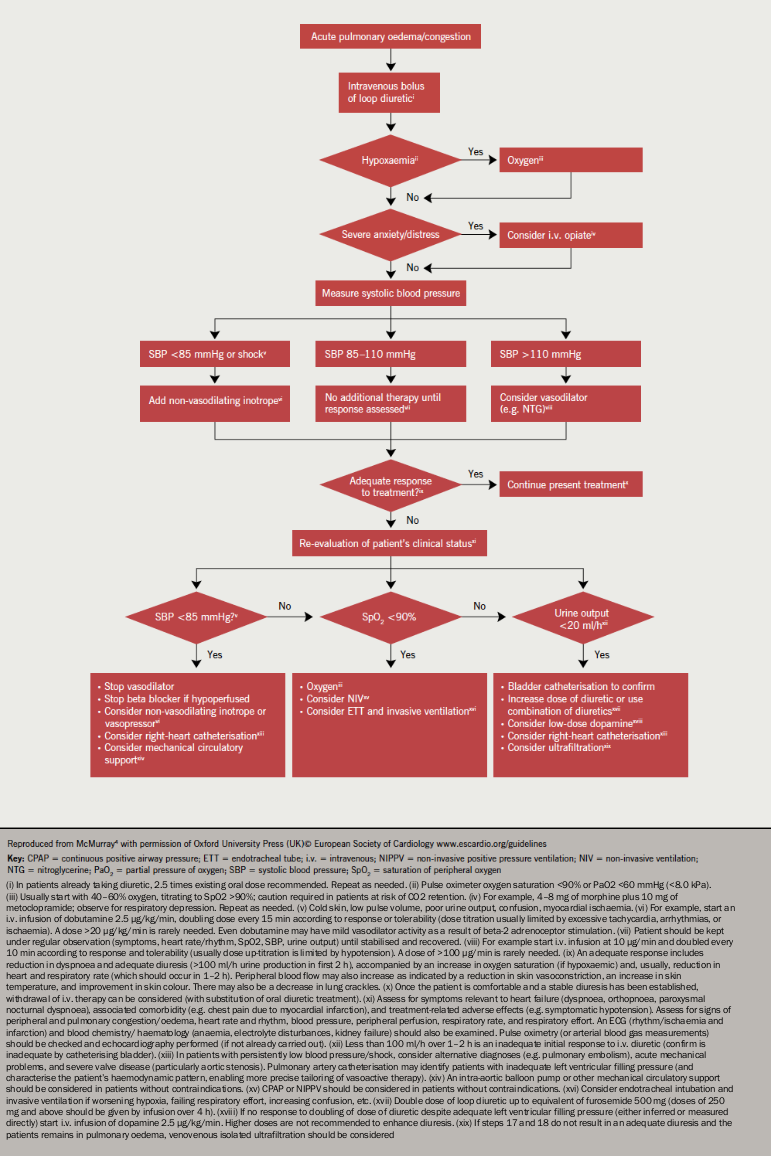
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists use in patients with heart failure and impaired renal function Abstract Aims: Impaired renal function is a major contributor to the low proportion of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) treatment in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).
Full Answer
Can mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists help heart failure patients with chronic kidney disease?
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in heart failure patients with chronic kidney disease: why, when, and how? It is recommended to use MRAs in CHF patients with normal potassium levels and a glomerular filtration rate of more than 30 ml/min.
What is the role of aldosterone receptor antagonists in heart failure treatment?
Aldosterone receptor antagonists have been shown to be a highly efficacious pharmacologic intervention in the treatment of HF patients with reduced LVEF and mild to severe symptoms. In these patients current evidence clearly shows that MRAs reduce morbidity and mortality. MRAs have also several effects that prevent cardiac remodeling and fibrosis.
Do mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists differ by race?
These findings suggest that safety and efficacy of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists may differ by race but mechanisms underlying this difference are unclear at this moment so further study will be necessary [33].
Can mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs) prevent the maladaptive effects of aldosterone?
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs) have been shown to prevent many of the maladaptive effects of aldosterone, in particular among patients with heart failure (HF).

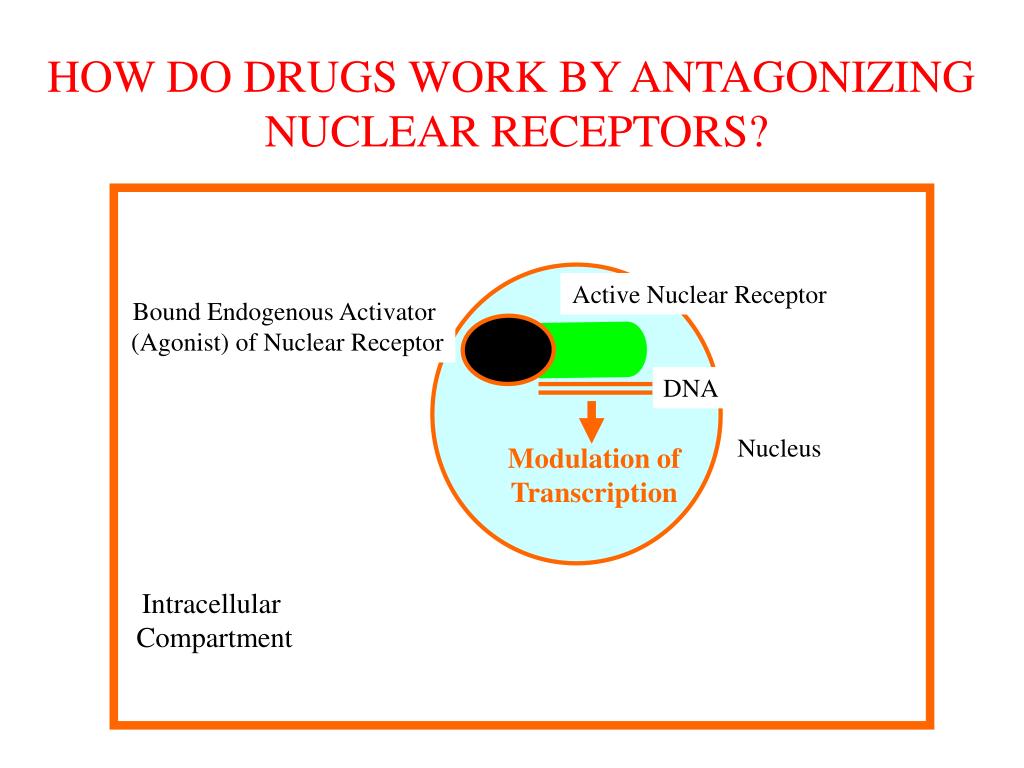
How do mineralocorticoid antagonists work?
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists decrease the aldosterone effect by binding to the mineralocorticoid receptor inhibiting aldosterone. This leads to higher levels of potassium in serum and increased sodium excretion, resulting in decreased body fluid and lower blood pressure.
How do aldosterone antagonists work in heart failure?
Aldosterone receptor antagonists block the effects of aldosterone. This causes reabsorption of sodium by the kidneys and other glands, which encourages water loss, and a subsequent decrease in blood pressure and reduction in fluid around the heart.
Why are MRAs used in heart failure?
Aims. Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs) have been demonstrated to improve outcomes in reduced ejection fraction heart failure (HFrEF) patients. However, MRAs added to conventional treatment may lead to worsening of renal function and hyperkalaemia.
Are aldosterone antagonists used in heart failure?
Aldosterone antagonists are an important pharmacologic therapy in the neurohormonal blockade necessary in the treatment of systolic heart failure. These drugs have been shown to decrease mortality and reduce hospital readmission rates.
How does aldosterone antagonists work?
These drugs treat high blood pressure and heart failure. They do it by helping your kidneys produce more urine. The more you pee, the more excess salt and water you flush out of your body.
Where do aldosterone receptor antagonists work?
The aldosterone antagonists (spironolactone, eplerenone) act on the collecting duct of the nephron, competing with aldosterone for the mineralocorticoid receptor and preventing aldosterone-induced potassium excretion and sodium resorption [13].
How do MRAs work?
MRA (magnetic resonance angiogram) is a type of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan that uses a magnetic field and pulses of radio wave energy to provide pictures of blood vessels inside the body. A standard MRI cannot provide a good picture of the blood vessels and blood flow.
What drug is a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist?
Spironolactone and eplerenone are both mineralocorticoid-receptor antagonists. These compounds block both the epithelial and nonepithelial actions of aldosterone, with the latter assuming increasing clinical relevance.
How do diuretics work in heart failure?
Diuretics, better known as "water pills," help the kidneys get rid of unneeded water and salt. This makes it easier for your heart to pump. These medicines may be used to treat high blood pressure and ease the swelling and water buildup caused by many medical problems, including heart failure.
How is spironolactone beneficial in heart failure?
Spironolactone in the management of HFpEF In this regard, effective reduction of blood pressure levels decreases LV hypertrophy, reduces LV end-diastolic pressure and improves LV relaxation and filling, thus resulting in a reduction of the progression of HF (18).
How do aldosterone antagonists cause hyperkalemia?
The pump acts to re-absorb sodium and water in exchange for potassium, which is then eliminated in the urine. Consequently, aldosterone antagonism can cause hyperkalemia. Hyperkalemia is an established adverse effect of both spironolactone and eplerenone. The symptoms of hyperkalemia begin with muscle weakness.
How do aldosterone inhibitors affect the blood?
Aldosterone receptor antagonists block the effects of aldosterone, preventing the the reabsorption of sodium, which encourages water loss. This leads to a decrease in blood pressure and a reduction in fluid around the heart.
What is the mechanism of action of aldosterone?
Aldosterone causes sodium to be absorbed and potassium to be excreted into the lumen by principal cells. In alpha intercalated cells, located in the late distal tubule and collecting duct, hydrogen ions and potassium ions are exchanged. Hydrogen is excreted into the lumen, and the potassium is absorbed.
Does aldosterone increase ejection fraction?
Aldosterone antagonists improve ejection fraction and functional capacity independently of functional class: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials | Heart.
What is the mechanism of action of spironolactone?
Mechanism of action: Aldactone (spironolactone) is a specific pharmacologic antagonist of aldosterone, acting primarily through competitive binding of receptors at the aldosterone-dependent sodium-potassium exchange site in the distal convoluted renal tubule.
How does aldosterone increase blood pressure?
Aldosterone causes an increase in salt and water reabsorption into the bloodstream from the kidney thereby increasing the blood volume, restoring salt levels and blood pressure.
What is the role of aldosterone in heart failure?
Aldosterone in the pathophysiology of heart failure. Aldosterone is a mineralocorticoid hormone produced in response to angiotensin II release, hyperkalemia, and corticotropin mainly by the adrenal cortex.
What is the half life of spironolactone?
Spironolactone is a widely used, non-selective aldosterone receptor antagonist marketed since the early 60s that is metabolized extensively in the liver to its active metabolites. Its plasma half-life is 1.4 h , although in CHF patients with hepatic congestion, this duration may increase 5-fold.
What receptors do aldosterones attach to?
Aldosterone binding to mineralocorticoid receptor results in reabsorption of sodium and water in exchange for potassium in various sites including the distal tubule and collecting duct of the nephron, causing an increased intravascular fluid retention and volume overload. In addition to these classical epithelial effects, ...
Does aldosterone affect cardiomyocytes?
Some studies confirm that aldosterone and MR activation have also direct effects on cardiomyocyte calcium-handling that may predispose to arrhythmias [14]. Aldosterone is also involved in endothelial dysfunction, mainly by decreasing the bioavailability of nitric oxide and promoting oxidative stress [16].
Does aldosterone help with heart rate variability?
Evidence suggests that aldosterone antagonists may improve cardiac vagal control (including heart rate variability and baroreflex sensitivity) immediately after intravenous administration, an effect that may be beneficial in decompensated heart failure and MI [38].
Does aldosterone cause heart failure?
Aldosterone has an important role in the pathogenesis of heart failure. Increased levels of aldosterone tend to promote myocardial hypertrophy and remodeling, induce fibrosis and apoptosis, contribute to endothelial dysfunction and reduce myocardial perfusion, thus increasing the incidence of cardiovascular events [3].
Is aldosterone a non-epithelial drug?
In addition to these classical epithelial effects, aldosterone has a variety of negative non-epithelial effects including induction of inflammation, vascular stiffening, collagen formation, myocardial necrosis and stimulation of fibrosis [1]. Aldosterone has an important role in the pathogenesis of heart failure.