How long does it take to cure gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea Treatment. If you have this STD, the CDC now recommends a single 500-mg IM dose (1000 mg in patients weighing ≥150 kg) of the third …
Is gonorrhea 100 percent curable?
Because treatment cannot be administered without a medical diagnosis, you must first be tested for gonorrhea. A typical doctor’s visit and test without insurance can range anywhere from $100 to $1,000 and will not include the cost of treatment which can range from $100 - $500.
How to cure gonorrhea without going to the Doctor?
For those without insurance or those who do not wish to file, we have simple Gonorrhea, Chlamydia, Trichomonas (Urine Only) Testing & Treatment – $145 (32) … 24. Free and Confidential STD Testing in Tarrant County How much does STD testing cost? Tarrant County Adult Health Services offers syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia and HIV testing for free.
What is the best medication for gonorrhea?
Cost of STI and STD Testing Without Insurance ; Fastmed, $149 to $299, Options for Rapid HIV, Syphilis, Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Trichomoniasis. (2) … But if you don’t have insurance or want to see someone else for treatment, there are other low-cost or free options. You can get tested and treated at your (3) … Reilly Insurance

How much is gonorrhea treatments?
...
Cost of Alternative Gonorrhea Treatments Without Insurance.
Can I buy gonorrhea treatment?
If you have tested positive for gonorrhoea, and are unable to have the first-line injection, you may be able to order gonorrhoea treatment online.
How much is treatment for chlamydia and gonorrhea?
Is gonorrhea cured in 7 days?
Does gonorrhea injection hurt?
Can I buy gonorrhea treatment over the counter?
How long does it take to cure gonorrhea after the shot?
Are STD treatments expensive?
How expensive is it to treat chlamydia?
Does gonorrhea have a smell?
Which is worse chlamydia or gonorrhea?
How long can you have gonorrhea without knowing?
What is the best treatment for gonorrhea?
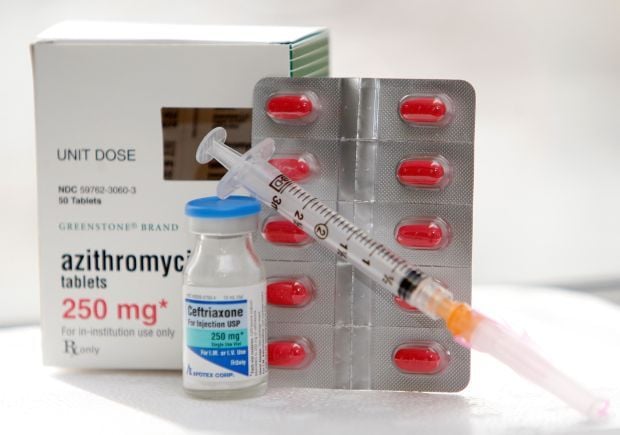
Adults with gonorrhea are treated with antibiotics. Due to emerging strains of drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that uncomplicated gonorrhea be treated with the antibiotic ceftriaxone — given as an injection — with oral azithromycin (Zithromax).
Can gonorrhea be tested for chlamydia?
Testing for other sexually transmitted infections. Your doctor may recommend tests for other sexually transmitted infections. Gonorrhea increases your risk of these infections, particularly chlamydia, which often accompanies gonorrhea.
How much does a gonorrhea test cost?
Because treatment cannot be administered without a medical diagnosis, you must first be tested for gonorrhea. A typical doctor’s visit and test without insurance can range anywhere from $100 to $1,000 and will not include the cost of treatment which can range from $100 - $500. STDAware offers a gonorrhea test for less than $100.
How to treat gonorrhea?
In order to treat a gonorrhea infection, it must first be medically diagnosed through an STD test. To find out more about the gonorrhea test offered by STDAware, click here. STD testing should be requested anytime there is a change in sexual partner or habits before initiating sexual contact.
How many gonorrhea infections are resistant to treatment?
The CDC believes that with rapid detection and treatment less than 2% of gonorrhea infections will be able to develop a resistance to the current treatment protocol. 1
How long does it take for gonorrhea to go away?
Once treatment is started, symptoms should start to abate within 2 – 10 days. When treating gonorrhea or any other STD, it is critical to abstain from any sexual activity (oral, manual, vaginal or anal) until treatment is complete and the doctor confirms it is okay to resume sexual activity.
What is STDAware testing?
STDAware is the ONLY online STD testing service provider that offers no-cost medical consultation and treatment solutions for anyone who tests positive for having gonorrhea, chlamydia, or HSV-2. STOP WORRYING. GET TESTED.
Can penicillin cause gonorrhea?
If someone has a penicillin allergy, there is potential to have an adverse reaction to the antibiotic treatment for gonorrhea. Depending on personal health history, a physician will be able to prescribe an effective alternative for treating anyone with a penicillin allergy or who has a history of gonorrhea infection (s).
Is gonorrhea a drug resistance?
While the dual therapy regime, above, has been successful at treating and curing gonorrhea for several decades past, new antibiotic-resistant strains of gonorrhea are emerging. Drug resistance strains have evolved due to the increase in gonorrhea infections, as a whole, in addition to improper and late treatment, as well as the need for repeated treatment due to high rates of reinfection.
How long does it take for gonorrhea to be retested?
Because reinfection within 12 months ranges from 7% to 12% among persons previously treated for gonorrhea ( 29, 30 ), persons who have been treated for gonorrhea should be retested 3 months after treatment regardless of whether they believe their sex partners were treated.
What is the best treatment for chlamydia?
Combination therapy, using a highly effective gonococcal therapeutic agent with cotreatment for chlamydia, has been recommended since 1985. In 2007, based on data from CDC’s Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project* (GISP) indicating widely disseminated quinolone-resistant gonococcal strains in the United States, CDC no longer recommended fluoroquinolones for treatment, leaving cephalosporins as the only remaining recommended antimicrobial class ( 6 ). Availability of sensitive C. trachomatis nucleic acid amplification tests were widespread by 2010, but CDC recommended gonococcal dual therapy with a cephalosporin (ceftriaxone 250 mg IM or cefixime 400 mg orally) and either azithromycin or doxycycline ( 4) to reflect concerns regarding emerging gonococcal resistance. By 2011, the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of cefixime necessary to inhibit N. gonorrhoeae growth in vitro were increasing. In 2012, cefixime was no longer a recommended gonococcal regimen ( 7 ), with ceftriaxone and azithromycin combination therapy the only recommended regimen for uncomplicated gonorrhea ( 5 ). Since publication of the 2015 Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) Treatment Guidelines, concerns regarding antimicrobial stewardship have increased, especially the impact of antimicrobial use on the microbiome and data indicating azithromycin resistance (elevated MICs) for gonorrhea and other organisms ( 1,3 ). Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling has also affected the understanding of optimal antimicrobial dosing for N. gonorrhoeae treatment. This update provides the rationale for the change in gonorrhea treatment recommendations to a higher dose (500 mg) of ceftriaxone and removal of azithromycin from the recommended regimen.
Is there a treatment for pharyngeal gonorrhea?
No reliable alternative treatments are available for pharyngeal gonorrhea. For persons with a history of a beta-lactam allergy, a thorough assessment of the reaction is recommended.*
Does ceftriaxone help with gonorrhea?
Emerging antimicrobial resistance affects gonorrhea treatment recommendations and other STIs. CDC recommends ceftriaxone monotherapy for treatment because N. gonorrhoeae remains highly susceptible to ceftriaxone, azithromycin resistance is increasing, and prudent use of antimicrobial agents supports limiting their use.
What is the best treatment for gonorrhea?
The most common treatment is a single antibiotic injection of ceftriaxone and a single dose of oral azithromycin, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ( CDC) treatment guidelines.
How to treat gonorrhea quickly?
Speak to your doctor, who will prescribe the most appropriate treatment of antibiotics. Gonorrhea should clear up quickly with effective antibiotic treatment.
What antibiotics are used for gonorrhea?
Another class of antibiotics commonly used to treat gonorrhea are macrolide antibiotics, specifically azithromycin (brand name Zithromax). Macrolides work by stopping the growth of bacteria. Taken as a tablet along with a ceftriaxone injection, a single dose is often all that is required to treat gonorrhea. If you vomit within an hour of taking your azithromycin tablet, contact your doctor immediately to determine if you require another dose. Like all drugs, there is the risk of side effects. Some side effects include, but are not limited to, nausea, headache, and diarrhea. More severe side effects can include rash, swelling, or vomiting. If you experience any of these or other side effects after taking this medication, seek out medical help immediately.
What are the two most common medications used for gonorrhea?
Two drug classes that are most popularly prescribed to cure and treat gonorrhea are cephalosporin and macrolide antibiotics.
How long does it take for gonorrhea to show up in urine?
A urine test to check for any bacteria (specifically gonorrhea) Test results are usually available in 24 hours to three days.
Can you take antibiotics for gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea can be cured with antibiotics prescribed by your doctor. Your healthcare provider will be able to advise on the best course of medication based on your medical history and condition.
Can gonorrhea go away on its own?
It is unclear if gonorrhea can go away on its own. If left untreated, it can cause painful complications and severe, permanent damage to reproductive organs. It can, however, be cured with antibiotics.
How much does gonorrhea cost?
In this article we present updated estimates of the direct medical cost per case of care for acute gonorrhea, which has previously been estimated at $93 to $168 per case (adjusted for inflation to 2007 dollars). 8 Updates of cost estimates are needed periodically owing to changes in diagnostic tests, treatment recommendations, and delivery services. The cost of acute care is an important component of the estimated lifetime cost per case of gonorrhea, which also includes sequelae costs. These cost estimates are vital in studies of the burden of disease as well as in cost-effectiveness and cost-benefit analyses of STD prevention programs and interventions.
What is the ICD-9 code for gonorrhea?
We used International Classification of Diseases 9th revision codes (ICD-9) to identify claims for gonorrhea diagnoses (codes 098.0–098.89) in the database. The codes were used to extract claims for all outpatient visits for which gonorrhea diagnoses were identified as the primary or secondary diagnosis, or both. We assumed that visits that occurred ≤30 days after the initial visit were part of the same episode of infection (our results did not vary substantially when we used a 45- or 60-day follow-up period to define an episode).
What are the names of the drugs used to treat gonococcal infections?
We identified all of the recommended drugs 11 used to treat gonococcal infections in the database; these were listed by generic and brand names: cefixime, cefotaxime, ceftozoxime, ceftriaxone, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, ofloxacin, and spectinomycin. We then used their corresponding National Drug Codes to identify drugs claims for gonorrhea in the MarketScan Database. We linked claims for outpatient visits with gonorrhea diagnoses to prescription drug claims with the assumption that prescription drugs received 7 days before through 30 days after the initial outpatient visit were associated with a given episode of an infection.
What is outpatient cost?
Outpatient costs included the costs of diagnosis, testing procedure, and office visits paid by both enrollee and insurance plan. Because we focused on actual payments, we assessed the actual cost of care to the payors. The resulting estimates may therefore be more reflective of the true economic “cost” than a “charge.”
What is the name of the organization that monitors sexually transmitted diseases?
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance, 2007. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, 2008.
Cost of STD Treatment
To get treated for an STD, you first need to get tested to determine the proper course of treatment. The cost of STD testing and treatment depends on the type of health insurance you have. If you have health insurance, you normally pay the copay charged by your provider.
STD Screening
The first step to getting treatment for STDs is to get tested. You should get a full STD panel if you are unsure which STD you have or do not have symptoms of. These tests can cost up to $600 depending on where you live and what type of provider you see.
Discount Programs for STD Treatment
If you are not eligible for Medicare and do not have prescription drug coverage, you may qualify for patient assistance programs. Additionally, there are clinics and online programs to help you access treatment after a positive test result. Below are a few options to help you get the treatment you need.
STD Treatment Cost Without Insurance Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
STDs are often associated with feelings of embarrassment, fear, dread, and worry. But if you are sexually active, routine STD screening is important for your health and the health of your partners. If you are diagnosed with an STD, it is important to be informed of the next steps.
Bottom Line
Staying up to date with preventive sexual health services like OB/GYN appointments and routine STD screening is essential for staying healthy. The cost of each STD treatment plan will vary, but without insurance, STD screening and treatment costs can add up.