Nutrition
Advise the receiving facility of your suspicion of epiglottitis Administer 100% humidified oxygen by mask, if tolerated DO NOT attempt vascular access (the added stress can be detrimental to the airway) Have the proper advanced airway adjuncts ready and at hand
Which antibiotics are used to treat epiglottitis?
Paramedic assessment and treatment of upper airway obstruction in pediatric patients: an exploratory analysis by the Children's Safety Initiative-Emergency Medical Services Am J Emerg Med . 2016 Mar;34(3):599-601. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2015.12.082.
What causes epiglottis not to function properly?
Epiglottitis is a medical emergency. The throat should not be examined due to the risk of complete airway obstruction. Epiglottitis is now very uncommon due to the routine Hib immunisation given in childhood. It used to be most prevalent in paediatric patients aged 2–6 years, but now is more common
How to improve epiglottic inversion?
Oct 13, 2020 · Treatment Treatment of epiglottitis involves first making sure you or your child can breathe, and then treating any identified infection. Helping you breathe The first priority in treating epiglottitis is ensuring that you or your child is receiving enough air. This may mean: Wearing a mask. The mask delivers oxygen to the lungs.
How to diagnose epiglottitis?
Apr 05, 2014 · Obstruction in acute epiglottitis can be reduced by using dexamethasone therapy or budesonide aerosols to treat pharyngeal edema. In addition, research suggests that length of stay in the intensive...

How do you treat someone with epiglottitis?
TreatmentWearing a mask. The mask delivers oxygen to the lungs.Having a breathing tube placed into the windpipe through the nose or mouth (intubation). ... Inserting a needle into the trachea (needle cricothyroidotomy).Oct 13, 2020
What is the nursing priority for a patient with epiglottitis?
Securing an airway is the overriding priority; an expert in pediatric airway management should always perform an endotracheal intubation on any child with suspected epiglottitis before radiography or blood work is performed.Feb 11, 2021
What is epiglottis EMT?
Epiglottitis is a more severe form of upper airway inflammation characterized by the swelling of the epiglottis. It is caused by a bacterial infection from the H. influenza type B bacteria (Hib). In recent decades, epiglottitis has become very rare due to immunization efforts.Jun 3, 2017
Do you intubate epiglottitis?
Awake intubation is frequently described in the literature as the preferred method for securing the airway in adult patients with epiglottitis, whereas children with epiglottitis are usually intubated following an inhalational induction.Jan 25, 2020
Which treatment is appropriate for the child with epiglottitis and severe respiratory distress?
Call 911 if you think your child has epiglottitis. Treatment involves emergency care and the opening the child's airway with a breathing tube. Your child may also get antibiotics or other medicines. The Hib vaccine can prevent most cases of epiglottitis.
How do you treat a child with epiglottitis?
The treatment for epiglottitis requires immediate emergency care to prevent complete airway occlusion. The child's airway will be closely monitored, and, if needed, the child's breathing will be assisted with machines. Also, intravenous (IV) therapy with antibiotics will be started immediately.
How do you treat epiglottis at home?
A few home remedies can help keep you strong and soothe your irritated throat:Cool your throat by sucking on ice chips. Frozen juice bars or ice cream may also do the trick.Gargle with warm salt water to ease your dry, scratchy throat.Get a full night's sleep and nap during the day if you can.
Can epiglottis be repaired?
Yes, epiglottis can be repaired using surgery. Swallowing is vital for life.Jan 11, 2021
Does epiglottis go away on its own?
Most people with epiglottitis recover without problems. However, when epiglottitis is not diagnosed and treated early or properly, the prognosis is poor, and the condition can be fatal. Epiglottitis also can occur with other infections in adults, such as pneumonia.
What happens if the epiglottis is damaged?
If not treated quickly, it can be fatal. The epiglottis is a flap of tissue at the base of the tongue that keeps food from going into the trachea, or windpipe, during swallowing. When it gets infected or inflamed, it can obstruct (block) or close off your windpipe, which makes you unable to breathe.Jul 19, 2020
Can you intubate a child with epiglottitis?
Orotracheal intubation or needle cricothyroidotomy (also known as percutaneous transtracheal ventilation or translaryngeal ventilation) may be necessary in emergent situations. Pediatric epiglottitis is one of the few instances in which the emergency physician may need to rapidly perform needle cricothyrotomy.Aug 17, 2017
Why is racemic epinephrine contraindicated in epiglottitis?
Racemic epinephrine should be avoided because of the rebound effect. Awareness of the possibility of epiglottitis in adults and close monitoring of the airway are the keys to management of this potentially life-threatening condition.
How to treat epiglottitis in children?
Children with acute epiglottitis are in danger of full airway obstruction and respiratory arrest that comes on rapidly and may be caused by minor irritation of the throat. For this reason; gentle handling of a child suspected of having epiglottitis is essential. The following guidelines should be observed when dealing with the potentially fatal illness: 1 DO NOT try to lay the patient flat or dictate their position of comfort 2 DO NOT visualize the airway if the airway if the child is still adequately ventilating 3 Advise the receiving facility of your suspicion of epiglottitis 4 Administer 100% humidified oxygen by mask, if tolerated 5 DO NOT attempt vascular access (the added stress can be detrimental to the airway) 6 Have the proper advanced airway adjuncts ready and at hand 7 Intercostal retractions with decreasing stridor is an ominous sign of impending respiratory failure 8 Transport the child in position of comfort with parent nearby 9 Decreasing mental status means decreasing respiratory drive; TREAT AGGRESSIVELY! 10 If respiratory arrest occurs before arrival at the ED, intubation should be attempted once, rapidly 11 If respiratory arrest occurs then IV/IO access is appropriate after airway control is initiated
Why is epiglottitis dangerous?
Children with acute epiglottitis are in danger of full airway obstruction and respiratory arrest that comes on rapidly and may be caused by minor irritation of the throat. For this reason; gentle handling of a child suspected of having epiglottitis is essential.
What is the best prehospital care for croup?
Good prehospital management of croup includes airway maintenance with the administration of humidified, or nebulized oxygen and rapid transport in the position of comfort to an appropriate medical facility. Symptoms may improve dramatically in patients with croup after the child is treated with O2 therapy.
What are the signs of respiratory insufficiency?
Nasal flaring, intercostal retractions, and cyanosis are late signs of respiratory insufficiency. Children with severe croup are at risk of serious airway compromise from the narrowed diameter of the trachea.
What does it mean when you have a croup?
A patient with croup that also is experiencing wheezes and is more than likely is suffering from an infection that has spread to the lower airway. A characteristic cough and various degrees of respiratory distress can be expected with these patients.
Is croup a respiratory infection?
Croup's upper respiratory infection may be mild, moderate, or severe. It tends to be worse at night and is most commonly identified by the classic “seal-bark cough”. Many of these children have recently had the flu and/or have experienced croup previously. Nasal flaring, intercostal retractions, and cyanosis are late signs ...
Is 104 F dangerous?
A serious fever above 104F (40C) often accompanies the illness and can be dangerous if the patient isn't treated promptly.
What is the first priority of a medical team when treating epiglottitis?
If the medical team suspects epiglottitis, the first priority is to ensure that your or your child's airway is open and that enough oxygen is getting through. The team will monitor your or your child's breathing and blood oxygen level.
Why is a blood culture taken for epiglottis?
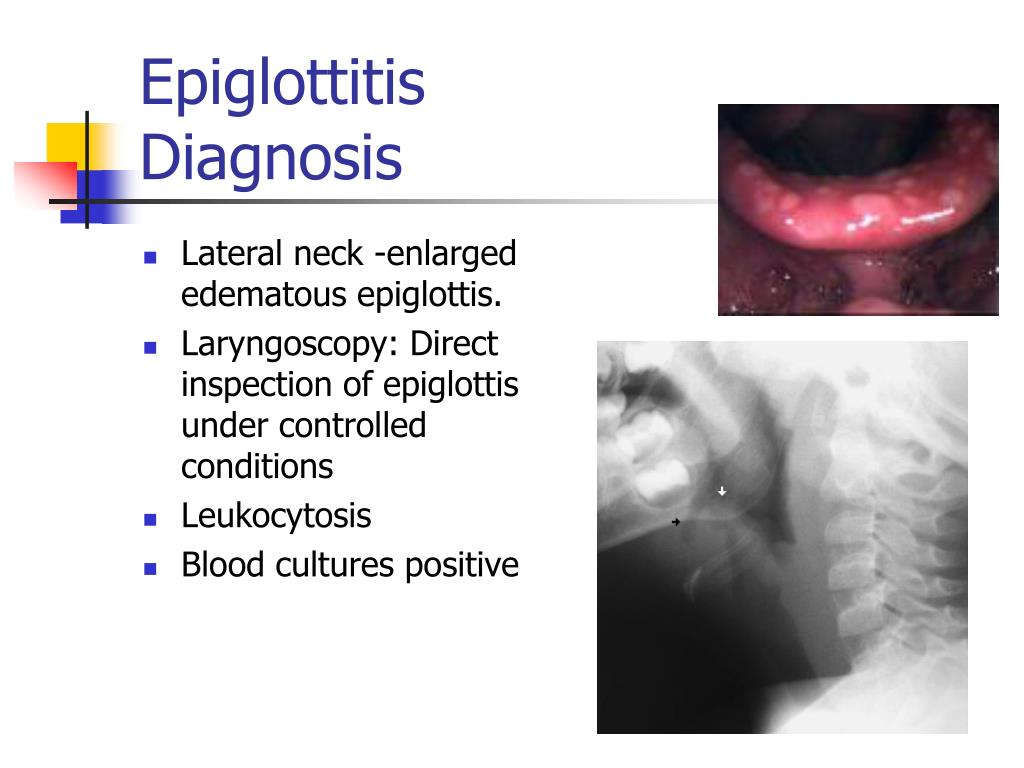
For the culture, the epiglottis is wiped with a cotton swab and the tissue sample is checked for Hib. Blood cultures are usually taken because bacteremia — a severe bloodstream infection — may accompany epiglottitis.
How does a mask work?
The mask delivers oxygen to the lungs. Having a breathing tube placed into the windpipe through the nose or mouth (intubation). The tube must remain in place until the swelling in your or your child's throat has decreased — sometimes for several days. Inserting a needle into the trachea (needle cricothyroidotomy).
Can a doctor look down your throat?
Using a flexible fiber-optic-lighted tube, the doctor may look down your or your child's throat to see what's causing the symptoms. A local anesthetic can help relieve any discomfort. Chest or neck X-ray. Because of the danger of sudden breathing problems, children may have X-rays taken at their bedsides rather than in the radiology department — ...
Can you insert a needle into a trachea?
Inserting a needle into the trachea (needle cricothyroidotomy). In extreme cases or if more-conservative measures fail , the doctor may need to create an emergency airway by inserting a needle directly into an area of cartilage in your or your child's trachea.
What is the best treatment for epiglottitis?
Optimally, initial treatment is provided by a pediatric anesthesiologist and either a pediatric surgeon or a pediatric otolaryngologist. Once the airway is controlled, a pediatric intensivist is required ...
What is the procedure to examine supraglottic structures?
When the endotracheal tube is in place, an otolaryngologist should examine the supraglottic structures using direct laryngoscopy and obtain appropriate surface cultures of the epiglottis. A secured nasotracheal tube usually replaces the orotracheal tube. Tracheostomy.
What is the mortality rate for children who do not receive endotracheal intubation?
Mortality rates for children who receive endotracheal intubation are less than 1%. Children who do not receive intubation have mortality rates as high as 10%. At a minimum, the team should include an anesthesiologist and a surgeon capable of establishing a pediatric surgical airway (ie, tracheostomy).
What is the best setting for endotracheal intubation?
The best setting for an endotracheal intubation is in an operating room with the patient under general anesthesia. Endotracheal intubation procedure details are as follows: Move the patient to the operating room and prepare the equipment needed for a tracheostomy and bronchoscopy.
How long does it take for an intravenous catheter to be removed?
The intravenous catheter may be removed when the patient can tolerate oral fluids and antibiotics. The total duration of antibiotic treatment is 7-10 days. After further observation for 24-36 hours, patients who are afebrile and doing well may be discharged. Previous.
How to manage respiratory arrest?
When a child has respiratory arrest, the first step is to administer bag-valve-mask ventilation with 100% oxygen. All of these children can be oxygenated and ventilated with good bag-valve-mask technique.
Can antibiotics be used for epiglottitis?
For epiglottitis due to other organisms, antibiotics should be tailored to the cause of the infection. Corticosteroid administration, although advocated in the past based on anecdotal reports, remains controversial. These agents have no proven efficacy for treating epiglottitis. Previous.
Can epiglottitis be controlled?
Epiglottitis is a clinical diagnosis and laboratory or other interventions should not preclude or delay timely control of the airway if epiglott itis is suspected. This includes examination of the oral cavity, starting intravenous lines, blood draws, or even separation of a child from a parent. Similar caution is required in fulminant acute epiglottitis in adults. The patient should be kept in an upright position as supine positioning can aggravate airway obstruction. [25] Lindquist B, Zachariah S, Kulkarni A. Adult Epiglottitis: a case series. Perm J. 2017;21:16-089. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5283781/ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28241903?tool=bestpractice.com
Can a tracheotomy be performed in an emergency?
Tracheotomy/cricothyroidotomy may be performed in an emergency in patients who cannot be safely intubated. Rarely, a patient will fail the initial extubation trial or the airway may not be ready for extubation after 72 hours and prolonged intubation until the patient meets criteria may be warranted. Plus – . .