Ionizing radiation and cancer risk
| Procedure | Average effective dose (mSv) | Range reported in the literature (mSv) |
| Bone density test+ | 0.001 | 0.00–0.035 |
| X-ray, arm or leg | 0.001 | 0.0002–0.1 |
| X-ray, panoramic dental | 0.01 | 0.007–0.09 |
How much radiation does it take to cause cancer?
These studies show a slightly but significantly increased risk of cancer in those exposed to the blasts, including a group of 25,000 Hiroshima survivors who received less than 50 mSv of radiation — an amount you might get from two or three CT scans.
Will I be exposed to radiation during cancer treatment?
The radiation usually doesn’t travel much farther than the area being treated, so the chances that others could be exposed to radiation is small. Still, you may be asked to stay in the hospital and might have to limit visitors during treatment. You also may be asked to stay a certain distance away from them.
What are the risks of radiation exposure?
In general, the potential risks of radiation exposure include: no risk from external radiation treatments. some risk from temporary internal radiation treatments, which is why these treatments are often done in a hospital in a shielded room.
How much radiation do we get from background radiation?
How much of this so-called background radiation you are exposed to depends on many factors, including altitude and home ventilation. But the average is 3 millisieverts (mSv) per year. (A millisievert is a measure of radiation exposure; see "Measuring radiation.")
How much radiation do you get from chemotherapy?
Conclusions: Chemotherapy increases BED by approximately 10 Gy(10) in standard and modified fractionated radiotherapy, equivalent to a dose escalation of 12 Gy in 2 Gy daily or 1.2 Gy twice daily.
Is radiation as hard on you as chemo?
Since radiation therapy is focused on one area of your body, you may experience fewer side effects than with chemotherapy. However, it may still affect healthy cells in your body.
How far away should you be from a patient with radiation?
Drink extra fluids to flush the radioactive material out of your body. No kissing or sexual contact (often for at least a week). Keep a distance away from others in your household. For example, you might be told to keep one arm's length, or maybe six feet, between yourself and others for a specific length of time.
Is the entire body exposed to treatment in radiation?
Most types of radiation therapy don't reach all parts of the body, which means they're not helpful in treating cancer that has spread to many places within the body. Still, radiation therapy can be used to treat many types of cancer either alone or in combination with other treatments.
Why do oncologists push chemo?
An oncologist may recommend chemotherapy before and/or after another treatment. For example, in a patient with breast cancer, chemotherapy may be used before surgery, to try to shrink the tumor. The same patient may benefit from chemotherapy after surgery to try to destroy remaining cancer cells.
How long does radiation stay in your body after treatment?
For most people, the cancer experience doesn't end on the last day of radiation therapy. Radiation therapy usually does not have an immediate effect, and it could take days, weeks or months to see any change in the cancer. The cancer cells may keep dying for weeks or months after the end of treatment.
Who is exposed to the most radiation in a single year?
Stevens died of heart disease some 20 years later, having accumulated an effective radiation dose of 64 Sv (6400 rem) over that period, i.e. an average of 3 Sv per year or 350 μSv/h....Albert StevensNationalityAmericanOccupationHouse painterKnown forSurviving the highest known radiation dose in any human4 more rows
How much radiation is too much?
Radiation exposure is commonly measured in millisieverts (mSv). The average person in the U.S. can expect to receive no more than 3 mSv of exposure per year from naturally occurring background radiation. An exposure of greater than 20 mSv is considered high, while greater than 3 mSv to 20 mSv is considered moderate.
Can you drive yourself to and from radiation treatments?
Unless you feel ill, you can typically drive yourself to treatment. In fact, many patients are able to work full-time during their treatment.
How many rads per hour is safe?
Health effects A dose of 100 to 200 rad delivered to the entire body in less than a day may cause acute radiation syndrome (ARS), but is usually not fatal. Doses of 200 to 1,000 rad delivered in a few hours will cause serious illness, with poor prognosis at the upper end of the range.
Does chemo have radiation?
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are both treatments for cancer – the uncontrolled growth and spread of cells to surrounding tissues. Chemotherapy, or “chemo,” uses special drugs to shrink or kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy, or “radiation,” kills these cells with high-energy beams such as X-rays or protons.
How do I reduce radiation in my body?
Gently washing with water and soap removes additional radiation particles from the skin. Decontamination prevents radioactive materials from spreading more. It also lowers the risk of internal contamination from inhalation, ingestion or open wounds.
How much radiation does thyroid cancer have?
7 The total radiation exposure from treated patients of their bedroom, bathroom, and living room during 4 weeks was 0.45 mSv (range, 0.088-1.38 mSv). Another study found that radiation levels in caregivers of patients with thyroid cancer who had received high-dose radioactive iodine ranged from 0.123 mSv to 0.718 mSv, depending on the dose of treatment the patient received. 8
How much radiation should be released from a care center?
The United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission states that patients treated with radiation can be released from a care center if the total effective dose equivalent from one individual to another is not expected to exceed 5 mSv, and instructions to limit exposure should be provided if the total effective dose is likely to exceed 1 mSv. 1 Most radiation treatments pose little risk to family members or caregivers, but in cases of high-dose systemic therapy, such as radioactive iodine treatment, precautions may be required.
Is external beam radiation safe?
Any radiation therapy that is transient, including external beam radiation or brachytherapy that is removed, poses no risk to family members. 2 For these types of therapy, patients are exposed to radiation only during active treatment, and radiation is not carried on the patient’s body.
Is radiation exposure low?
Sexual Health and Cancer Treatment . Many studies have suggested, however, that familial radiation exposure is very low. In one study of patients undergoing brachytherapy for prostate cancer, Pd-103 seeds posed little risk for family exposure, and the authors concluded that no safety precautions were required.
When should radiation therapy be given?
Radiation therapy may be given before, during, or after these other treatments to improve the chances that treatment will work. The timing of when radiation therapy is given depends on the type of cancer being treated and whether the goal of radiation therapy is to treat the cancer or ease symptoms.
Why do people with cancer need radiation?
Why People with Cancer Receive Radiation Therapy. Radiation therapy is used to treat cancer and ease cancer symptoms . When used to treat cancer, radiation therapy can cure cancer, prevent it from returning, or stop or slow its growth. When treatments are used to ease symptoms, they are known as palliative treatments.
What is intraoperative radiation therapy?
During surgery, so that it goes straight to the cancer without passing through the skin. Radiation therapy used this way is called intraoperative radiation.
What is the treatment for cancer pain?
Pain from cancer that has spread to the bone can be treated with systemic radiation therapy drugs called radiopharmaceuticals.
How does radiation help cancer?
When radiation is combined with surgery, it can be given: 1 Before surgery, to shrink the size of the cancer so it can be removed by surgery and be less likely to return. 2 During surgery, so that it goes straight to the cancer without passing through the skin. Radiation therapy used this way is called intraoperative radiation. With this technique, doctors can more easily protect nearby normal tissues from radiation. 3 After surgery to kill any cancer cells that remain.
What is targeted radiotherapy?
Another type of systemic radiation therapy, called targeted radionuclide therapy, is used to treat some patients who have advanced prostate cancer or gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (GEP-NET). This type of treatment may also be referred to as molecular radiotherapy.
What is the best radiation treatment for thyroid cancer?
A systemic radiation therapy called radioactive iodine, or I-131, is most often used to treat certain types of thyroid cancer.
How much radiation is exposed to a chest xray?
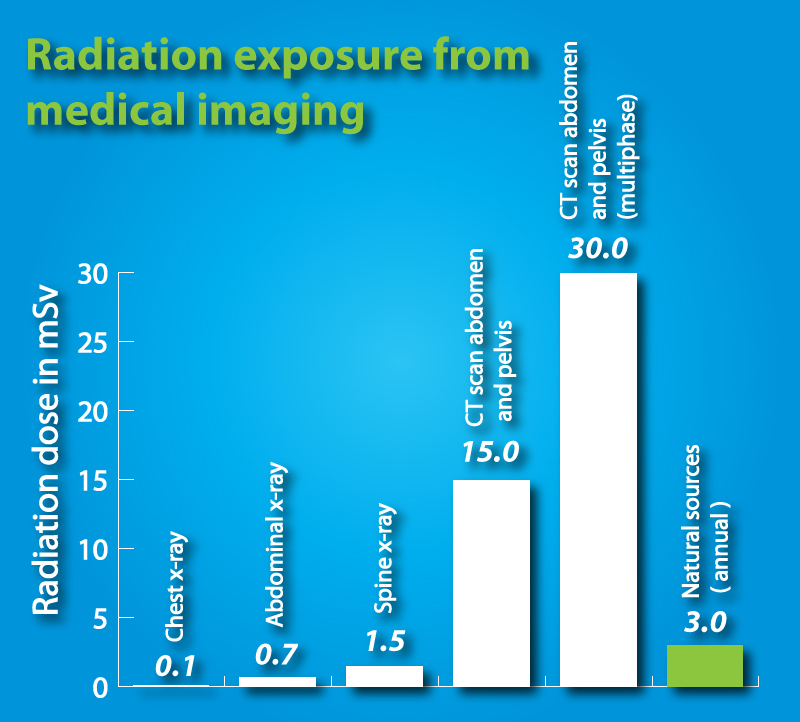
For instance: A single chest x-ray exposes the patient to about 0.1 mSv. This is about the same amount of radiation people are exposed to naturally over the course of about 10 days.
How much radiation does the average American get?
The average American is exposed to about 3 mSv ( millisieverts) of radiation from natural sources over the course of a year. (A millisievert is a measure of radiation exposure.) But background radiation exposure varies throughout the United States, and the world. The largest source of background radiation (typically about 2 mSv per year) is radon, ...
How much radiation is in a CT scan?
A CT scan of the abdomen (belly) and pelvis exposes a person to about 10 mSv. A PET/CT exposes you to about 25 mSv of radiation. This is equal to about 8 years of average background radiation exposure. Keep in mind that these are estimates for an average-sized adult.
What is background radiation?
We are constantly exposed to radiation from a number of sources, including radioactive materials in our environment, radon gas in our homes, and cosmic rays from outer space. This is called background radiation and it varies across the country.
Why do we need to keep a medical imaging record?
You may also want to keep a medical imaging record to track your own history of imaging tests and share it with your health care providers. This may help prevent repeat tests from being ordered. English and Spanish examples of imaging records for adults can be found online at www.imagewisely.org.
What is the best way to look for cancer?
But if there’s a reason to believe that an x-ray, CT scan, or nuclear medicine scan (such as a PET scan) is the best way to look for cancer or other diseases, the person will most likely be helped more than the small dose of radiation can hurt.
What to do if you have concerns about radiation?
If you have concerns about the radiation you may get from a CT scan, PET scan, or any other imaging test that uses radiation, talk to your health care provider. Ask whether the test is needed and if it’s the best one to use in your case. You may also want to know what you and your health care provider can expect to learn from it.
How early can a fetus be exposed to radiation?
Fetuses are particularly sensitive to radiation during their early development, between weeks 2 and 18 of pregnancy. The health effects to the fetus can be severe, ...
Why is a developing fetus highly susceptible to radiation exposure?
A developing fetus is highly susceptible to health effects from radiation exposure because of the rapid rate of cell division. Prenatal radiation exposure occurs when the mother’s abdomen is exposed to radiation from outside her body.
What are the effects of radiation on a fetus?
Fetuses are particularly sensitive to radiation during their early development, between weeks 2 and 18 of pregnancy.#N#The health effects to the fetus can be severe, even at radiation doses too low to make the mother sick.#N#These can include stunted growth, deformities, abnormal brain function, or cancer that may develop sometime later in life. 1 The health effects to the fetus can be severe, even at radiation doses too low to make the mother sick. 2 These can include stunted growth, deformities, abnormal brain function, or cancer that may develop sometime later in life.
Where does radioactive material pass through the umbilical cord?
From the mother’s blood, radioactive materials may pass through the umbilical cord to the fetus or concentrate in areas of the mother’s body near the womb (such as the urinary bladder) and expose the fetus to radiation.
When are fetuses less sensitive to radiation?
Fetuses are less sensitive to radiation during later stages of pregnancy (after 18 weeks). Since the fetus is shielded by the mother’s abdomen, it is partially protected in the womb from radioactive sources outside the mother’s body.
Can radiation make a woman sick?
The health effects to the fetus can be severe, even at radiation doses too low to make the mother sick. These can include stunted growth, deformities, abnormal brain function, or cancer that may develop sometime later in life. Women have an increased risk of fetal miscarriage.
Can radiation cause cancer?
Cancer. People who receive high doses of radiation could have a greater risk of developing cancer later in life, depending on the radiation exposure. Health officials will monitor people affected by radiation emergencies for long-term health effects, including cancer.
How to avoid radiation therapy?
Avoid contact with pets for a specific amount of time. Avoid public transportation for a specific amount of time. Plan to stay home from work, school, and other activities for a specific amount of time. Again, the information here describes some safety concerns of different types of radiation therapy.
How long after radiation treatment should you follow safety precautions?
In most cases for systemic radiation treatment, the safety precautions must be followed only the first few days after treatment.
How does radiation therapy work?
Internal radiation therapy uses a sealed source of radiation that is implanted (put inside your body) where the cancer is located. Depending on the type of implant used, your body may give off a small amount of radiation for a short time.
Why is it important to keep radiation exposure to the people around you?
If you're getting systemic radiation treatment , sometimes safety measures are needed to protect the people around you. This is because the radioactive materials can leave your body through saliva, sweat, blood, and urine and that makes these fluids radioactive. It's very important to keep radiation exposure to the people around you as limited as possible.
Why is it important to know that not all radiation treatments work the same way or have the same safety precautions?
This is because they must meet certain regulations that help to limit their exposure to radiation when caring for patients who need treatment and imaging tests. It's important to know that not all radiation treatments work the same way or have the same safety precautions.
What is external beam radiation?
External radiation therapy is given from an outside source, involves a beam of radiation aimed at a part of the body, and affects cells in your body only for a moment. Because there’s no radiation source inside your body, you are not radioactive at any time during or after treatment.
How long after radiation treatment should you wash your clothes?
In most cases for systemic radiation treatment, the safety precautions must be followed only the first few days after treatment. Here are examples of things you might be told to do if you're getting systemic radiation treatment: Wash your laundry separately from the rest of the household, including towels and sheets.
How often should you check for radiation?
During your treatment, your radiation oncologist will check how well it is working. Typically, this will happen at least once a week. If needed, they may adjust your treatment plan.
What to expect when getting radiation therapy?
What to Expect When Having Radiation Therapy. It is normal to feel worried or overwhelmed when you learn that you will need radiation therapy. However, learning more about this type of cancer treatment may help you feel more prepared and comfortable.
What is the role of a dosimetrist in radiation?
Dosimetrist. The dosimetrist helps your radiation oncologist calculate the right dose of radiation.
What type of doctor is responsible for radiation therapy?
Radiation oncologist. This type of doctor specializes in giving radiation therapy to treat cancer. A radiation oncologist oversees radiation therapy treatments. They work closely with other team members to develop the treatment plan. Radiation oncology nurse.
What is simulation in radiation therapy?
Simulating and planning treatment. Your first radiation therapy session is a simulation. This means it is a practice run without giving radiation therapy. Your team will use imaging scans to identify the tumor location.
What is radiation oncology nurse?
Radiation oncology nurse. This nurse specializes in caring for people receiving radiation therapy. A radiation oncology nurse plays many roles, including:
How long does radiation therapy last?
It is the most common radiation therapy treatment for cancer. Each session is quick, lasting about 15 minutes. Radiation does not hurt, sting, or burn when it enters the body.
How much radiation does a chest CT scan give?
Most of the increased exposure in the United States is due to CT scanning and nuclear imaging, which require larger radiation doses than traditional x-rays. A chest x-ray, for example, delivers 0.1 mSv, while a chest CT delivers 7 mSv (see the table) — 70 times as much.
What is the radiation that is used to detect cancer?
The radiation you get from x-ray, CT, and nuclear imaging is ionizing radiation — high-energy wavelengths or particles that penetrate tissue to reveal the body's internal organs and structures. Ionizing radiation can damage DNA, and although your cells repair most of the damage, they sometimes do the job imperfectly, leaving small areas of "misrepair." The result is DNA mutations that may contribute to cancer years down the road.
Why is X-rays not accurate?
It won't be completely accurate because different machines deliver different amounts of radiation, and because the dose you absorb depends on your size, your weight, and the part of the body targeted by the x-ray. But you and your clinician will get a ballpark estimate of your exposure.
How accurate is X-ray?
Keep track of your x-ray history. It won't be completely accurate because different machines deliver different amounts of radiation, and because the dose you absorb depends on your size, your weight, and the part of the body targeted by the x-ray. But you and your clinician will get a ballpark estimate of your exposure.
Where does ionizing radiation come from?
We're exposed to small doses of ionizing radiation from natural sources all the time — in particular, cosmic radiation, mainly from the sun, and radon, a radioactive gas that comes from the natural breakdown of uranium in soil, rock, water, and building materials.
Can you increase time between CT scans?
If you're getting regular CT scans for a chronic condition, ask your clinician if it's possible to increase the time between scans. And if you feel the CT scans aren't helping, discuss whether you might take a different approach, such as lower-dose imaging or observation without imaging. Don't seek out scans.
Is the atomic bomb harmful?
Still, most experts believe that can be almost as harmful as getting an equivalent dose all at once.
How long does radiation last?
“Small doses of radiation may be administered daily over a period ranging from several days to several weeks.
What happens if you leave a radiation source in place?
If the radiation source is left in place, the amount of radiation lessens over time. However, the possibility of exposure to others is present.
What are the two most common cancer treatments?
The two most common types of cancer treatment that patients and their family members worry about are chemotherapy and radiation therapy . Here Snyder explains what you and your loved ones need to know about each.
What is internal radiation?
Internal radiation means that the radiation source is put into the body, Snyder says. Some examples of internal radiation are brachytherapy, in which doctors implant a seed, ribbon or wire that contains radiation in or around a tumor, the implant emits a dose of radiation to the surrounding area that kills cancer cells.
How long does chemo stay in your system?
For the most part, after a patient receives chemotherapy, the medications stay in the patient’s body for about 24 hours to 48 hours. The body clears itself of the medications through body fluids such as urine or stool, so this means avoiding contact with these body fluids.
Why do some treatments need a little extra caution?
Why some treatments need a little extra caution. If you’re undergoing treatment for cancer, you know that the medicines and procedures have side effects. You may worry that these lifesaving treatments could somehow be harmful to your loved ones. It’s a concern that many cancer patients and their family members often have, ...
Does radiation continue after therapy?
The treated tissue does not continue to hold the radiation after the therapy session ends. So patients receiving external beam radiation need not worry about transmitting radiation to their loved ones.”. Internal radiation means that the radiation source is put into the body, Snyder says.
How to limit exposure to radiation?
How to Limit Your Exposure to Medical Radiation. First, assess risk vs reward. You can often make this assessment through a conversation with your doctor. For example, when it comes to cancer treatment, the destruction or reduction in the size of a tumor will likely be worth the risk of the radiation load.
Why is too much radiation harmful?
In some cases, "too much" is a result of errors. Those high doses being used for radiation oncology purposes can be harmful if the beam isn't accurately targeted. Patients may overdose when radiation testing equipment has not been correctly calibrated, or when a human being makes a mistake inputting dosage settings. 6 .
What is radiation used for?
All three use radiation to help diagnose medical problems. You may know them by other names, too. Mammograms use radiation to diagnose breast cancer. DXA (DEXA) scans use X-rays to diagnose osteoporosis. 3. In addition to diagnostics, radiation is a tool for medical treatment, too.
What is radiation oncology?
Radiation oncology is the term used to describe this form of treatment. 4. For cancer treatments, a very specific, targeted beam of radiation is pointed at cancerous problem spots, and radiation energy is then used to kill the bad cells and destroy those tumors.
How is radiation transmitted?
1 Very low levels of radiation are transmitted through everyday man-made objects like TVs and radios, cell phones, automatic garage door openers, microwave ovens — anything that relies on certain types of radio waves to work. 2 Much larger and more dangerous amounts of radiation are generated by objects such as nuclear power plants or medical equipment used for imaging and treatment.
Why are CT scans not targeted?
Because it can be so well-targeted, the healthy cells in surrounding areas will be spared. The various radiation-based medical tests like CT scans are not as targeted. They produce images that are broader, covering both healthy and cancer-damaged tissues and organs.
Is radiation too much?
When it comes to medical applications, there don't seem to be specific guidelines that tell us how much radiation is too much. Further, a definition of "too much" could vary from patient to patient.
