Full Answer
What is urinary retention and how is it managed?
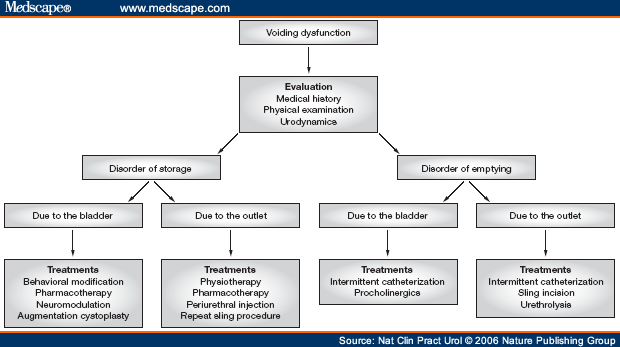
Urinary retention is a disorder that needs to be managed immediately and correctly to prevent complications. Urinary Retention is characterized by the following signs and symptoms: The following are the common goals and expected outcomes for Urinary Retention:
What is the rate of incidence for urinary retention?
There are an estimated 3 cases per 100000 women every year, and the female to male ratio is 1 to 13. Compare this with men, where about one-third over the age of 80 will have acute urinary retention.
What is the nursing assessment for urinary retention?
Nursing Assessment. There is a wide range of “normal” voiding frequency. Acute urinary retention requires immediate medical intervention. With chronic urinary retention, one is able to urinate but may have trouble starting the stream or emptying the bladder completely.
How is urinary retention diagnosed in urinary tract infection (UTI)?
Examine verbalization of discomfort, pain, fullness, and difficulty of voiding. A distended bladder could be felt by the patient in the suprapubic area. Perception of bladder fullness, bladder distention above symphysis pubis implies urinary retention. Monitor urinalysis, urine culture, and sensitivity. Urinary tract infection can cause retention.
How much urine is needed for urinary retention?
A normal bladder acts Page 2 2 Urinary Retention like a reservoir and can hold 1.5 to 2 cups of urine. How often a person needs to urinate depends on how quickly the kidneys produce the urine that fills the bladder.
How much urine can you retain?
A healthy human bladder can hold between 400 to 500 milliliters of urine, or about 2 cups, before it reaches capacity. Though a healthy bladder can stretch and accommodate larger volumes of urine, it's important to urinate at regular intervals.
What amount of residual urine is considered abnormal in CC?
In adults, 100 ml of residual urine is considered to be an abnormal level; in children, a residual urine level in excess of 10 per cent of bladder capacity is considered to be abnormal.
How much PVR is significant?
According to AHCPR guidelines, a PVR of less than 50 mL is indicative of adequate bladder emptying, while a PVR of 200 or greater indicates inadequate emptying.
How many ml can a bladder hold?
The urinary bladder can store up to 500 ml of urine in women and 700 ml in men. People already feel the need to urinate (pee) when their bladder has between 200 and 350 ml of urine in it.
Can your bladder hold 32 ounces?
A healthy adult bladder can hold up to 16 ounces, or 2 cups, of urine. This is great news if you've only had one cup of coffee, but not so much if you find yourself on cup number three with no restroom in sight. The bladder capacity for children under the age of 2 is about 4 ounces.
How much PVR is normal?
A PVR volume of less than 50 mL is considered adequate bladder emptying; in the elderly, between 50 and 100 mL is considered normal. In general, a PVR volume greater than 200 mL is considered abnormal and could be due to incomplete bladder emptying or bladder outlet obstruction.
What is urinary retention?
Urinary retention is as an inability to pass urine. It can be divided into either acute or chronic urinary retention. Acute urinary retention is defined as a new onset inability to pass urine*, which subsequently leads to pain and discomfort, with significant residual volumes.
What is high pressure urinary retention?
High Pressure Urinary Retention refers to the urinary retention causing such high intra-vesicular pressures that the anti-reflux mechanism of the bladder and ureters is overcome and ‘backs up’ into the upper renal tract leading to hydroureter and hydronephrosis, impairing the kidneys’ clearance levels.
What causes urethral sphincter to close?
Other common obstructive causes include urethral strictures or prostate cancer. Urinary tract infections can cause the urethral sphincter to close, especially in those with already narrowed outflow tracts (e.g. BPH). Constipation can also cause acute retention, through compression on the urethra.
Can chronic retention be aetiology?
Patients with chronic retention can also enter acute retention, either as an acute deterioration of the underlying pathology causing their chronic retention or a new aetiology superimposed on a background of chronic retention.
Can pain cause acute retention?
Severe pain can often cause patients to enter acute retention. Medications, such as anti-muscarinics or spinal or epidural anaesthesia, can affect innervation to the bladder, resulting in acute retention.
Can a urinary tract infection cause acute retention?
BPH). C onstipation can also cause acute retention, through compression on the urethra. Severe pain can often cause patients to enter acute retention.
What is the best way to find out what is causing urinary retention?
uses a combination of x-rays and computer technology to create images of your urinary tract. A health care professional may use urinary tract imaging tests such as an ultrasound, VCUG, MRI, or CT scan to find out what’s causing your urinary retention.
What is the best test for urinary retention?
Imaging tests . Your health care professional may use the following urinary tract imaging tests to diagnose other conditions that may be causing your urinary retention. . Voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG) uses x-rays to show how urine flows through the bladder and urethra.
What tests are used to determine if you have urinary retention?
Health care professionals use your medical history, a physical exam, and a postvoid residual urine measurement to diagnose urinary retention. Your health care professional may also order lab and other diagnostic tests to help find the cause of your urinary retention.
What lab test is used to determine if a kidney is causing urinary retention?
Your health care professional may order the following lab tests to look for signs of certain diseases and conditions that may be causing your urinary retention. Urinalysis. NIH external link. is used to find medical conditions that may be causing urinary retention, such as a urinary tract infection (UTI), a kidney problem, or diabetes.
What are the symptoms of urinary tract infection?
symptoms, also sometimes called lower urinary tract symptoms. current and past medical problems such as operations and use of a catheter. prostate problems. pregnancy and childbirth history. over-the-counter and prescription medicines. eating and drinking habits. bowel habits.
What is the purpose of video urodynamics?
Video urodynamics takes pictures and videos of your bladder as it fills and empties. Cystometry measures how much urine your bladder can hold, how much pressure builds up in your bladder as it stores urine, and how full your bladder is when you begin to feel the urge to urinate.
What are the symptoms of urinary retention?
Urinary Retention is characterized by the following signs and symptoms: 1 Abdominal discomfort 2 Bladder distention 3 Decreased (less than 30 ml/hr) or absent urinary output for 2 consecutive hours 4 Frequency 5 Hesitancy 6 Inability to empty bladder completely 7 Incontinence 8 Residual urine 9 Sensation of bladder fullness 10 Urgency
How often should you void a urinary sphincter?
Privacy aids in the relaxation of urinary sphincters. Encourage the patient to void at least every 4 hours. Voiding at frequent intervals empties the bladder and reduces risk of urinary retention. Allow the patient to listen to the sound of running water, or dip hands in warm water/pour lukewarm water over perineum.
What are the complications of untreated urinary retention?
Severe complications of untreated urinary retention include bladder damage and chronic kidney failure.
What is the purpose of urine assessment in nursing?
Nursing Assessment for Urinary Retention. Assessment is required to determine potential problems that may have lead to Urinary Retention as well as manage any difficulty that may appear during nursing care. Ascertain quantity, frequency, and character of urine, such as color, odor, and specific gravity.
Why is urine retained in the bladder?
Retention of urine in the bladder predisposes the patient to urinary tract infection and may indicate the need for an intermittent catheterization program. If an indwelling catheter is in place, assess for patency and kinking. An occluded or kinked catheter may lead to urinary retention in the bladder.
How to stimulate voiding reflex?
Sufficient urine volume is necessary to stimulate the voiding reflex. Perform Credé’s maneuver. Credé’s method (pressing down over the bladder with the hands) enhances urinary bladder pressure, and this consequently induces relaxation of sphincter to allow voiding. Decompress bladder moderately.
How does retention of urine affect the kidneys?
Take down decreased urinary output. Determine specific gravity as ordered. Retention of urine increases pressure in the kidneys and ureters which may lead to renal insufficiency. Insufficiency of blood circulation to the kidney alters its capability to filter and concentrate substances.
How common is acute urinary retention?
Acute urinary retention is common in older men, and the likelihood of experiencing acute urinary retention increases with age. Over a five-year period, approximately 1 in 10 men over the age of 70 and almost one in three men in their 80s will develop acute urinary retention. 1. Acute urinary retention is much less common in women.
Who is more likely to have urinary retention?
Who is more likely to develop urinary retention? Urinary retention affects both men and women, but it occurs more often in men, especially as they get older. Men who have benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)—a condition in which the prostate gland is enlarged—are more likely to develop urinary retention. As the prostate enlarges, it pushes ...
What happens if you have a urinary retention infection?
Serious problems can occur if the infection spreads to your kidneys. Bladder damage. If urinary retention is not treated, your bladder may become stretched too far or for long periods. When stretched too far or for too long, the muscles in your bladder may become damaged and no longer work correctly. Kidney damage.
What does it mean when you poop when your bladder is empty?
Urinary incontinence. When your bladder does not fully empty, it can lead to you leaking urine, called overflow incontinence. Working with a health care professional to prevent and treat these complications is important for both the health of your urinary tract and your overall health.
What happens when you urinate?
Urinary tract infection. When your urinary tract is emptying completely, bacteria that normally enter your urinary tract are flushed out when you urinate. With urinary retention, your urine doesn’t completely flow out, which allows the normally harmless bacteria a chance to multiply and infect your urinary tract.
Is urinary retention a disease?
Urinary retention is not a disease, but a condition that may be related to other health problems, such as prostate problems in men or a cystocele in women. Urinary retention can be acute—a sudden inability to urinate at all, or chronic—a gradual inability to empty the bladder.
Can you urinate if you have a full bladder?
People with acute urinary retention are unable to urinate even though they have a full bladder. Acute urinary retention can cause severe pain and be life threatening. If you are suddenly unable to urinate, it’s important that you seek emergency medical treatment right away.
