
Many second-line therapies for multiple myeloma can positively influence survival rates for these cases. The second-line treatment combination of lenalidomide-dexamethasone resulted in a 37% reduction in death or further progression of the disease in one study. 9 Multiple Myeloma: Understanding Your Treatment Options What You Can Do
Full Answer
How long can you Live after a multiple myeloma diagnosis?
Analysis showed myeloma overall response rate of 84%, with 42% of patients with improvement of renal function. Lenalidomide/dexamethasone is highly effective, with acceptable toxicity in the renally impaired patient group. Purpose: Renal impairment is one of the main complications of multiple myeloma associated with unfavorable prognosis. Lenalidomide in combination with …
What is the life expectancy for multiple myeloma?
Multiple myeloma can also be treated using drugs, which can be given by mouth or directly into the bloodstream. These systemic therapies can reach cancer cells anywhere in the body. Drug Therapy for Multiple Myeloma. Stem Cell Transplant for Multiple Myeloma. CAR T-cell Therapy for Multiple Myeloma.
How deadly is multiple myeloma?
Apr 27, 2022 · There is no cure for multiple myeloma, but better treatments are extending life expectancy. "Multiple myeloma is an incurable blood cancer that produces a lot of proteins that can cause damage to various organs," says Rahma Warsame, M.D., a Mayo Clinic hematologist.
What are the stages of multiple myeloma?
Jul 11, 2016 · The diagnostic evaluation of multiple myeloma comprises thorough history-taking and physical examination, various laboratory tests including analysis of a 24-hour urine sample, a bone-marrow biopsy, and skeletal radiography. Systemic treatment should be administered only when organ damage has been diagnosed. The type of treatment to be given is ...
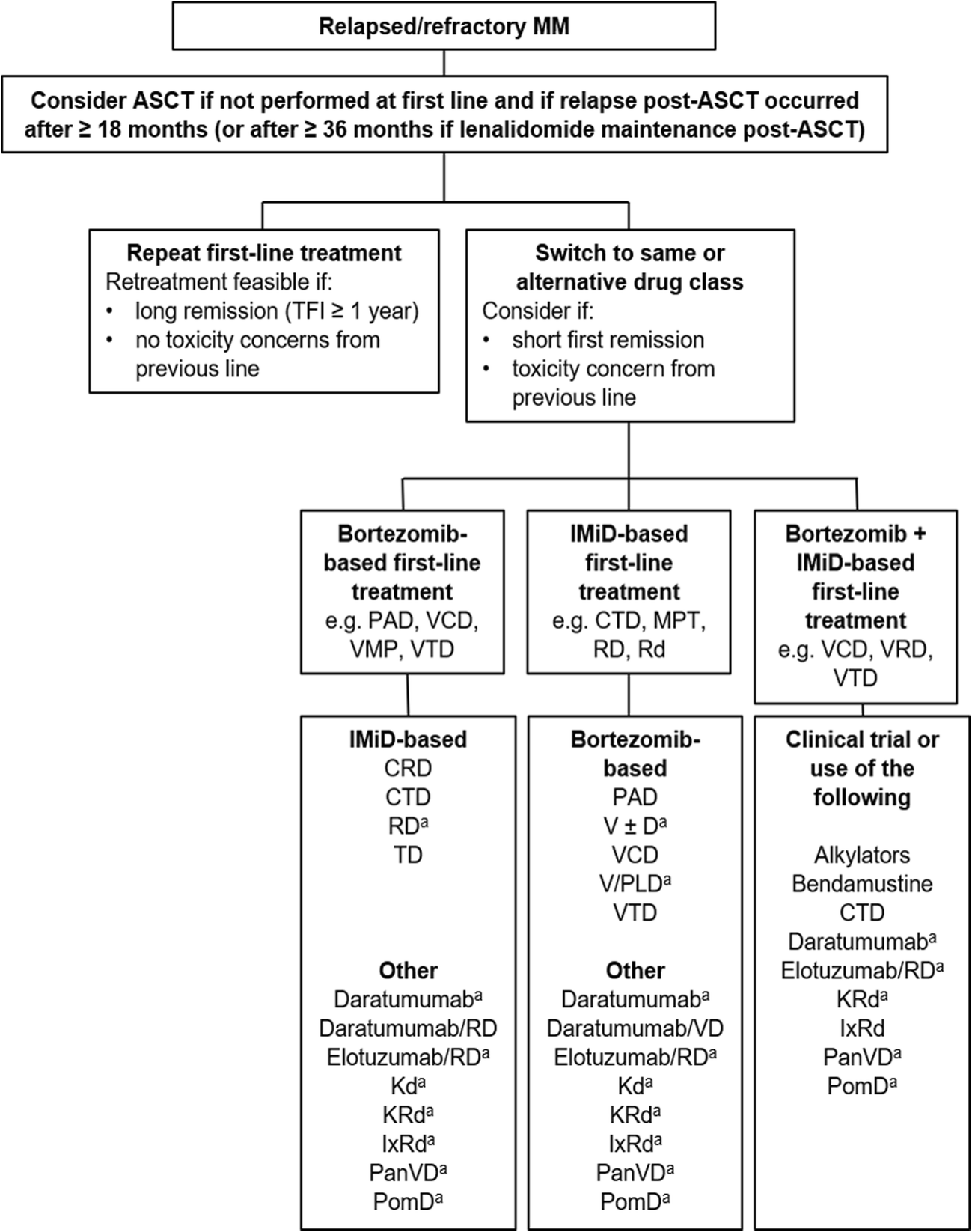
What is the success rate of treating multiple myeloma?
...
5-year relative survival rates for myeloma.
| SEER stage | 5-year relative survival rate |
|---|---|
| Distant (multiple myeloma) | 55% |
| All SEER stages combined | 56% |
How Long Can multiple myeloma patients live with treatment?
Can multiple myeloma be cured completely?
What is life expectancy after multiple myeloma diagnosis?
How do you know when multiple myeloma is getting worse?
Is multiple myeloma a death sentence?
Can you live a normal life with myeloma?
...
Multiple Myeloma Survival Rates.
| A revised international staging system | Median survival |
|---|---|
| Stage I | 62 months (5 years, 2 months) |
| Stage II | 42 months (3.5 years) |
| Stage III | 29 months (2 years, 5 months) |
Is multiple myeloma curable 2021?
Can you live a normal life with multiple myeloma?
How do I know final stages of multiple myeloma?
- Being sick to your stomach.
- Bone pain in your back or ribs.
- Bruising or bleeding easily.
- Feeling very tired.
- Fevers.
- Frequent infections that are hard to treat.
- Losing a lot of weight.
- Not feeling like eating.
Is multiple myeloma curable 2020?
Can you live 10 years with multiple myeloma?
How to treat multiple myeloma?
Multiple myeloma can also be treated using drugs, which can be given by mouth or directly into the bloodstream. These systemic therapies can reach cancer cells anywhere in the body.
Can stem cell transplants be combined?
Depending on the stage of the cancer, whether or not you are a candidate for a stem cell transplant, and other factors, different types of treatment may be combined at the same time or used after one another.
What kind of doctor treats cancer?
Based on your treatment options, you might have different types of doctors on your treatment team. These doctors could include: 1 An orthopedic surgeon: a doctor who uses surgery to treat diseases of the bones 2 A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy 3 A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with medicines such as chemotherapy or targeted therapy 4 A bone marrow transplant specialist: A cancer doctor who specializes in performing bone marrow transplants
What is local therapy?
Some treatments are called local therapies. This means they treat the tumor without affecting the rest of the body. These treatments are more likely to be useful for earlier stage (less advanced) cancers, although they might also be used in some other situations.
Why are clinical trials important?
Clinical trials are one way to get state-of-the art cancer treatment. In some cases they may be the only way to get access to newer treatments. They are also the best way for doctors to learn better methods to treat cancer. Still, they're not right for everyone.
What is complementary medicine?
Complementary methods refer to treatments that are used along with your regular medical care. Alternative treatments are used instead of a doctor’s medical treatment. Although some of these methods might be helpful in relieving symptoms or helping you feel better, many have not been proven to work.
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
How long do you live with multiple myeloma?
Survival rates tell you what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time (usually 5 years) after they were diagnosed.
What is the survival rate of a myeloma?
Survival rates for myeloma are generally based on if a single plasmacytoma is found or if multiple myeloma is diagnosed. But other factors, such as the tumor’s cytogenetics (chromosome changes), the levels of certain proteins and other substances in the blood, your kidney function, your age and overall health, can also affect your outlook.
What is SEER database?
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the SEER* database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer. The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for multiple myeloma in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. ...
Can you get treatment for multiple myeloma?
If you have multiple myeloma but aren't experiencing any symptoms (also known as smoldering multiple myeloma), you might not need treatment right away. Immediate treatment may not be necessary for multiple myeloma that is slow growing and at an early stage.
What is the best treatment for myeloma?
Corticosteroids. Corticosteroid medications regulate the immune system to control inflammation in the body. They are also active against myeloma cells. Bone marrow transplant. A bone marrow transplant, also known as a stem cell transplant, is a procedure to replace your diseased bone marrow with healthy bone marrow.
Can multiple myeloma be diagnosed?
Sometimes multiple myeloma is diagnosed when your doctor detects it accidentally during a blood test for some other condition. It can also be diagnosed if your doctor suspects you could have multiple myeloma based on your signs and symptoms.
How to diagnose multiple myeloma?
Tests and procedures used to diagnose multiple myeloma include: Blood tests . Laboratory analysis of your blood may reveal the M proteins produced by myeloma cells. Another abnormal protein produced by myeloma cells — called beta-2-microglobulin — may be detected in your blood and give your doctor clues about the aggressiveness of your myeloma.
What is the abnormal protein in myeloma?
Another abnormal protein produced by myeloma cells — called beta-2-microglobulin — may be detected in your blood and give your doctor clues about the aggressiveness of your myeloma. Additionally, blood tests to examine your kidney function, blood cell counts, ...
What stage of myeloma is the most aggressive?
Stage I indicates a less aggressive disease, and stage III indicates the most aggressive disease. Your multiple myeloma may also be assigned a risk category, ...
What kind of doctor treats multiple myeloma?
If you're diagnosed with multiple myeloma, you'll likely be referred to a doctor who specializes in treating blood and bone marrow disorders (hematologist) or a doctor who specializes in treating cancer (oncologist).
