Bone marrow transplants can cure sickle cell disease in some patients. Research on the condition has advanced other areas of medicine including genetics and molecular biology. Researchers have learned that periodic blood transfusions in children at high risk of stroke help reduce the risk of having a first stroke.
Full Answer
What is the best medicine for sickle cell anemia?
Nov 18, 2019 · In 2017, considerable excitement was generated by the announcement of the commercial availability of L-glutamine (Endari), touted as the first new drug approved by the FDA for treatment of sickle cell disease in 30 years. 102,103 This agent’s use is based upon the fact that the sickle red cell, because of decreased redox potential, is more susceptible to oxidant …
What are the long - term effects of sickle cell anemia?
May 20, 2020 · Pathophysiology of Sickle Cell Disease. Sickle cell disease is caused by an abnormal HbS (α 2 β S 2) in which glutamic acid at position 6 of the β-globin chain of hemoglobin is changed to valine. Goldstein et al. (1963) showed that this amino acid substitution arose from a single base change (A>T) at codon 6 (rs334).The genetic causes of SCD include homozygosity …
How do you treat sickle cell anemia?
Apr 13, 2022 · NHLBI research that really made a difference. NHLBI-funded scientists found an effective sickle cell treatment in 1995. Results from the NHLBI Multicenter Study of Hydroxyurea showed that hydroxyurea reduced the number of painful episodes by 50% in severely affected adults with sickle cell disease.
How does sickle cell anemia affect life expectancy?
Apr 12, 2012 · The NHLBI is supporting research on more and better treatments to ease the burden of sickle cell disease on those affected. Trials using new bone marrow and stem-cell transplant procedures have cured a small number of some adults with sickle cell disease. More research is needed to understand possible health implications of sickle cell trait.
How long has the National Heart Institute been researching sickle cell disease?
The NHLBI has researched sickle cell disease since its founding as the National Heart Institute in 1948. Since 1972, when the National Sickle Cell Anemia Control act was passed, the NHLBI has spent more than $1 billion researching the condition.
Is sickle cell research reaching enough people?
Some of the medical benefits coming out of sickle cell disease research are not reaching enough people. We must educate providers and patients about current advances in diagnosis and treatments.
What happens when red cells with hemoglobin S lose their oxygen?
When red cells with Hemoglobin S lose their oxygen, they become distorted and shaped like crescents or sickles. These cells are sticky and can block blood vessels, leading to organ damage, and severe episodes of pain known as crises. Sickle cell disease causes life-long anemia.
What is the disease that causes anemia?
Sickle cell disease causes life-long anemia. Damage to the spleen causes an increased risk of serious infection. Persons with sickle cell disease are also at risk of pneumonia, bone infections, and other infections. Some people have mild symptoms, while others have very severe symptoms and are hospitalized frequently for treatment.
Where does sickle cell disease come from?
Sickle cell disease is most common in people whose families come from Africa, South or Central America, Caribbean islands, Mediterranean countries, India, and Saudi Arabia. Sickle cell disease occurs in approximately one out of every 500 African American births and one out of every 36,000 Hispanic American births.
How long can you live with sickle cell disease?
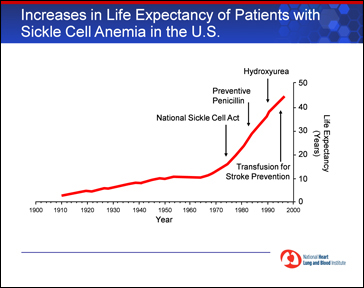
Progress from Research. Research has helped patients live longer. In the 1970s, life expectancy for individuals with sickle cell disease was about 14 years. Today, many individuals live into their 40s and longer. FDA approval in the 1990s of the drug hydroxyurea to treat adults with the disease was a major advance.
How long do sickle cell patients live?
Research has helped patients live longer. In the 1970s, life expectancy for individuals with sickle cell disease was about 14 years. Today, many individuals live into their 40s and longer.
What is sickle cell disease?
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation in both copies of a person’s HBB gene. This gene encodes a component of hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells. The mutation causes hemoglobin molecules to stick together, creating sickle-shaped red blood cells. This can lead to blood cell rupture, anemia, ...
Can bone marrow transplants cure SCD?
Bone marrow transplants can cure SCD, but appropriate donors are hard to come by . The procedure also carries risks of dangerous side effects. Several new SCD treatments are currently under development . These involve gene editing of the patient’s own bone marrow cells to produce normal-functioning hemoglobin.
Can base editing reverse a mutated gene?
While base editing can't reverse this change, it can convert the T to a C instead. This produces a naturally occurring, non-pathogenic variant of hemoglobin called Hb-Makassar. The researchers designed a molecular tool called an adenine base editor that recognizes the mutated part of the gene and converts the T to a C.
Can red blood cells survive in mice?
Red blood cells derived from these stem cells had significantly reduced sickling. Since human red blood cells can’t survive in mice long enough for extensive testing, the team next took stem cells from a mouse SCD model, edited them, and transplanted the edited cells into another set of mice.
How long does it take for Makassar to make up 80% of hemoglobin?
After 16 weeks , the Makassar variant made up almost 80% of the hemoglobin in the recipient mice. Control mice that received unedited cells had characteristic SCD symptoms: anemia, abnormal blood cell counts, sickle-shaped red blood cells, and an enlarged spleen. Mice given the edited stem cells had greatly improved symptoms.
Did mice have edited stem cells?
Mice given the edited stem cells had greatly improved symptoms. The researchers took bone marrow from the mice that had received the edited stem cells and transplanted it into a new set of mice. The new recipients had healthy blood cell counts, confirming the durability of the gene editing.
What is the molecular tool that recognizes the mutated part of the gene and converts the T to
The researchers designed a molecular tool called an adenine base editor that recognizes the mutated part of the gene and converts the T to a C. The researchers used the adenine base editor on blood-forming stem cells from human SCD patients.
How many drugs are there for sickle cell disease?
Sickle cell disease (SCD) researchers expect powerful new treatments to come in the next few years. About 30 drugs are currently in late-stage clinical trials to treat SCD. These drugs work in different ways to reduce the effects of abnormal sickle hemoglobin. 1
Does hydroxyurea increase hemoglobin F?
Fetal hemoglobin (hemoglobin) F is normally only present in newborns and protects them from complications of SCD. Increasing the amount of hemoglobin F in older children and adults can reduce complications of SCD. This is how hydroxyurea works. Drugs that increase hemoglobin F in clinical trials include: 2,3
What is the body's way of fighting infections and injuries?
Inflammation is the body’s way of fighting infections and injuries. The body releases chemicals that trigger a response from the immune system. People with SCD often have chronic inflammation , which contributes to blocked blood flow. Drugs that reduce inflammation in clinical trials for SCD include: 2-4
What is the first treatment for sickle cell?
First treatment for sickle cell is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) The World Health Organization recognizes sickle cell as a global health crisis; the United States implements mandatory newborn screenings in every state. Blood stem cell transplants are shown to stop progression in sickle cell.
Is sickle cell research lacking?
Even though the underlying cause of sickle cell has been understood for more than a century, advocacy and research have been lacking. Funding for research and treatment has always been far less than other diseases.
How many copies of HBB are there in a sickle cell?
As you may have already learned, a person has sickle cell trait when they inherit one copy of an abnormal (sickle) HBB gene and one copy of a normal HBB gene. What’s interesting to note is that humans began developing the abnormal HBB gene as an evolutionary response to malaria.
Why do people have sickle cell traits?
As you may have already learned, a person has sickle cell trait when they inherit one copy of an abnormal (sickle) HBB gene and one copy of a normal HBB gene. What’s interesting to note is that humans began developing the abnormal HBB gene as an evolutionary response to malaria. This is because the parasite that causes malaria is halted by sickled ...
When was sickle cell first identified?
While sickle cell symptoms have been documented in medical texts since the 1870s, it was not formally identified in the United States until 1910. Dr. James Herrick described the disease as a "peculiar, elongated sickle-shaped. erythrocytes. ×.
What is the sickle shaped disease?
James Herrick described the disease as a "peculiar, elongated sickle-shaped. ", noting the unusual red blood cells were sickle shaped. Sickle cell is a disease that impacts people of all races, but disproportionately affects Black Americans in the United States.
What is sickle cell?
Sickle cell is a disease that impacts people of all races, but disproportionately affects Black Americans in the United States. It is often perceived as a “Black disease”, which unfortunately has caused racial bias and prevented people with sickle cell from receiving the highest-quality care.
