Following the injection of a radioactive tracer near the suspected cancer, the gamma detector can be used pre, intra or postoperatively. During a preoperative scan, the detector will assist the surgeon in identifying the location of the mass to be removed or biopsied.
Full Answer
How is a gamma detector used to detect cancer?
Following the injection of a radioactive tracer near the suspected cancer, the gamma detector can be used pre, intra or postoperatively. During a preoperative scan, the detector will assist the surgeon in identifying the location of the mass to be removed or biopsied.
What are radioactive tracers used for?
Radioactive tracers are also used in hydraulic fracturing. This is the fracturing of underground rock layers (and is often called fracking). A pressurised liquid is forced into the rock layers which fracture and release natural gas which is collected and sold.
How are radiation rays used in cancer treatment?
In therapy, the rays are used as weapons. One would shell tumors with an external source or by means of radioactive implants located near the malignant cells. The use of radioisotopes for diagnosis is by far the most widespread.
What are the clinical applications of gamma rays for thyroid cancer?
Widely used in treating thyroid cancer and in imaging the thyroid; also in diagnosis of abnormal liver function, renal (kidney) blood flow, and urinary tract obstruction. A strong gamma emitter, but used for beta therapy.

What are radioactive tracers and how are they used in medicine?
Radioactive tracers are used in imaging tests that help find problems inside the body. These tracers give off particles that can be detected and turned into a picture to help find problems in organs or other structures. The tracer is usually given through an intravenous (IV) line placed in a vein.
How are gamma rays used in medical tracers?
A radioactive tracer is used to investigate inside a patient's body without surgery. Gamma (and sometimes beta) emitters are introduced into the body to be used as tracers. Radiation from a radioisotope used as a tracer is emitted inside the body. The radiation can penetrate tissues and leave the body to be detected.
How are radioactive tracers useful in medicine give an example?
Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty that uses radioactive tracers (radiopharmaceuticals) to assess bodily functions and to diagnose and treat disease. Specially designed cameras allow doctors to track the path of these radioactive tracers.
Why is gamma radiation used in radioactive tracers?
Emitters of beta radiation or gamma radiation are used because these types of radiation readily pass out of the body, and they are less likely to be absorbed by cells than alpha radiation. Radioactive tracers are also used in hydraulic fracturing.
What are the benefits of radioactive tracers?
A radioactive tracer is a chemical compound having at least one radioactive element. Frequently used in medicine to follow the progress of substances in living tissues, it gives doctors a precise way to “see” into the circulatory system and other organs.
What is a gamma scan used for?
It can be used to diagnose various conditions and examine the structure and function of many different parts of the body, including the heart, brain, lungs, and kidneys. It may be used to assess if the patient's organs or tissues are healthy enough to undergo a certain operation or to assess if they need one.
Which of the following is an example of a tracer used in medical tracers?
According to the NRC, some of the most commonly used tracers include antimony-124, bromine-82, iodine-125, iodine-131, iridium-192, and scandium-46.
Which radioactive isotopes can be beneficial in diagnosing and treating diseases?
The most common radioisotopes used in the medical industry are Technetium-99m, Iodine-131, and Molybdenum-99. 85% of all nuclear medical examinations use Mo/Tc generators for diagnosing problems with the liver, bones, or lungs [6].
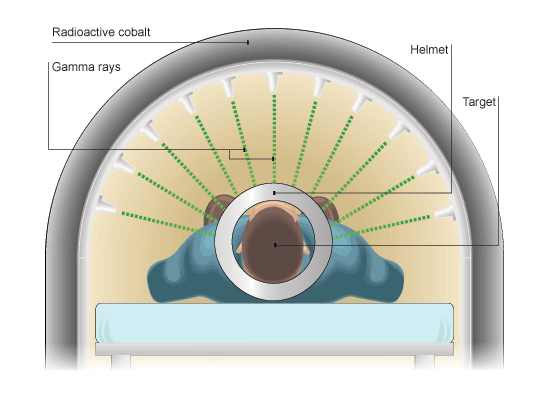
What Is Radiation Therapy?
Radiation therapy uses high-energy particles or waves, such as x-rays, gamma rays, electron beams, or protons, to destroy or damage cancer cells.Yo...
Who Gets Radiation Therapy?
More than half of people with cancer get radiation therapy. Sometimes, radiation therapy is the only cancer treatment needed.
What Are The Goals of Radiation Therapy?
Most types of radiation therapy don’t reach all parts of the body, which means they’re not helpful in treating cancer that has spread to many place...
How Is Radiation Therapy given?
Radiation therapy can be given in 3 ways: 1. External radiation (or external beam radiation): uses a machine that directs high-energy rays from out...
Who Gives Radiation Therapy Treatments?
During your radiation therapy, a team of highly trained medical professionals will care for you. Your team may include these people: 1. Radiation o...
Does Radiation Therapy Cause Cancer?
It has long been known that radiation therapy can slightly raise the risk of getting another cancer. It’s one of the possible side effects of treat...
Does Radiation Therapy Affect Pregnancy Or Fertility?
Women: It’s important not to become pregnant while getting radiation – it can harm the growing baby. If there’s a chance you might become pregnant,...
Questions to Ask About Radiation Therapy
Before treatment, you’ll be asked to sign a consent form saying that your doctor has explained how radiation therapy may help, the possible risks,...
Will I Be Radioactive During Or After External Radiation Treatment?
External radiation therapy affects cells in your body only for a moment. Because there’s no radiation source in your body, you are not radioactive...
What is radioactive tracers used for?
Radioactive tracers are also used in hydraulic fracturing. This is the fracturing of underground rock layers (and is often called fracking). A pressurised liquid is forced into the rock layers which fracture and release natural gas which is collected and sold. The tracers help locate the created fractures. previous.
What is a radiation detector?
Radiation detectors placed outside the body detect the radiation emitted and, with the aid of computers, build up an image of the inside of the body. When a radioactive chemical is used in this way it is not normally harmful, because:
What are the dangers of radioactive substances?
When a radioactive chemical is used in this way it is not normally harmful, because: 1 it has a short half-life and so decays before it can do much damage 2 it is not poisonous
Is gamma radiation poisonous?
it is not poisonous. Emitters of beta radiation or gamma radiation are used because these types of radiation readily pass out of the body, and they are less likely to be absorbed by cells than alpha radiation. Radioactive tracers are also used in hydraulic fracturing.
How is radiation given?
Radiation therapy can be given in 3 ways: 1 External radiation (or external beam radiation): uses a machine that directs high-energy rays from outside the body into the tumor. It’s done during outpatient visits to a hospital or treatment center. It's usually given over many weeks and sometimes will be given twice a day for several weeks. A person receiving external radiation is not radioactive and does not have to follow special safety precautions at home. 2 Internal radiation: Internal radiation is also called brachytherapy. A radioactive source is put inside the body into or near the tumor. With some types of brachytherapy, radiation might be placed and left in the body to work. Sometimes it is placed in the body for a period of time and then removed. This is decided based on the type of cancer. Special safety precautions are needed for this type of radiation for a period of time. But it's important to know if the internal radiation is left in the body, after a while it eventually is no longer radioactive. 3 Systemic radiation: Radioactive drugs given by mouth or put into a vein are used to treat certain types of cancer. These drugs then travel throughout the body. You might have to follow special precautions at home for a period of time after these drugs are given.
What doctor is trained to treat cancer?
Radiation oncologist: This doctor is specially trained to treat cancer with radiation. This person oversees your radiation treatment plan. Radiation physicist: This is the person who makes sure the radiation equipment is working as it should and that it gives you the exact dose prescribed by your radiation oncologist.
What is the treatment for cancer that has returned?
To treat cancer that has returned (recurred) If a person's cancer has returned (recurred), radiation might be used to treat the cancer or to treat symptoms caused by advanced cancer. Whether radiation will be used after recurrence depends on many factors.
How does radiation help cancer cells?
But cancer cells grow and divide faster than most normal cells. Radiation works by making small breaks in the DNA inside cells. These breaks keep cancer cells from growing and dividing and cause them to die.
Why do people get radiation to their head?
This is done to help prevent cancer from spreading to the head even before it can.
How does cancer spread?
Cancer can spread from where it started to other body parts. Doctors often assume that a few cancer cells might already have spread even when they can’t be seen on imaging scans like CT scans or MRIs. In some cases, the area where the cancer most often spreads to may be treated with radiation to kill any cancer cells before they grow into tumors. For instance, people with certain kinds of lung cancer may get radiation to the head, even when there is no cancer known to be there, because their type of lung cancer often spreads to the brain. This is done to help prevent cancer from spreading to the head even before it can. Sometimes, radiation to prevent future cancer can be given at the same time that radiation is given to treat existing cancer, especially if the area the cancer might spread to is close to the tumor itself.
How many people with cancer get radiation?
More than half of people with cancer get radiation therapy. Sometimes, radiation therapy is the only cancer treatment needed and sometimes it's used with other types of treatment. The decision to use radiation therapy depends on the type and stage of cancer, and other health problems a patient might have.
How long does it take to get a thyroid scan?
For a thyroid scan, you take the radioactive tracer as a liquid or pill about 24 hours before the scan. The scan takes less than 30 minutes. MUGA scans can take up to 3 hours, depending on how many pictures are needed. Gallium scans take several days between the injection and the actual scan.
What type of scan is used for cancer?
The specific type of nuclear scan you’ll have depends on which organ the doctor wants to look into. Some of the nuclear medicine scans most commonly used for cancer (described in more detail further on) are: Bone scans. PET (positron emission tomography) scans. Thyroid scans.
How long before a gallium scan can you get a tracer?
For example, in a bone scan, the tracer is put into a vein in your arm about 2 hours before the test begins. For gallium scans, the tracer is given a few days before the test.
Why are bone scans used?
Because of this, they’re often used along with other imaging tests to give a more complete picture of what’s going on. For instance, bone scans that show hot spots on the skeleton are usually followed by x-rays of the affected bones, which are better at showing details of the bone structure.
What is nuclear medicine scan?
These nuclear medicine scans are commonly used for cancer: Bone scans: Bone scans look for cancers that may have spread (metastasized) from other places to the bones. They can often find bone changes much earlier than regular x-rays. The tracer collects in the bone over a few hours, then the scans are done.
How long does it take for a tracer to work?
Over time the tracer collects in the part of the body that’s being tested. This can take from a few seconds to several days. The collected tracer sends out gamma rays that are picked up by a special camera (a gamma camera, rectilinear scanner, or scintiscan ).
What is nuclear scan?
Nuclear scans make pictures based on the body’s chemistry (like metabolism) rather than on physical shapes and forms (as is the case with other imaging tests). These scans use liquid substances called radionuclide s (also called tracers or radiopharmaceuticals) that release low levels of radiation. Body tissues affected by certain diseases, such as ...
How many people use radioisotopes in a year?
There is widespread awareness of the use of radiation and radioisotopes in medicine, particularly for diagnosis (identification) and therapy (treatment) of various medical conditions. In developed countries (a quarter of the world population) about one person in 50 uses diagnostic nuclear medicine each year, and the frequency ...
What is short range radiotherapy?
This is radionuclide therapy (RNT) or radiotherapy. Short-range radiotherapy is known as brachytherapy , and this is becoming the main means of treatment. Although radiotherapy is less common than diagnostic use of radioactive material in medicine, it is nevertheless widespread, important, and growing.
Why are radioisotopes important?
In combination with imaging devices which register the gamma rays emitted from within, they can study the dynamic processes taking place in various parts of the body.
What is radioisotopes used for in medicine?
(Updated April 2021) Nuclear medicine uses radiation to provide diagnostic information about the functioning of a person's specific organs, or to treat them. Diagnostic procedures using radioisotopes are now routine.
How many hospitals use radioactive tracer?
Five Nobel Laureates have been closely involved with the use of radioactive tracers in medicine. Over 10,000 hospitals worldwide use radioisotopes in medicine, and about 90% of the procedures are for diagnosis.
How many nuclear procedures are performed annually?
Over 40 million nuclear medicine procedures are performed each year, and demand for radioisotopes is increasing at up to 5% annually. Sterilization of medical equipment is also an important use of radioisotopes.
What is a LU-177?
Lu-177 is essentially a low-energy beta-emitter (with some gamma) and the carrier attaches to the surface of the tumour. A new field is targeted alpha therapy (TAT) or alpha radioimmunotherapy, especially for the control of dispersed (metastatic) cancers.
What radioelement is used in scintigraphy?
Technetium 99m is by far the most commonly used radioelement (as it is used in 80-90% of all scintigraphy scans), as it allows for the exploration of numerous body parts and emits only gamma rays whose energy (of 140 keV) is well adapted to the gamma-camera detectors.
What are radioactive atoms?
The radioactive atoms, that are radioisotopes, have brought a lot to biology. They are also at the core of nuclear medicine. These unstable atoms behave like ordinary stable atoms apart from the one and extremely short moment when they emit their radiation.
What do radioisotopes bind to?
They bind like them with other atoms to form molecules. The alpha, beta, or gamma rays they emit during their fugitive radioactive decay signal their presence. Tiny objects of the infinitely small, radioisotopes are innumerable even in minute proportion in the matter.
What gases are used for lung scans?
Tracers can be reduced to a marker itself : this is the case of krypton 81m or xenon 133 , noble gases used for lung scans.
Why do isotopes have to be chemically attached to a molecule?
The isotope has to be chemically attached to the relevant molecule without altering its properties and metabolism. The bond must also be a solid one in order to follow the molecule and not an eventually shaken off radioactive atom.
When were radioisotopes first used?
The use of radioisotopes for diagnosis is by far the most widespread. Ever since the 1934 discovery of artificial radioactivity, doctors have been armed with a panoply of radioactive isotopes for use as markers or tracers.
Can a nuclear tracer be used to trace a single atom?
Thanks to these radioactive isotopes it is now possible to follow the path of a single atom or chemical element around the body without disturbing its physical, chemical or biological behaviour. In the areas of biology and medicine, nuclear tracers are usually radiopharmaceutical products whose molecules contain a radioactive element - a marker.
What is the Alliance for Radiation Safety in Pediatric Imaging?
The Alliance for Radiation Safety in Pediatric Imaging (also called the Image GentlyAlliance) recommends that parents ask questions before their children have tests suchas a CT scan to make sure that the facility adjusts the radiation doses for children. Theyalso recommend asking if the facility is accredited in CT by the American College ofRadiology.
What is gamma radiation?
This can be in the form of radiation that penetrates fromoutside the body, or radioactive particles that are swallowed or inserted into the body.
Why do airports use body scanners?
In recent years, some airports have begun to use whole body scanners as a way todetect objects hidden by clothing. These scanners are different from the metal detectorsmost people are familiar with.
What is the most common source of radiation?
The largest source of natural background radiation for most people is radon. This is anodorless, colorless gas that is formed from the breakdown of radioactive elements in theground. Radon levels are usually higher inside buildings and homes, especially in levelscloser to the ground such as basements. Radon levels can vary a great deal, dependingon where you live or work. For example, exposure is higher for people who work inmines. For more detailed information on radon and its possible health effects, see
Why is ionizing radiation used?
Ionizing radiation can be used to kill bacteria and other germs on certain foods, which may make them safer to eat and help them last longer. Some people may be concernedthat irradiated food may itself contain radiation.
How did the atomic bombs affect people?
The atomic bombs dropped on Nagasaki and Hiroshima, Japan exposed many peopleto radiation from x-rays, gamma rays, and neutrons. Some people died fairly quickly asa result of burns and radiation sickness, but many survived. The survivors wereexposed to different amounts of radiation, depending largely on how far they were fromthe explosions. Only about 2% of the survivors were exposed to high amounts ofradiation (1000 mSv or more), while almost one-third were exposed to doses that arerelatively low (less than 5 mSv). Much of the information that we have about radiationand cancer risks comes from studies of more than 105,000 of the survivors.
What is the best way to treat cancer?
X-rays, gamma rays, and other forms of ionizing radiation offer an effective way to treatcertain kinds of cancer. During radiation therapy5, high doses of ionizing radiation (muchhigher than those used for imaging tests) are directed at the cancer, resulting in thedeath of the cancer cells. However, this can lead to DNA mutations in other cells thatsurvive the radiation, which may eventually lead to the development of a second cancer.Radiation therapy is also sometimes used to treat serious medical conditions besidescancer.
