
Higher doses of chemotherapy are too harsh for older adults. People become more prone to infections as they age. Older people have more cellular mutations. However, leukemia in older adults can still be successfully treated and even cured.
What is the success rate of leukemia?
The lymphocyte count in the peripheral blood before treatment was 1.7 x 10(4) cells/ … Successful treatment of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma with MACOP-B, M-FEPA and VEPP-B combination chemotherapy
What is the cure for leukemia?
Treatment success depends on a range of factors. Treatment can include: chemotherapy radiation therapy stem cell transplant antibiotics Treatment can last several months or even years depending on...
What are the symptoms of end stage leukemia?
Adult T-cell leukemia (ATL) was diagnosed based on proliferation of CD4-positive lymphocytes, positive anti-HTLV-I antibody and monoclonal integration of proviral DNA. By 30 mg/day of ubenimex (Bestatin), the abnormal lymphocytes positive for CD4 in the peripheral blood were gradually reduced. Complete remission was maintained for 9 months without any …
What is the outcome of leukemia?
This study reports the first well-documented case of adult T-cell leukemia (ATL) successfully treated with unrelated cord blood transplantation (UCBT). A 49-year-old woman was diagnosed with acute-type of ATL. Chemotherapy induced complete remission, but the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV- …

What is the survival rate of leukemia in adults?
Survival rates by typeTypeAge rangeSurvival rateAcute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)This type of leukemia is most common in older adults, but it can be diagnosed at any age. Most deaths occur in people ages 65 to 84.Relative survival rate for all ages 5 years after diagnosis is about 29.5% .4 more rows•Aug 18, 2021
What is the success rate of treating leukemia?
The cure rates and survival outcomes for patients with ALL have improved over the past few decades. Today, nearly 90 percent of adults diagnosed with ALL achieve a complete remission, which means that leukemia cells can no longer be seen in the bone marrow with a microscope.
What is the success rate of chemotherapy for leukemia?
With current standard chemotherapy regimens, approximately 40-45% of adults younger than 60 years survive longer than 5 years and are considered cured. Results in older patients are more disappointing, with fewer than 10% surviving over the long term.
Is leukemia curable in older adults?
The Truth About Leukemia in Older Adults: It's Still Treatable. If you are an older adult diagnosed with leukemia, you have treatment options — even at age 99. Learn more from a doctor who specializes in treating leukemia in older adults.Nov 22, 2019
Which type of leukemia is most curable?
Treatment outcomes for APL are very good, and it is considered the most curable type of leukemia. Cure rates are as high as 90%.Nov 14, 2019
Can you live 20 years with leukemia?
Most people live for about 10 years, but this varies depending on how CLL behaves. People in stages 0 to II may live for 5 to 20 years without treatment. CLL has a very high incidence rate in people older than 60 years.Nov 16, 2021
Is leukemia curable if caught early?
Leukemia is the cancer of the blood-forming tissues that includes bone marrow and lymphatic system. Adults and children are equally affected by Leukemia, which is seen as production of abnormal white blood cells by the bone marrow.Mar 7, 2016
How many rounds of chemo is needed for leukemia?
You'll usually be given a combination of 2 or more chemotherapy drugs. Most people have 2 rounds of induction chemotherapy. The treatment will be carried out in hospital or in a specialist centre, as you'll need very close medical and nursing supervision. You may be able to go home between treatment rounds.
What triggers leukemia in adults?
Certain genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome, are associated with an increased risk of leukemia. Exposure to certain chemicals. Exposure to certain chemicals, such as benzene — which is found in gasoline and is used by the chemical industry — is linked to an increased risk of some kinds of leukemia. Smoking.
How long can an elderly person live with leukemia with treatment?
For people ages 70 years and older, the median overall survival rate for ALL is 4 months, and the survival rate for AML is 6 to 12 months. Targeted therapies such as immunotherapies can increase survival rates of people with acute leukemias.Aug 30, 2021
Can you live a normal life with leukemia?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) can rarely be cured. Still, most people live with the disease for many years. Some people with CLL can live for years without treatment, but over time, most will need to be treated.May 10, 2018
Can you survive leukemia without chemotherapy?
Without treatment, survival is usually measured in days to weeks. With current treatment regimens, 65%–70% of people with AML reach a complete remission (which means that leukemia cells cannot be seen in the bone marrow) after induction therapy. People over the age of 60 usually have a lower response rate.
How long do you live after leukemia?
A 5-year survival rate looks at how many people are still alive 5 years after their diagnosis. Leukemia is most common in people aged over 55, with the median age of diagnosis being 66. It is also one of the most common cancers for people under age 20. The survival rate is higher for younger people.
What are the causes of leukemia?
Leukemia can either be: 1 Acute, which is when the majority of affected white blood cells cannot function normally, causing rapid degeneration. 2 Chronic, which occurs when only some of the affected blood cells cannot function normally, causing a slower degeneration.
What is the difference between leukemia and leukemia?
There are many different types of leukemia. Which type a person develops depends on which white blood cells are affected, as well as some other factors. Leukemia can prevent white blood cells from fighting infections and cause them to multiply uncontrollably.
What are the factors that affect the chances of survival?
Factors include: age. time of diagnosis. progression and spread of the cancer. type of leukemia. a family history of blood conditions and leukemia. the extent of bone damage. exposure to certain chemicals, such as benzene and some petrochemicals.
Is there a cure for leukemia?
While there is currently no cure for leukemia, it is possible to treat the cancer to prevent it coming back. Treatment success depends on a range of factors. Treatment can include: chemotherapy. radiation therapy. stem cell transplant. antibiotics. Treatment can last several months or even years depending on the type and severity of the condition.
Is leukemia a cancer?
Seeking support. Leukemia is a broad category of cancers that affect white blood cells. The chances of survival depend on a variety of factors, including a person’s age and response to treatment.
What tests can you do for leukemia?
If this happens, or if you have signs or symptoms that suggest leukemia, you may undergo the following diagnostic exams: Physical exam. Your doctor will look for physical signs of leukemia, such as pale skin from anemia, swelling of your lymph nodes, and enlargement of your liver and spleen. Blood tests. By looking at a sample of your blood, your ...
What is the treatment for bone marrow transplant?
Radiation therapy may be used to prepare for a bone marrow transplant. Bone marrow transplant. A bone marrow transplant, also called a stem cell transplant, helps reestablish healthy stem cells by replacing unhealthy bone marrow with leukemia-free stem cells that will regenerate healthy bone marrow.
How to remove bone marrow from hip?
Bone marrow test. Your doctor may recommend a procedure to remove a sample of bone marrow from your hipbone. The bone marrow is removed using a long, thin needle. The sample is sent to a laboratory to look for leukemia cells.
What does a blood test show?
A blood test may also show the presence of leukemia cells, though not all types of leukemia cause the leukemia cells to circulate in the blood.
How does immunotherapy work?
Immunotherapy works by interfering with that process. Engineering immune cells to fight leukemia.
What is targeted therapy?
Targeted therapy. Targeted drug treatment s focus on specific abnormalities present within cancer cells. By blocking these abnormalities, targeted drug treatments can cause cancer cells to die. Your leukemia cells will be tested to see if targeted therapy may be helpful for you. Radiation therapy.
What is clinical trial?
Clinical trials are experiments to test new cancer treatments and new ways of using existing treatments. While clinical trials give you or your child a chance to try the latest cancer treatment, treatment benefits and risks may be uncertain. Discuss the benefits and risks of clinical trials with your doctor.
What is the treatment for acute myeloid leukemia?
Treatment of adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) during the remission phase depends on the subtype of AML and may include the following: Combination chemotherapy. High-dose chemotherapy, with or without radiation therapy, and stem cell transplant using the patient's stem cells . High-dose chemotherapy and stem cell transplant using donor stem ...
What is the name of the drug that kills leukemia cells?
Arsenic trioxide and all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) are anticancer drugs that kill leukemia cells, stop the leukemia cells from dividing, or help the leukemia cells mature into white blood cells. These drugs are used in the treatment of a subtype of AML called acute promyelocytic leukemia.
What is the difference between AML and AML?
Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloblasts (a type of white blood cell), red blood cells, or platelets. Adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. This type of cancer usually gets worse quickly if it is not treated.
What is the subtype of AML?
Most AML subtypes are based on how mature (developed) the cancer cells are at the time of diagnosis and how different they are from normal cells. Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) is a subtype of AML that occurs when parts of two genes stick together.
What is the extent of cancer?
In adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the subtype of AML and whether the leukemia has spread outside the blood and bone marrow are used instead of the stage to plan treatment.
What is radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing. External radiation therapy uses a machine outside the body to send radiation toward the cancer. Total-body irradiation sends radiation toward the whole body. It is a type of external radiation that may be used to prepare the body for a stem cell transplant when the leukemia has recurred.
What is PDQ cancer?
This PDQ cancer information summary has current information about the treatment of adult acute myeloid leukemia. It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers. It does not give formal guidelines or recommendations for making decisions about health care.
Watch and wait
If you have a chronic type of leukemia and are relatively healthy, your doctor may recommend watching and waiting before beginning treatment. Because some treatments may be harmful to older adults, this helps make sure you’re not treated until you need to be.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a common treatment for leukemia in people of all ages. If you’re otherwise healthy and have the necessary social support, your doctor may recommend intensive chemotherapy, which has a higher chance of curing your leukemia.
Stem cell transplant
Stem cell transplants may not be offered to older people often, but they can be very successful in preventing leukemia relapse. A relapse is when your leukemia returns after treatment has ended. You need to be generally healthy (besides the leukemia) to have a stem cell transplant.
Medications
There are several types of medications available for treating leukemia, including immunotherapies and kinase inhibitors. Immunotherapies help your immune system kill cancer cells, while kinase inhibitors help stop the cancer from growing.
Acute leukemias
For people ages 70 years and older, the median overall survival rate for ALL is 4 months, and the survival rate for AML is 6 to 12 months.
Chronic leukemias
For chronic leukemias, treatment is usually used to control the spread of cancer and manage your symptoms. It’s generally not expected to cure the leukemia, although you can live for many years with chronic leukemia. If you go into remission after treatment, a stem cell transplant can further increase your survival rate.
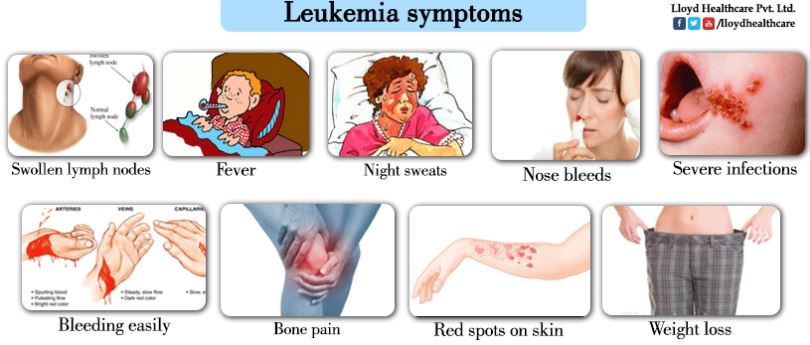
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Treatment for your leukemia depends on many factors. Your doctor determines your leukemia treatment options based on your age and overall health, the type of leukemia you have, and whether it has spread to other parts of your body, including the central nervous system. Common treatments used to fight leukemia include: 1. Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is the major form o…
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and Support
- A diagnosis of leukemia may be devastating — especially for the family of a newly diagnosed child. With time you'll find ways to cope with the distress and uncertainty of cancer. Until then, you may find it helps to: 1. Learn enough about leukemia to make decisions about your care. Ask your doctor about your leukemia, including your treatment options and, if you like, your prognosis. As …
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Start by seeing your family doctor if you have signs or symptoms that worry you. If your doctor suspects you have leukemia, you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in diseases of the blood and bone marrow (hematologist). Because appointments can be brief, and because there's often a lot of information to discuss, it's a good idea to be prepared. Here's some information to …