact from the results of the laboratory Jar test, which mimics full-scale operation in water treatment plants.
Why use jar testing for your water treatment?
- Materials Talks Why use jar testing for your water treatment process? Control of the flocculation process and adjustment of coagulant dose during the course of water and wastewater treatment is often a challenging step in the water treatment process. How much coagulant to dose? Too much and affects water pH values.
How are the results of the jar test calculated?
All results of the jar tests are in parts per million or milligrams per liter. (1 ppm = 1 mg/L). You will need to prepare a stock solution for each type of chemical used.
What is a jar test for coagulants?
The way that jar testing is most often conducted, the test doesn’t help find the most effective coagulant or coagulant dose. ” With a jar test, we are attempting to predict the performance of our flash mixing, flocculation, and sedimentation processes by duplicating the plant performance in a small volume test.
Is there a single jar test procedure for all plants?
There is no single jar test procedure will duplicate all of these processes for all plants, however, experience shows that jar test procedures can be individually tailored to accurately predict performance for almost every plant. DAM 2B: Jar Testing Student Guide Page 2

What is the purpose of jar testing in water treatment?
A laboratory procedure that simulates coagulation/flocculation with differing chemical doses. The purpose of the procedure is to estimate the minimum coagulant dose required to achieve certain water quality goals.
What are the two objectives of jar tests?
The objectives of the jar test experiment are to estimate the optimum concentration of aluminum sulfate for the removal of suspended matter and to investigate the change in alkalinity as a result of aluminum sulfate addition.
What is the procedure for jar test?
11:3317:53Jar Test Procedure for Water Treatment - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe standard Jar test procedure consists of for mixing stages a one-minute rapid mix followed by aMoreThe standard Jar test procedure consists of for mixing stages a one-minute rapid mix followed by a three-stage tapered flocculation and concludes with filtration.
What is the purpose of varying pH in the jar test?
While a pH of 8.5 is normally recommended for the polishing effect — the pH value will vary depending on the presence of chelating and/or complexing agents in the wastewater. A jar test procedure as described above can help to establish the optimum pH within the 7.5 to 11 range.
What is coagulation in jar test?
Jar Test. Coagulation/flocculation is the process of binding small particles in the water together into larger, heavier clumps which settle out relatively quickly. The larger particles are known as floc.
Which coagulant is used in the jar test?
The choice and dosing of the chemical coagulants derive in fact from the results of the laboratory Jar test, which mimics full-scale operation in water treatment plants. The most used coagulants are Lime (calcium hydroxide), Alum (aluminum sulphate) and Iron salts (ferric or ferrous).
What are the steps of water treatment?
Public water systems often use a series of water treatment steps that include coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection.
What is the purpose of rapid mixing in jar test?
Rapid mixing aims to instantly and efficiently disperse coagulant species into raw water, before flocculation, sedimentation, and filtration processes.
What is flocculation and coagulation?
Coagulation and flocculation are two separate processes, used in succession, to overcome the forces stabilising the suspended particles. While coagulation neutralises the charges on the particles, flocculation enables them to bind together, making them bigger, so that they can be more easily separated from the liquid.
Why is alkalinity measured during jar tests?
Alkalinity and pH can be used to predict the amount of CO2 in the water, which can also contribute to corrosion. If alkalinity is too low, anything added to the water will immediately affect the pH, which can cause scaling or corrosion.
How does pH affect coagulation in water treatment?
pH EFFECTS pH that is too low may not allow the coagu- lation process to proceed, while high pH can cause a coagulated particle to redisperse. The size of the coagulated particles is also affected by pH, which, in turn, determines the density of the flocculated slime and its tendency and rate of settling out.
What is the reason for adjusting pH before adding the coagulant in jar test?
Since pH values affect the surface charges and forms of the coagulants and impurities to be removed, controlling the level of pH would significantly improve the coagulation process. Therefore, not only coagulant dosage, but also pH value should be optimized to maximize the removal of impurities present in raw water.
What acid is used in jar testing?
Your local grocery store will have a quart of white vinegar, which is typically a 5 % solution of acetic acid, and quite adequate for jar testing.
How to raise pH in a beaker?
To raise your pH, you’ll need to prepare a 5 % baking soda solution (baking soda directly from the box is 100 % sodium bicarbonate). Half-fill one of your 100 ml beakers with water, add a level teaspoon of the baking soda, mix, fill the beaker to the 100 ml mark with some more water, and mix again.
What is the best solution for chlorination?
For chlorination, it is common to use a 5.25 % bleach solution of sodium hypochlorite. Some customers prefer to use this solution directly, without dilution. Some prefer to dilute this solution with water (preferably softened water), for ease in handling and longer solution life. Others, with greater flow volumes, ...
Is it safe to use soda ash in water treatment?
Domestic water treatment often requires the pH to be raised, most commonly by soda ash ( sodium carbonate), since it is comparatively safe to handle. Sometimes a weak solution of sodium hydroxide is used. If so, both the sodium carbonate and sodium hydroxide are typically made up at a 5 % concentration by weight with water.
Can sodium bicarbonate be used to test pH?
For our purposes, however, we can test with sodium bicarbonate, or baking soda, and get a relative measure of the amount of caustic solution needed to raise the pH as much as necessary. To do that, you can prepare a 5 % solution by weight in water of the baking soda.
Can you overtreat with a jar test?
You can overtreat with large additions, test, and then work backward to the correct jar test result, or if you prefer to put in small amounts, mix, and test after each step of the chemical addition. Be sure to draw at least two more water samples for testing to establish an average result.
What is a jar test?
Jar testing can be used as a tool to help select the proper coagulant and dose for the reduction of pathogens and disinfection by-product pre-cursors. However, existing jar testing procedures can be involved, time consuming and may not provide the necessary data to make informed decisions on the selected coagulant type and dose for transferable full-scale plant performances.
How often should you perform a jar test?
Ideally, performing at least one set of jar testing per week will help keep procedures fresh in memory and to maintain skills and confidence. Maintain database record of coagulant, doses, filtrate and indirect DOC performances for any operator/engineer to review for seasonal water quality. Initial skill and confidence building will require several hours of jar testing and practice.
What is the effect of pre-oxidation on a jar?
Pre-oxidation can improve filtrate turbidity, enhance DOC reduction, improve taste and odors and reduce coagulant dose. Jar testing with and without ozonation, potassium permanganate and chlorine as pre-oxidants were evaluated.
What is a jar test?
The jar test is a method of measuring the effect of coagulation, flocculation, and sedimentation on turbidity. Although the procedure is not outlined in Standard Methods, it is used in most water treatment plants to find the best coagulant dosages under varying conditions.
How to prepare a stock solution?
Once you decide on the strength and volume of stock solution to prepare, the procedure is as follows: Weigh out the proper quantity of the chemical using the analytical balance. Put an empty weigh boat on the balance and tare it. Then add the chemical slowly to the weigh boat until the desired weight has been achieved.
How long to record floc?
Record a description of the floc in each beaker 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 minutes after addition of the chemicals. Stop the stirring apparatus and allow the samples in the beakers to settle for 30 minutes. Record a description of the floc in each beaker after 15 minutes of settling and again after 30 minutes of settling.
Can you use a magnetic stirrer to test for lime?
If lime is used , it is best to use a magnetic stirrer since lime is not completely soluble in water. In other cases, magnetic stirrers can still be useful. Collect a two gallon sample of the water to be tested. This should be the raw water. Measure 1,000 mL of raw water and place in a beaker.
Do surface water plants have turbidity?
Surface water plants, in contrast, tend to treat water with a high turbidity which is susceptible to sud den changes in water quality . Operators at these plants will perform jar tests frequently, especially after rains, to adjust the coagulant dosage and deal with the changing source water turbidity. Equipment .
What is the best pH for a jar test?
A jar test procedure as described above can help to establish the optimum pH within the 7.5 to 11 range. For adjusting pH, sodium hydroxide is recommended. However, other common chemicals can be used — such as soda ash and lime. For some applications (nickel complexes) magnesium hydroxide is an effective reagent.
What is the insoluble particle formed by adding a precipitating reagent to a wastewater solution?
The suspended stability of such particles is due to both their small size and to the electrical charge (usually negative) on their surface causing them to repel their neighboring particles.
What happens when oxidizers are added to wastewater?
These reaction are: 1) the reduction of the oxidizers and 2) the precipitation of the metals. This, of course, increases the amount of precipitant required for total metals precipitation.
What is the function of cationic polymers in precipitants?
Some precipitants contain cationic polymers that neutralize the precipitated particles. The cations (positive charges) from the polymer reduce or reverse the negative charges of the precipitate which, in turn, permits the coagulation and flocculation of the particles.
How can heavy metals be precipitated?
That is, dissolved heavy metal ions can be precipitated chemically by adjusting the pH of a wastewater stream. The pH is important because all metals have a pH at which their solubility is minimal. Although this pH differs for all metals, it generally lies between 7.5 and 11.
What is the effect of low solubility on precipitants?
These precipitants, with low solubility, can achieve very high removal efficiencies. When used as a “polishing” precipitant, the dosage of a precipitant can be lowered depending on the quantity of metals that are precipitated as hydroxides by pH adjustment.
What is precipitation in science?
Precipitation is the chemical conversion of soluble substances (including metals) into insoluble particles. Coagulation and flocculation causes a chemical reaction that promotes the formation, agglomeration or clumping of such particles to facilitate their removal from solution. The amount or dosage of a precipitant, ...
What is a successful jar testing procedure?
A successful jar testing procedure must successfully incorporate all the mixing factors for flash mixing and flocculation and settling in order to be an effective predictor of the performance of the plant.
What is dynamic jar test?
Dynamic jar tests can be used to identify the optimum mixing intensity in the flocculator of the full scale plant. They can also be used to select the appropriate mixing intensity and flocculation time that will be used during conventional jar tests.
Why do surface water treatment plants use a multi-barrier approach?
Because of the potential to transmit pathogens or other harmful constituents in surface water to the customers, surface water treatment plants (SWTPs) use a multi-barrier approach to remove and inactivate bacteria, viruses, and protozoa and protect public health. SWTP barriers . Removal and inactivation .
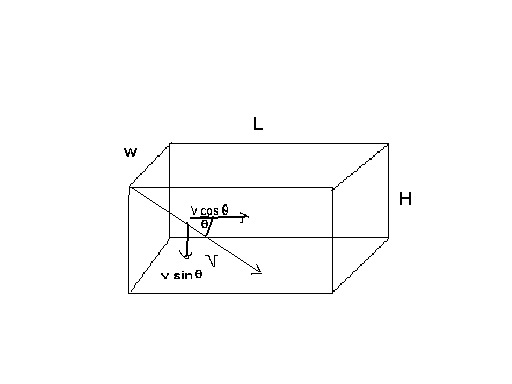
What is the SOR for sedimentation basins?
The design of sedimentation basins is normally based on Hydraulic Detention Time (HDT) or Surface Overflow Rate (SOR). In jar testing, the SOR is the most convenient term to work with.
What would happen if we fed a dry chemical, such as HTH, the only difference we would have to
If we were feeding a dry chemical, such as HTH, the only difference we would have to make to this equation would be a Concentration factor. Equation 7 would become:
What is surface overflow rate?
The surface overflow rate is a useful parameter in designing or analyzing the design of a clarifier. It is the flow rate divided by the surface area of the clarifier:
What is the purpose of surface water treatment?
The purpose of surface water treatment is to eliminate pathogens, which are microbes that can make people sick. Lakes and rivers are subject to contamination by numerous sources of pathogens, from septic fields to animal waste.