
What is the success rate of ECT therapy?
What is the Success Rate of Electroconvulsive Therapy? ECT is an effective medical treatment option, helping as many as 80-85 percent of patients who receive it. Most patients remain well for many months afterwards. The tendency to relapse after a favorable treatment outcome can often be countered by medication after a series of treatments.
What is the success rate of ECT?
What is the Success Rate of Electroconvulsive Therapy? ECT is an effective medical treatment option, helping as many as 80-85 percent of patients who receive it.
How many ECT treatments does it take to work?
Many people begin to notice an improvement in their symptoms after about six treatments with electroconvulsive therapy. Full improvement may take longer, though ECT may not work for everyone. Response to antidepressant medications, in comparison, can take several weeks or more.
What is the maximum number of ECT treatments?
What is the maximum number of ECT treatments? The ECT taper from an acute series to a maintenance schedule is generally once a week for 4 treatments, then every 2 weeks for 4 treatments, then every 3 weeks for 4 treatments, then every 4 weeks. There is no limit on how long a patient can receive maintenance ECT provided the treatment is effective.
See more
What is the success rate of ECT therapy?
Typically, ECT (whether inpatient or outpatient) is given two to three times a week for a total of six to twelve sessions. Some patients may need more or fewer treatments. These sessions improve depression in 70 to 90 percent of patients, a response rate much higher than that of antidepressant drugs.
What is the failure rate of ECT?
Not only does it work better than medications (according to Weeks, medications have a success rate of 50–60 percent of patients getting better, while ECT succeeds at a rate of 70–90 percent), it works faster. Medications typically take up to eight weeks to show improvement.
How long does it take for ECT to work?
Results. Many people begin to notice an improvement in their symptoms after about six treatments with electroconvulsive therapy. Full improvement may take longer, though ECT may not work for everyone. Response to antidepressant medications, in comparison, can take several weeks or more.
What to expect after ECT treatment?
After the Procedure When you awaken, you may experience a period of disorientation lasting from a few minutes to several hours. Headaches, jaw pain, and muscle soreness may occur. ECT requires a series of treatments, often initiated two to three times a week for a few weeks and then the frequency is tapered down.
Who is a good candidate for ECT?
People who have had ECT before and responded well are good candidates for ECT. Other first-line indications for the procedure include people who are catatonic or suffering from a form of depression known as psychotic depression (depression associated with delusions and hallucinations).
What happens if ECT doesn't work?
If nothing else has helped, including ECT, and you are still severely depressed, you may be offered neurosurgery for mental disorder (NMD), deep brain stimulation (DBS) or vagus nerve stimulation (VNS).
Can you feel worse after ECT?
ECT can't prevent future depression, or fix any ongoing stresses or problems that are contributing to how you're feeling. Some people have very bad experiences of ECT, for example because they feel worse after treatment or are given it without consent. You might not want to risk the possibility of getting side effects.
Can ECT change your personality?
ECT does not change a person's personality, nor is it designed to treat those with just primary “personality disorders.” ECT can cause transient short-term memory — or new learning — impairment during a course of ECT, which fully reverses usually within one to four weeks after an acute course is stopped.
How many sessions of ECT are needed?
People undergoing ECT need multiple treatments. The number needed to successfully treat severe depression can range from 4 to 20, but most people need a total of 6 to 12 treatments. The treatments are usually given three times a week — Monday, Wednesday, and Friday.
When should ECT not be used?
The following strategies should not be used routinely: augmentation of an antidepressant with a benzodiazepine for more than 2 weeks as there is a risk of dependence. augmentation of an antidepressant with buspirone*, carbamazepine*, lamotrigine* or valproate* as there is insufficient evidence for their use.
Does ECT damage the brain?
The review of literature and present evidence suggests that ECT has a demonstrable impact on the structure and function of the brain. However, there is a lack of evidence at present to suggest that ECT causes brain damage.
Does ECT worsen anxiety?
The concern of some psychiatrists is that while ECT may help with depressive symptoms, it could worsen anxiety symptoms, including obsessional thoughts or panic attacks.
How many sessions of ECT did Jane have?
Jane suffered anxiety and paranoia before having ECT and had 19 sessions of ECT. She remembers going on holiday after the treatments and planning the next day and realising “there was a point in living”, but it was only much later she made the connection that having the ECT had made her better.
What did Tania say about the ECT?
She describes the effect of the ECT as ‘quite incredible’: She ‘just woke up and the whole thing had lifted’.
How long did Tristan's wife relapse after ECT?
Tristan felt huge relief when ECT appeared to work dramatically for his wife. However, his wife had a relapse 6 to ten weeks after the treatment and he thought that antidepressant medication helped improve her well-being in the longer term.
How many treatments did Catherine Z have?
Catherine Z had 4 treatments over a short period and within a week was well enough for “home-leave’ and was discharged with weekly outpatient appointments after that. She describes ECT as the best thing that could have happened to her and she has not had a recurrence of her mental health problems in twenty three years.
Did Enid have ECT?
When it got worse in his forties, he found that anti-depressant medication didn’t work and that ECT was the only thing that lifted his mood. Although Enid had felt depressed a lot during her life, she only had ECT after she retired when she found that she couldn’t do anything and was crying all the time.
Did ECT work for Carys?
Where the ECT didn’t work , some carers felt desperate and like they had “let down” their loved one. Carys said ECT had not helped her daughter and “it was almost like another way of hurting her”, “quite cruel”. Tristan felt huge relief when ECT appeared to work dramatically for his wife.
Does Steve's wife have ECT?
She had to be admitted to hospital to recover (for more see ‘ Side effects of having ECT ’). Steve’s wife first had ECT in the 1970s and has had several courses of ECT treatments over the years. Steve thinks that although ECT does work, she now seems to need more treatments before she responds.
Is ECT safe?
ECT: An Effective and Safe Treatment. There is consistent evidence of benefits following state-of-the-art modified ECT. The article by John Read, PhD, and colleagues argues in favor of suspending the use of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) due to a lack of efficacy data and unacceptable adverse effects, specifically, brain damage.
Is ECT an established treatment?
Key Efficacy Findings From Recent Studies. Since ECT is considered to be an established treatment, it can be used as an active comparator in a noninferiority paradigm, avoiding the ethical dilemma of treating very ill patients with a placebo treatment.
Is ECT outdated?
In summary, the concerns that were raised about ECT are commonly shared by the general public, and they are based on data from older studies that used the methodology now considered outdated both in terms of ECT practice and analytic techniques. Read and colleagues did not consider more recent, state-of-the-art clinical trial data that corroborate more than 75 years of clinical experience supporting the efficacy of ECT in a population of patients who suffer significant disability, increased medical comorbidity, and increased mortality.
Does ECT cause heart rate to increase?
The other safety concerns raised were an increased risk of major cardiac adverse events and an increased risk of death from ECT. While ECT does cause dramatic swings in heart rate and blood pressure, these effects are transient and well known.
Does ECT cause brain damage?
The main safety concern raised by Read and coauthors is that ECT causes brain damage. Specifically, they argued that the changes to autobiographical memory and the memory difficulties reported by patients following ECT treatment are evidence of brain damage.
Does ECT affect memory?
Perhaps the most interesting finding regarding the memory effects of ECT is that the hippocampal volume, which has been shown to decrease in major depression, increases following a course of ECT treatment. 11 This finding has been supported by 2 recent studies.
Electroconvulsive Therapy Success and Failure – Two Patients Discuss Their Different ECT Outcomes
This guest audio is from the Emotional Self Reliance Podcast, Sarah Hancock and her friend, Greg Threadgold have both had electroconvulsive therapy with remarkably different outcomes. In this episode they compare their different ECT experiences and discuss the need for better regulation of this procedure to ensure good outcomes for all patients.
Additional Resources
Testing Functional Brain Injury caused by electrical injury. (Electroconvulsive Therapy)
Sarah P. Hancock
Sarah Price Hancock, MS, CRC, lived for nearly two decades misdiagnosed with severe mental illness. She was given 116 bilateral ECT treatments and now lives with delayed electrical injury. Sarah holds a Master’s in Rehabilitation Counseling and taught for four years in San Diego State University’s Rehabilitation Counseling program.
How does ECT work?
ECT works by delivering a shock to the mind that creates a seizure. In many ways, it seems to reboot the entire brain so that it can lift the veil of depression. It might even be able to reconnect nerves or neuroconnections that have stopped functioning properly for some reason.
What age group is most likely to receive ECT?
People are more likely to receive ECT between the ages of 50-69 more than any other age group. This accounts for nearly half of all treatments. 6. ECT is rarely a first-time treatment option in youth – only 35 kids between 16-19 years of age received a treatment in the last year. 7.
What comes to mind when you think about Electroconvulsive Therapy?
What comes to mind when you think about Electroconvulsive Therapy [ECT]? For many, visions of the old-fashioned shock therapies that required patients to wear a helmet covered in electrodes and endure large amounts of voltage come to mind. It’s often thought of as something from the Stone Age of medicine and is barbaric at best. What you might not know is that ECT is not only still in use today, but it is often prescribed more often than you might think.
How high is the fatality rate for ECT?
1. Some studies have found that the fatality rate in ECT treatments is as high as 2.9 per 10,000 patients. Others have found fatality rates to be as low as 4.5 per 100,000 patients. 2. Up to 40% of ECT patients in New York receive treatments based on court orders.
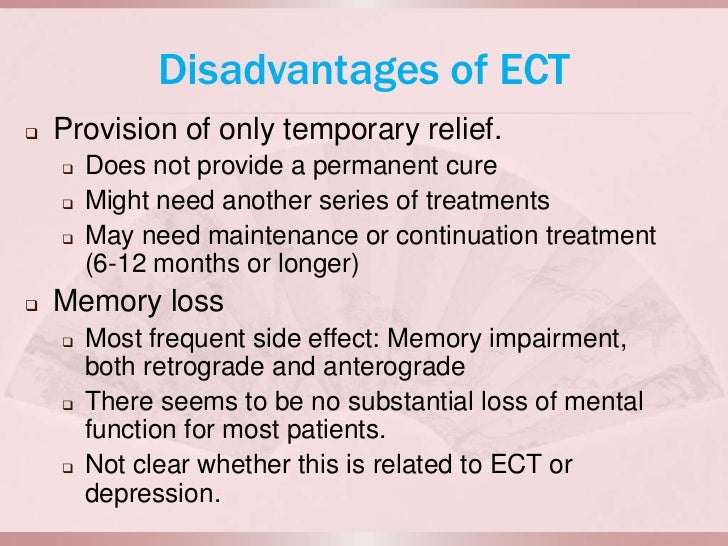
How long does memory last after ECT?
Memory complications can easily last for up to 3 years past the procedure date.
How many people are diagnosed with manic depression after ECT?
The number of people diagnosed with manic depression after an ECT treatment: 1 in 2. 14. More than 35% of people who receive an ECT treatment are later diagnosed with schizophrenia. 15. According to the Royal College of Psychiatrists, over 80% of depressed patients who receive ECT respond well to it.
Why should side effects be considered with patient consent?
It should always be with patient consent, however, because the risks of side effects are so great. If more than half of people report long term complications, then the risks of the procedure must not be greater than the rewards. Unfortunately it seems that the risks are just too great in many cases.
Why is ECT used?
Understandably, people benefiting from ECT want normalcy without the label of mental illness. ECT is often used in critical situations in an effort to avoid suicide. I know from personal experience. After three suicide attempts, ECT provided a quick and clear path out of my depression.
Does ECT have a lifetime guarantee?
Health does not come with a lifetime guarantee. As with any major medical procedure, patients must compare risks to benefits, then decide if the upside outweighs the risks. ConnECT group films a piece about their experience with ECT. Some who consider ECT worry about memory loss.
Is ECT good for depression?
For those who are profoundly depressed, the medical community often cites ECT as the gold standard, with a high remission of symptoms, far better than antidepressants alone.
Does ECT cause brain damage?
When ECT is properly administered, brain damage does not occur. In fact, research has shown that ECT increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor, which stimulates brain cell growth.
Does ECT work temporarily?
Some argue that ECT only works temporarily, the high relapse rate invalidating the procedure. Sackeim et. al. reported in the Journal of American Medical Association in 2001 that 61% of the patients treated with a combination of medication and ECT were in remission at 6 months.

Why It's Done
Risks
Self help information for family, friends and colleagues
- Loosen tight clothing
- Protect the person from injury
- If they have fallen, place something soft under their head
- Stay with them until they recover fully
Do not:
- Try to restrain the person
- Put anything between their teeth
- Move them, unless they are in danger
- Give them food to eat or drink
Person who have had seizure
- Avoid triggers
- Avoid unprotected heights and unsupervised areas of water
- Seizure lasts less than 5 minutes
- None of the below mentioned incidents occur during the episode
See a doctor immediately if you notice:
- Seizure lasts longer than five minutes
- Breathing or consciousness doesn't return after the seizure stops
- A second seizure follows immediately
- The seizure happened in water
- High fever
- Heat exhaustion
- Person is pregnant
- Person has diabetes
- Person is injured during the seizure
How You Prepare
What You Can Expect
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: 1. Severe depression,particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to e…
Results
- Although ECT is generally safe, risks and side effects may include: 1. Confusion.Immediately after treatment, you may experience confusion, which can last from a few minutes to several hours. You may not know where you are or why you're there. Rarely, confusion may last several days or longer. Confusion is generally more noticeable in older adults. 2. Memory loss.Some people hav…