
Explore
We took a health system cost perspective, and addressed input uncertainty with sensitivity analyses. Results: The mean annual cost per patient for melanoma stage 0/I/II was AU$1681 (US$1175) rising to AU$37,729 (US$26,365) for stage III resectable, and AU$115,109 (US$80,440) for stage III unresectable/IV.
How much does melanoma treatment cost?
With current treatments, about 30 percent to 40 percent of patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer will have a relapse about two or three years after surgery that’s caused by stray cancer cells that have moved elsewhere in the body, Şahin said. “The question is if we add a vaccine, can we prevent these relapses?” Şahin said.
What is the cure rate for melanoma?
To assign a stage to your melanoma, your doctor will:
- Determine the thickness. The thickness of a melanoma is determined by carefully examining the melanoma under a microscope and measuring it with a special tool. ...
- See if the melanoma has spread to the lymph nodes. ...
- Look for signs of cancer beyond the skin. ...
What steps might a doctor take to treat melanoma?
While the best treatment for melanoma is dependent on the stage of cancer and the individual’s overall health, alternative methods are often used in addition to standard medical care. Remedies like eggplant, bloodroot, and essiac tea have been found to deliver natural components to treat and eliminate the affected skin cells.
Is there a cure for melanoma?

How serious is melanoma in the eye?
Large eye melanomas often cause vision loss in the affected eye and can cause complications, such as retinal detachment, that also cause vision loss. Small eye melanomas can cause some vision loss if they occur in critical parts of the eye. You may have difficulty seeing in the center of your vision or on the side.
How long can you live with eye melanoma?
5-year relative survival rates for eye melanomaSEER stage5-year relative survival rateLocalized85%Regional66%Distant15%All SEER stages combined82%Mar 2, 2022
Is eye melanoma treatable?
These rare cancers can be treated with either surgical removal of the tumor, if it is small enough, or radiation therapy. In more advanced cases or if there is serious eye damage, enucleation (removal of the eyeball) may be needed.
How do you get rid of melanoma in the eye?
Surgery to remove the melanoma and a band of healthy tissue that surrounds it may be an option for treating small melanomas. Surgery to remove the entire eye (enucleation). Enucleation is often used for large eye tumors. It may also be used if the tumor is causing eye pain.
Is ocular melanoma a death sentence?
If your doctor catches and treats ocular melanoma (a kind of eye cancer) before it spreads to other organs, you have an 85% chance of being alive five years after diagnosis. If it's metastasized to distant organs (as opposed to nearby lymph nodes, for example), the five-year survival rate drops to 13%.
How fast does eye melanoma spread?
Approximately 50% of patients with OM will develop metastases by 10 to 15 years after diagnosis (a small percentage of people will develop metastases even later i.e. 20-25 years after their initial diagnosis).
Can you survive ocular melanoma?
The 5-year survival rate for eye melanoma is 82%. When melanoma does not spread outside the eye, the 5-year relative survival rate is about 85%. The 5-year survival rate for those with disease that has spread to surrounding tissues or organs and/or the regional lymph nodes is 71%.
Is melanoma of the eye common?
Melanoma is the most common type of eye tumor in adults. Even so, melanoma that starts in the eye is rare. Too much exposure to sunlight is an important risk factor for melanoma. People who have fair-skin and blue eyes are most affected.
Can ocular melanoma spread brain?
Metastasis of the ocular malignant melanoma to the brain is extremely rare and most often occurs simultaneously with liver metastases. Lorigan et al., in clinical and radiological studies, found a total of five cases of brain metastases in 110 cases of metastatic choroidal melanoma [3].
How do you know if ocular melanoma has spread?
After intraocular melanoma has been diagnosed, tests are done to find out if cancer cells have spread to other parts of the body. The process used to find out if cancer has spread to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease.
Is eye biopsy painful?
After you have the local or general anaesthetic, the specialist puts a thin needle attached to a syringe into your eye. They draw out some cells from the tumour. This usually takes a few minutes. If you have a local anaesthetic you may be aware of something going on, but you shouldn't have discomfort or pain.
Is eye radiation painful?
In most cases, the total dose of radiation is divided into daily fractions (usually given Monday thru Friday) over several weeks. The treatment is typically not painful.
What is the treatment for large melanomas?
Large melanomas: The standard treatment for these cancers is usually radiation. Proton beam therapy and stereotactic radiation therapy are usually used first. Additional treatment with surgery or lasers may also be considered if the radiation does not work completely. Surgery with enucleation ...
What is the best treatment for melanomas?
Surgery with enucleation (removal of the entire eye) is the preferred surgery for large melanomas when radiation is not an option. Enucleation might also be considered for cancers that take up more than half of the eye orbit, that cause significant pain, or that have caused loss of vision in the eye. In rare cases where the cancer has grown ...
What is the treatment for a tumor in the eye?
Laser therapy, including transpupillary thermotherapy (T TT), most often along with brachytherapy. Surgery, which may require removing only the tumor or might need to be as extensive as enucleation (removing the entire eye). This might be necessary if the eye is severely damaged by the tumor.
How to treat melanomas?
Medium-sized melanomas: These tumors can usually be treated by many of the same approaches used for small melanomas: 1 Radiation therapy, such as brachytherapy (plaque therapy), proton beam therapy, or stereotactic radiation therapy 2 Laser therapy, including transpupillary thermotherapy (TTT) or laser coagulation, along with brachytherapy 3 Surgery, which may require removing only the tumor or might need to be as extensive as enucleation (removing the entire eye). This might be necessary if the eye is severely damaged by the tumor.
What is the name of the small, slow growing tumor that grows in the eye?
Iris melanomas. Melanomas of the iris (the colored part of the eye) are usually small, slow-growing tumors. One option for people with an early stage iris melanoma is to watch it closely to see if it grows. A series of special photographs are taken to help monitor the tumor.
Where does melanoma come back?
When melanoma recurs outside the eye (called extraocular recurrence ), it most often comes back in the liver. It might also come back in other areas, like the lungs or bones. These cancers are often hard to treat.
Can melanoma spread outside the eye?
Most uveal melanomas are still only within the eye when they are first diagnosed. It is rare for the cancer to have already spread outside of the eye. But unfortunately, in about half of all patients the melanoma will come back at some point after treatment. Cancer that comes back after treatment is called recurrent.
What is the least serious eye cancer?
Melanoma of the iris is the least serious of the three types. Cancers of the ciliary body may be hardest to treat. When cancer is in the ciliary body, it can push the lens of the eye out of place and blur your vision. Continued.
Where does melanoma develop?
Symptoms. The cancer usually develops in the middle layer of the eyeball, which holds the blood vessels that feed your inner eye. You may not notice any symptoms at first. People with choroidal or ciliary body melanoma often don't have symptoms. Your eye doctor might find the cancer during a routine eye exam.
What is the name of the cancer that develops in the skin and hair?
Melanoma is a kind of cancer that develops in cells that give your skin, eyes, and hair their color. These cells are called melanocytes. Melanoma usually shows up on the skin, but it also can happen in your eyes. When it does, doctors call it ocular melanoma. Some ocular cancers form on the surface of the eye and the eyelid.
Where does ocular cancer grow?
But ocular melanoma can also form inside the eye. Cancer cells grow in the uvea, a layer of tissue under the white part of your eye. The uvea contains melanocytes.
What is the best way to take pictures of the inside of your eye?
Ultrasound: High-frequency sound waves are used to make images of the inside of your eye. Fluorescein angiography: You’ll get a special dye put into your bloodstream through a vein in your arm. The dye will travel up to your eye. Your doctor then uses a special camera to take pictures of the inside of your eye.
Can ocular melanoma be caused by UV rays?
Doctors don't know exactly what causes ocular melanoma. As with skin cancer, people with fair skin, blond or red hair, and light-colored eyes are more likely to get it. But unlike skin cancer, there's no hard evidence that links ocular melanoma to ultraviolet (UV) rays, the kind you're exposed to from sunlight or a tanning bed. Still, you should avoid too much UV exposure for other health reasons.
Can ocular melanomas be treated?
Treatment. If your ocular tumor is small or noncancerous, you might not have to get it treated right away. Your doctor may just want to check it regularly to see if it grows or causes problems. If caught before it spreads outside the eye, doctors can successfully treat most ocular melanomas.
Histopathology Features Predicting Prognosis
The histopathologic features predicting poor prognosis of uveal melanoma include epithelioid cell type, high mitotic activity, large mean diameter of the 10 largest nucleoli, high microvascular density, presence of microvascular loops and networks, increased tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and macrophages, and higher expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor, and HLA class I and II antigens.
Having An Eye Removed
Sometimes the only choice a doctor has in treating intraocular melanoma is to remove the eye. Because of this visual loss, a person with one eye may have trouble with depth perception. Most people adjust to these differences.
Life After Cancer Treatment
After you finish treatment for cancer, give yourself time to adjust to the physical and emotional changes. We are still here to support you after your treatment finishes.
Clinical Features Predicting Prognosis
Although the influence of age on the prognosis of uveal melanoma is uncertain, recent studies indicate that a poor prognosis is more likely associated with increasing age.
Prognosis And Survival For Eye Cancer
If you have eye cancer, you may have questions about your prognosis. A prognosis is the doctors best estimate of how cancer will affect someone and how it will respond to treatment. Prognosis and survival depend on many factors.
What Causes Intraocular Melanoma
Genes, which are made of DNA, give instruction to cells about how to multiply. But if a gene mutates , it might allow cells to multiply out of control. That leads to cancer.
Treatment Decisions For Eye Cancer
The main treatments for eye cancer are surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy. But you may have other treatments that your eye specialist will discuss with you. Your treatment will depend on:
How many sizes of melanoma are there?
Intraocular melanoma of the ciliary body and choroid has four size categories. The category depends on how wide and thick the tumor is. Category 1 tumors are the smallest and category 4 tumors are the largest.
What is intraocular melanoma?
Key Points. Intraocular melanoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the eye. Being older and having fair skin may increase the risk of intraocular melanoma. Signs of intraocular melanoma include blurred vision or a dark spot on the iris.
How do melanoma cells look under a microscope?
How the melanoma cells look under a microscope. The size and thickness of the tumor. The part of the eye the tumor is in (the iris, ciliary body, or choroid). Whether the tumor has spread within the eye or to other places in the body. Whether there are certain changes in the genes linked to intraocular melanoma.
How does melanoma spread?
The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body. If intraocular melanoma spreads to the optic nerve or nearby tissue of the eye socket, it is called extraocular extension.
What tests are used to diagnose intraocular melanoma?
Tests that examine the eye are used to help diagnose intraocular melanoma. The following tests and procedures may be used: Physical exam and health history: An exam of the body to check general signs of health, including checking for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual.
How long does melanoma last after radiation?
The seeds give off radiation which kills the cancer. The plaque is removed at the end of treatment, which usually lasts for several days . The way the radiation therapy is given depends on the type and stage of the cancer being treated. External and internal radiation therapy are used to treat intraocular melanoma.
Can intraocular melanoma cause early symptoms?
Intraocular melanoma may not cause early signs or symptoms. It is sometimes found during a regular eye exam when the doctor dilates the pupil and looks into the eye. Signs and symptoms may be caused by intraocular melanoma or by other conditions. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following:
What is ocular melanoma?
Ocular melanoma is a rare form of cancer that affects the eye. The most common type of ocular melanoma is called uveal melanoma, as it develops in the uvea, the part of the eye that contains the iris, ciliary body and choroid.
What is the survival rate for ocular melanoma?
The overall 5-year survival rate for all eye-related melanoma is 82 percent.
How is ocular melanoma treated?
Ocular melanoma is frequently treated with radiation therapy, surgery or laser therapy. The most effective treatment plan will be dependent on the location, size and stage of the cancer, as well as the rate at which it is progressing.
What causes melanoma in the eye?
The risk of eye melanoma increases with age. Certain inherited skin disorders. A condition called dysplastic nevus syndrome, which causes abnormal moles, may increase your risk of developing melanoma on your skin and in your eye.
What are the risk factors for melanoma of the eye?
Risk factors for primary melanoma of the eye include: Light eye color. People with blue eyes or green eyes have a greater risk of melanoma of the eye. Being white. White people have a greater risk of eye melanoma than do people of other races. Age.
What is the name of the cancer that develops in the cells that produce melanin?
Melanoma is a type of cancer that develops in the cells that produce melanin — the pigment that gives your skin its color. Your eyes also have melanin-producing cells and can develop melanoma. Eye melanoma is also called ocular melanoma. Most eye melanomas form in the part of the eye you can't see when looking in a mirror.
Why do my eyes get melanoma?
Causes. It's not clear what causes eye melanoma. Doctors know that eye melanoma occurs when errors develop in the DNA of healthy eye cells. The DNA errors tell the cells to grow and multiply out of control, so the mutated cells go on living when they would normally die.
What are the complications of melanoma?
Complications. Complications of eye melanoma may include: Increasing pressure within the eye (glaucoma). A growing eye melanoma may cause glaucoma. Signs and symptoms of glaucoma may include eye pain and redness, as well as blurry vision. Vision loss.
How do you know if you have melanoma?
When they do occur, signs and symptoms of eye melanoma can include: A sensation of flashes or specks of dust in your vision (floaters) A growing dark spot on the iris. A change in the shape of the dark circle (pupil) at the center of your eye. Poor or blurry vision in one eye. Loss of peripheral vision.
Which part of the eye is affected by melanoma?
The uvea has three parts and each can be affected by eye melanoma: The iris, which is the colored part in the front of the eye. The choroid layer, which is the layer of blood vessels and connective tissue between the sclera and the retina at the back of the uvea. The ciliary body, which is in the front of the uvea and secretes ...
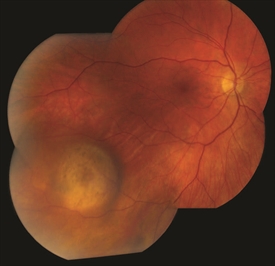
Treatment
- Your eye melanoma treatment options will depend on the location and size of the eye melanoma, as well as your overall health and your preferences.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and Support
- Coping with vision changes
If your cancer treatment causes total loss of vision in one eye, such as happens when an eye is removed, it's still possible to do most things you were able to do with two working eyes. But it may take a few months to adjust to your new vision. Having only one eye affects your ability to judge …
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Start by seeing your family doctor if you have any signs or symptoms that worry you. If your doctor suspects you have an eye problem, you may be referred to an eye specialist (ophthalmologist). If you have eye melanoma, you may be referred to an eye surgeon who specializes in treating eye melanoma. This specialist can explain your treatment options and ma…