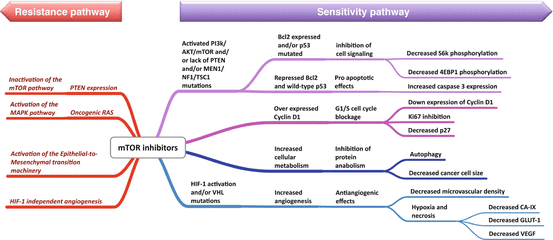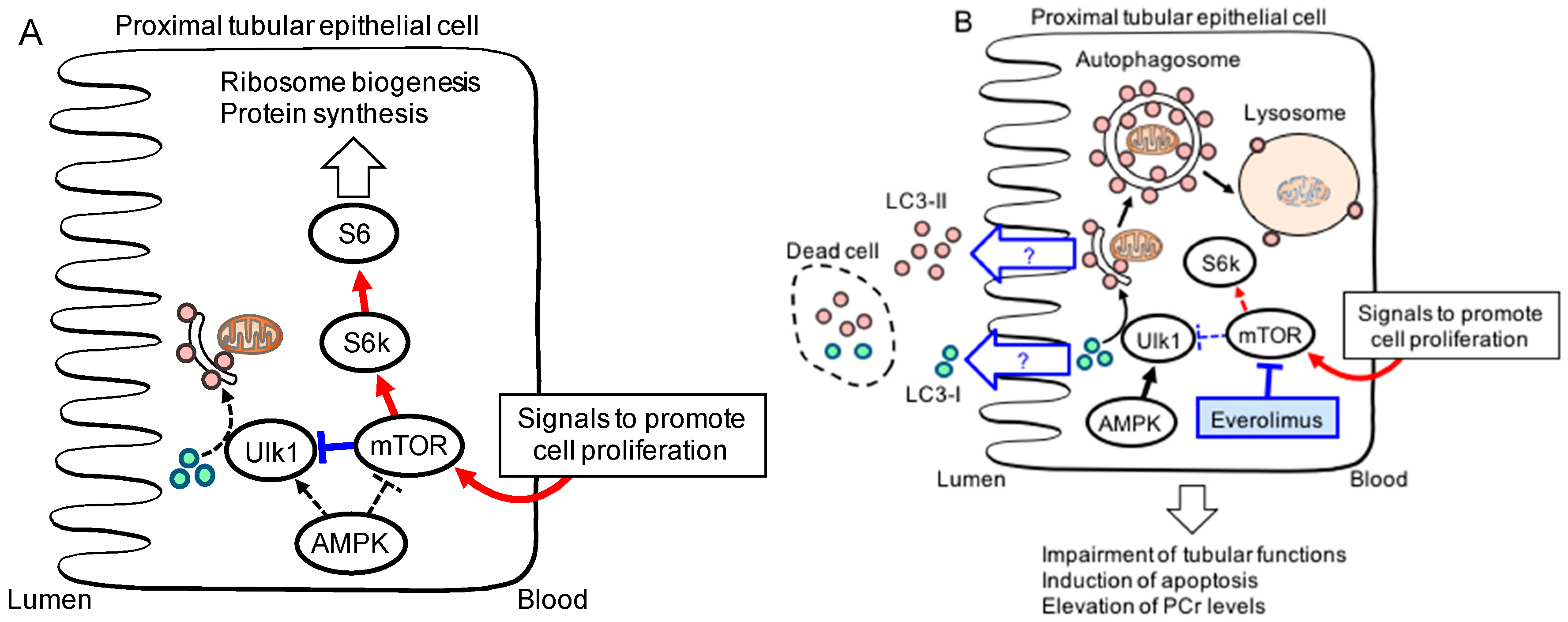
Background: The mTOR pathway, which consists of mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) and mTOR complex 2 (mTORC2), is activated in polycystic kidney disease (PKD) kidneys. Sirolimus and everolimus indirectly bind and inhibit mTORC1. A novel group of drugs, the mTOR kinase inhibitors, directly bind to mTOR kinase, thus inhibiting both mTORC1 and 2.
Full Answer
What is the best inhibitor of mTOR?
The best-known inhibitor of mTOR is rapamycin, from which mTOR’s name derives. Rapamycin was originally applied as an immunosuppressant, blocking T-cell activation, and has been in use since around 2000 to prevent kidney graft rejection. As a consequence, it inhibits only some of the functions of mTORC1.
What are dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors?
Dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors The FAT, FATC, and kinase domain of mTOR are widely conserved in a group of protein kinases which display prominent structural similarities to PIKK (PI3K-related kinases) ( Figure 2and Table 1).
Is inhibiting mTORC1 signaling effective for anti-cancer treatment?
Inhibiting mTORC1 signaling has therefore attracted great attention as an anti-cancer therapy.
What are second-generation mTOR inhibitors?
The second-generation mTOR inhibitors are ATP-competitive mTOR inhibitors which act as ATP analogues and compete with ATP for the binding to the kinase domain of mTOR.

What does an mTOR inhibitor do?
What are MTOR inhibitors? Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors block the activity of the mammalian target of rapamycin. Mammalian target of rapamycin is a protein kinase, which regulates growth factors that stimulate cell growth and angiogenesis. In certain cancers the mTOR pathway is more active.
What happens when mTOR is activated?
The mTOR signaling pathway, which is often activated in tumors, not only regulates gene transcription and protein synthesis to regulate cell proliferation and immune cell differentiation but also plays an important role in tumor metabolism.
How do you slow the progression of PKD?
Drinking water and fluids throughout the day may help slow the growth of kidney cysts, which in turn could slow down a decline in kidney function. Following a low-salt diet and eating less protein might allow kidney cysts to respond better to the increase in fluids. Pain.
What inhibits the mTOR pathway?
These two complexes consist of unique mTOR-interacting proteins that determine their substrate specificity. Rapamycin, the first defined mTOR inhibitor, specifically inhibits mTOR, resulting in inhibition of cell growth, cell cycle progression and cell proliferation [13].
What is the purpose of mTOR?
mTOR, as the catalytic subunit of two distinct protein complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2, is the major regulator of growth in animals and controls most anabolic and catabolic processes in response to nutrients and nutrient-induced signals, like insulin (Fig. 1).
What protein activates mTOR?
Specifically insulin activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and protein kinase B (PKB/Akt). Akt phosphorylates and inhibits tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC2) which relieves inhibition on Rheb (Ras homologue enriched in brain) and allows activation of mTOR.
What is the best treatment for polycystic kidney disease?
Tolvaptan is a medication that's recommended by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) to treat ADPKD in adults. It can be used to slow down the growth of cysts, reducing overall kidney growth and preserving kidney function for longer.
Does tolvaptan work in PKD?
On April 24, 2018, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted approval of tolvaptan to be the first treatment in the United States for adult patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), the most common form of polycystic kidney disease (PKD).
Do PKD kidneys shrink after transplant?
Polycystic kidneys volume significantly reduces after kidney transplantation, and this would reduce the need for prophylactic bilateral nephrectomy in asymptomatic patients.
How does the mTOR pathway work?
There are 4 main functions of the mTOR signaling pathway: cell growth and proliferation, angiogenesis, bioenergetics through nutrient availability and boosting of metabolism, and cell survival through DNA repair and decreasing autophagy and apoptosis.
How does rapamycin suppress immune system?
Rapamycin exerts its immunosuppressive effects by inhibiting the activation and proliferation of T cells. It acts specifically on FK-binding protein 12 (FKBP12), a substance commonly referred to as an immunophilin because it binds to immunosuppressive drugs.
How does mTOR regulate protein synthesis?
Multiple factors and pathways affect mTORC1 activity to regulate skeletal muscle mass. mTORC1 is activated by IGF-I/insulin, mechanical stimulation and amino acids (blue lines) and inhibited by glucocorticoids and myostatin (red lines). Activated mTORC1 increases protein synthesis in skeletal muscle.
What is the best inhibitor of mTOR?
Rapamycin and the first generations of mTOR inhibitors. The best-known inhibitor of mTOR is rapamycin, from which mTOR’s name derives. Rapamycin was originally applied as an immunosuppressant, blocking T-cell activation, and has been in use since around 2000 to prevent kidney graft rejection.
How many generations of mTOR inhibitors are there?
Domains of the mTOR protein and three generations of mTOR inhibitors.
What is the FRB binding protein?
The FRB—FK506 binding protein 12 (FKBP12)–rapamycin binding—domain, as its name implies, is the binding site of mTOR to FKBP12 and rapamycin. FAT, kinase, and FATC domains are conserved within the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinases (PIKKs) and are essential for maintaining the activity of PIKKs.
What is the role of mTOR in cancer?
The mammalian target of rapamycin, mTOR, plays key roles in cell growth and proliferation, acting at the catalytic subunit of two protein kinase complexes: mTOR complexes 1 and 2 (mTORC1/2). mTORC1 signaling is switched on by several oncogenic signaling pathways and is accordingly hyperactive in the majority of cancers.
What activates mTORC1?
Typically, hormones and growth factors activate mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) through the SOS/Ras/Raf-MEK-ERK (MAPK) or the IRS1/PI3K-PDK1-PKB pathways or both. mTORC2 also contributes to the activation of PKB through the direct phosphorylation of its turn motif as well as its hydrophobic motif. These pathways impinge on the tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC), which serves as a GTPase activator protein for the small G-protein Rheb. Upon inhibitory phosphorylation evoked by upstream kinases such as PKB, the activity of TSC is suppressed, promoting the accumulation of GTP-bound Rheb, which in turn activates mTORC1 on the surface of lysosomes. Amino acids also activate mTORC1 by bringing the latter onto lysosomes via the Rag GTPases. S6K-rpS6 and 4EBP1-eIF4E are the best-characterized mTORC1 downstream targets and are responsible for controlling a variety of anabolic effects driven by mTORC1. Dashed lines indicate feedback mechanisms. mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase.
Is mTORC1 and mTORC2 important for cancer?
Despite the strong evidence that mTORC1 and mTORC2 control events that are important for cell growth and survival, which are processes of key importance in cancer cells, progress in successfully applying rapamycin and rapalogs as anti-cancer agents has been limited.