
What percentage of health care costs are related to obesity?
In addition to its serious health consequences, obesity has real economic costs that affect all of us. The estimated annual health care costs of obesity-related illness are a staggering $190.2 billion or nearly 21% of annual medical spending in the United States.
How does obesity affect medical care?
The increased prevalence of obesity has been associated with increases in cardiovascular disease, cancer, type 2 diabetes, degenerative joint disease requiring joint replacement, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, sleep apnea, cognitive dysfunction and others.
How much more do obese people spend on healthcare?
RESULTS: Adults with obesity in the United States compared with those with normal weight experienced higher annual medical care costs by $2,505 or 100%, with costs increasing significantly with class of obesity, from 68.4% for class 1 to 233.6% for class 3.
Does obesity overwhelm the healthcare system?
A 2009 study found that childhood obesity alone is responsible for $14.1 billion in direct medical costs annually. By some estimates, nearly 21 percent of all current medical spending in the United States is now obesity related.
How does obesity strain the healthcare system?
Obesity can lead to Type 2 diabetes, chronic heart disease, hypertension, and many other syndromes and diseases that are covered by Medicaid and Medicare. As obesity has increased, so has the incidence of these diseases, thereby increasing the cost of healthcare.
Why should obese people pay more for healthcare?
According to the literature, the obese contract chronic diseases at a higher rate than the non-obese, and consequently pay more for medical care. The lifetime medical costs related to diabetes, heart disease, high cholesterol, hypertension, and stroke among the obese are $10,000 higher than among the non-obese.
What is a direct cost of obesity?
According to a report by the Milken Institute, in 2016, obesity/overweight and its associated chronic diseases were estimated to account for more than $480 billion in direct healthcare costs and $1.24 trillion in indirect work loss costs in the US.
How much does obesity cost the US annually?
Obesity costs the US health care system $147 billion a year.
How much does obesity cost the world?
Obesity also has staggering financial and social impacts, as well as an impact on future generations. It has been estimated that the total cost of high BMI to health services globally is US$990 billion per year [9,10], with the highest costs in the Eastern Mediterranean and America regions [see table 5].
How will obesity affect clinical practice?
Accurate data and monitoring around the prevalence of obesity among children and adults are vital. Obesity is a major risk factor for chronic and preventable conditions such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, hypertension, stroke, musculoskeletal disorders and impaired psychosocial functioning.
How much does obesity cost the US 2020?
Estimates of the medical cost of adult obesity in the United States (U.S.) range from $147 billion to nearly $210 billion per year. The majority of the spending is generated from treating obesity-related diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease, among others.
How does childhood obesity influence a person's health and a country's health care system?
Overweight and obesity in childhood are known to have significant impact on both physical and psychological health. Overweight and obese children are likely to stay obese into adulthood and more likely to develop non-communicable diseases like diabetes and cardiovascular diseases at a younger age.
Can a doctor prescribe medicine for obesity?
When healthy eating and physical activity habits are not enough, your doctor may prescribe medicines to treat overweight and obesity. You should try to stick with your healthy eating plan and continue getting regular physical activity while taking weight-loss medicines. that claim to help you lose weight.
How to treat obesity?
Treatment for Overweight & Obesity 1 help lower your chances of developing health problems related to overweight and obesity 2 improve health problems related to overweight and obesity, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels
Can obesity cause you to lose weight?
Some people who have obesity are unable to lose enough weight to improve their health or are unable to keep from regaining weight. In such cases, a doctor may consider adding other treatments, including weight-loss medicines, weight-loss devices, or bariatric surgery.
How to treat obesity and overweight?
Healthy eating plan and regular physical activity. Following a healthy eating plan with fewer calories is often the first step in trying to treat overweight and obesity. People who are overweight or have obesity should also start regular physical activity when they begin their healthy eating plan.
Is bariatric surgery good for obesity?
Bariatric surgery also may be an option at lower levels of obesity if you have serious health problems, such as type 2 diabetes or sleep apnea, related to obesity. Bariatric surgery can improve many of the medical conditions linked to obesity, especially type 2 diabetes.
How does bariatric surgery help you lose weight?
Bariatric surgery includes several types of operations that help you lose weight by making changes to your digestive system. Bariatric surgery may be an option if you have extreme obesity and haven’t been able to lose enough weight to improve your health or keep from gaining back the weight you lost with other treatments. Bariatric surgery also may be an option at lower levels of obesity if you have serious health problems, such as type 2 diabetes or sleep apnea, related to obesity. Bariatric surgery can improve many of the medical conditions linked to obesity, especially type 2 diabetes.
How does intermittent fasting help you lose weight?
Intermittent fasting is another way of reducing food intake that is gaining attention as a strategy for weight loss and health benefits. Alternate-day fasting is one type of intermittent fasting that consists of a “fast day” (eating no calories to one-fourth of caloric needs) alternating with a “fed day,” or a day of unrestricted eating. Researchers have conducted only a few studies of intermittent fasting as a strategy for weight loss. They have no long-term data on the safety and effectiveness of intermittent fasting for long-term weight maintenance.
What are some tips for healthy eating?
Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fat-free or low-fat milk and dairy products.
How much physical activity does an adult need?
Getting enough physical activity is an important way to help prevent or reduce the risk of overweight and obesity and related health problems.
Citations
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2012). How are overweight and obesity treated? Retrieved August 8, 2012, from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/overweight-and-obesity
What are the effects of obesity?
Obesity has a variety of impacts on the body. The increased pressure from the accumulation of fatty tissue causes pressure on internal organs leading to conditions such as: 2 1 High blood pressure 2 Type 2 diabetes 3 Esophagitis 4 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 5 Sleep Apnea 6 Varicose veins 7 Stress incontinence 8 Lymphedema 9 Hernias 10 Venous insufficiency and poor circulation leaves patient more susceptible to infection, skin breakdown and dehiscence of surgical wounds
How does obesity affect the health system?
#3: Financial impact on health system 1 Increased spend on pharmaceuticals: Obesity affects the pharmacokinetics of the body, which can lead to the patient requiring more frequent administration or higher doses of medication, 4 as well as more frequent care and vital sign monitoring by the nurse. This has the potential to increase the cost of pharmaceuticals that hospitals are currently spending. 2 Non-reimbursable treatment: Due to the additional pressure the accumulation of fatty tissue creates, the obese patient is more at risk for infection and dehiscence of surgical wounds. 5 In some cases, Centers for Medicare Services (CMS) standards call for hospitals and other healthcare systems not to be reimbursed for care related to conditions such as surgical site infections. 6 Obesity also creates impaired mobility to the patient, leading to an increased risk for falling. CMS will not reimburse a hospital for patient fall complications and skin breakdown that is acquired while the patient is hospitalized. 3 Cost of equipment: Hospitals may have to consider ordering new bariatric equipment including hospital beds, wheelchairs, bedside commodes, and walkers to accommodate obese patients. At a national convenience store, the standard size bedside commode costs under $80. The bariatric version of the same commode costs over $170. According to The American Institute of Architects (2016), 7 hospitals that are seeing increased numbers of obese patients are turning to design experts to help create new doorways and hallways to accommodate the growing physical size of their patients.
How does obesity affect the body?
Obesity has a variety of impacts on the body. The increased pressure from the accumulation of fatty tissue causes pressure on internal organs leading to conditions such as: 2. Venous insufficiency and poor circulation leaves patient more susceptible to infection, skin breakdown and dehiscence of surgical wounds.
How much does the US spend on obesity?
Over the next 30 years, this is expected to reach an annual outlay of almost $655 per person – 14% of the country’s total annual healthcare expenditure.
Is obesity a burden?
Rising obesity levels place a heavy burden on healthcare provisions, leaving some countries facing an increasingly hefty bill, according to a new report from the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development.
What are the health effects of obesity?
The Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity 1 All-causes of death (mortality) 2 High blood pressure (Hypertension) 3 High LDL cholesterol, low HDL cholesterol, or high levels of triglycerides (Dyslipidemia) 4 Type 2 diabetes 5 Coronary heart disease 6 Stroke 7 Gallbladder disease 8 Osteoarthritis (a breakdown of cartilage and bone within a joint) 9 Sleep apnea and breathing problems 10 Many types of cancer#N#external icon 11 Low quality of life 12 Mental illness such as clinical depression, anxiety, and other mental disorders 4,5 13 Body pain and difficulty with physical functioning 6
Does losing weight help with diabetes?
If you are overweight, losing some weight could help you better manage your diabetes. Obesity trends, economic consequences, state-based programs and other resources for the health professional. *Overweight is defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 25 or higher; obesity is defined as a BMI of 30 or higher.
Is obesity higher in women than men?
Obesity was higher in women (about 40 percent) than men (35 percent) Extreme obesity was higher in women (9.9 percent) than men (5.5 percent) Almost 3 in 4 men (73.7 percent) were considered to be overweight or have obesity; and about 2 in 3 women (66.9) were considered to be overweight or have obesity.
What percentage of children are obese?
Less than 2 percent of young children were considered to have extreme obesity. Among children and youth ages 6 to 11, about 1 in 6 (17.4 percent) were considered to have obesity, and about 1 in 23 (4.3 percent) were considered to have extreme obesity.
What is the BMI?
BMI is the tool most commonly used to estimate and screen for overweight and obesity in adults and children. BMI is defined as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared. For most people, BMI is related to the amount of fat in their bodies, which can raise the risk of many health problems.
Is BMI related to weight?
For most people, BMI is related to the amount of fat in their bodies, which can raise the risk of many health problems . A health care professional can determine if a person’s health may be at risk because of his or her weight. The tables below show BMI ranges for overweight and obesity.
What are the factors that contribute to weight gain?
Factors that may contribute to weight gain among adults and youth include genes, eating habits, physical inactivity, TV, computer, phone, and other screen time, sleep habits, medical conditions or medications, and where and how people live, including their access to healthy foods and safe places to be active. 1,6
What is the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases?
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) and other components of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) conduct and support research into many diseases and conditions.
What is the NCHS?
The data presented on prevalence are from the 2013–2014 NHANES survey of the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) unless noted otherwise. NCHS is part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 2,3,4,5
What are the health problems associated with obesity?
Obesity is a term that means you have a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher. It makes you more likely to have conditions including: 1 Heart disease and stroke 2 High blood pressure 3 Diabetes 4 Some cancers 5 Gallbladder disease and gallstones 6 Osteoarthritis 7 Gout 8 Breathing problems, such as sleep apnea (when a person stops breathing for short episodes during sleep) and asthma
Is obesity linked to cancer?
Cancer. Cancers of the colon, breast (after menopause ), endometrium (the lining of the uterus), kidney, and esophagus are linked to obesity. Some studies have also reported links between obesity and cancers of the gallbladder, ovaries, and pancreas.
Does losing weight help with heart disease?
Extra weight makes you more likely to have high blood pressure and high cholesterol. Both of those conditions make heart disease or stroke more likely. The good news is that losing a small amount of weight can reduce your chances of developing heart disease or a stroke . Losing even more weight has been shown to lower the risk even more.
Does weight loss cause heart disease?
The good news is that losing a small amount of weight can reduce your chances of developing heart disease or a stroke .
What is the disease that affects the joints?
Gout . Gout is a disease that affects the joints. It happens when you have too much uric acid in your blood. The extra uric acid can form crystals that deposit in the joints. Gout is more common in overweight people. The more you weigh, the more likely you are to get gout.
How to reduce risk of diabetes?
You can cut your risk of developing type 2 diabetes by losing weight, eating a balanced diet, getting adequate sleep, and exercising more. If you have type 2 diabetes, losing weight and becoming more physically active can help control your blood sugar levels.
Can weight loss cause gallstones?
Ironically, weight loss itself, particularly rapid weight loss or loss of a large amount of weight, can make you more likely to get gallstones. Losing weight at a rate of about 1 pound a week is less likely to cause gallstones. Osteoarthritis is a common joint condition that most often affects the knee, hip, or back.
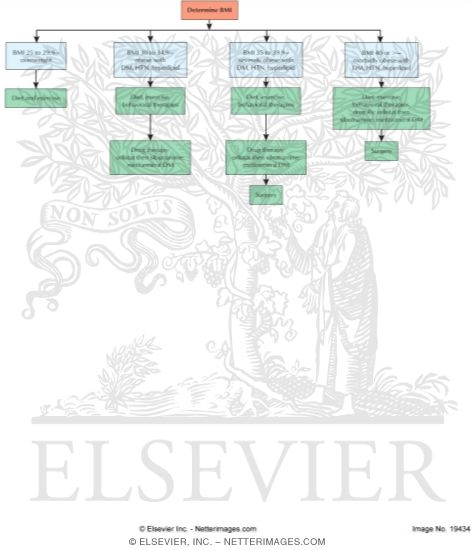
Healthy Eating Plan and Regular Physical Activity
Changing Your Habits
Weight-Management Programs
Weight-Loss Medicines
Weight-Loss Devices
Bariatric Surgery
Special Diets
- Calorie-restricted diets
Your doctor may recommend a lower-calorie diet such as 1,200 to 1,500 calories a day for women and 1,500 to 1,800 calories a day for men. The calorie level depends on your body weight and physical activity level. A lower calorie diet with a variety of healthy foods will give you the nutrien… - Intermittent fasting
Intermittent fasting is another way of reducing food intake that is gaining attention as a strategy for weight loss and health benefits. Alternate-day fasting is one type of intermittent fasting that consists of a “fast day” (eating no calories to one-fourth of caloric needs) alternating with a “fed …