
Water Treatment Process: Follow Water Through a Surface Water Treatment Plant
- Coagulation. Coagulation is defined as the water treatment process of increasing the tendency of small particles to...
- Flocculation. Following the coagulant chemical addition and the rapid mix processes, the raw water will continue on to a...
- Sedimentation (or Clarification). The water...
What are the 5 stages of water treatment?
Introduction to HWTS Step 1 – Water source protection Step 2 – Sedimentation Step 3 – Filtration Step 4 – Disinfection Step 5 – Safe water storage. Step 1 – Water Source Protection There are many pollution problems which may threaten drinking water quality at the source, or point of collection.
How is water purified in a water treatment plant?
Jun 19, 2018 · There are 5 steps in the water treatment process hope this helps!!! Answer 4.3 /5 5 kendyllmcampi There are A, 5. Screening, coagulation, sedimentation, filtration, and …
How do you treat waste water?
Mar 16, 2015 · Although drinking water treatment practices vary, most water treatment plants follow a six-step process to remove undesirable contaminants. Grit Removal. The first step in the treatment process is the removal of harsh grit particles (sand, gravel, cinder, etc.) and other large objects (cans, bottles, tree limbs, etc.).
What is sewage water and its treatment process?
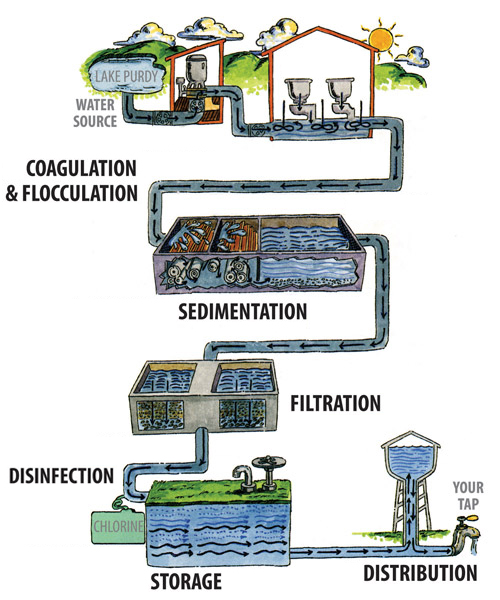
The water treatment process is a series of steps including pumping water from freshwater sources, coagulation, sedimentation, filtration, disinfection and storage.
What are the 5 steps of water treatment?
The 5 major unit processes include chemical coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection (described below). There are chemicals added to the water as it enters the various treatment processes.
How many stages of water treatment are there?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment. In some applications, more advanced treatment is required, known as quaternary water treatment.Dec 6, 2018
What are the 4 steps of water treatment?
4 Steps of Community Water TreatmentCoagulation and Flocculation. ... Sedimentation. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection. ... Learn More. ... Recommended Readings.
How many steps are in the water treatment process quizlet?
Six Steps of Wastewater Treatment Flashcards | Quizlet.
What are the 6 steps of water treatment?
CONVENTIONAL SURFACE WATER TREATMENT These include: (1) Collection ; (2) Screening and Straining ; (3) Chemical Addition ; (4) Coagulation and Flocculation ; (5) Sedimentation and Clarification ; (6) Filtration ; (7) Disinfection ; (8) Storage ; (9) and finally Distribution.
What are the 3 steps of water treatment?
The three stages of wastewater treatment are known as primary, secondary and tertiary. Each stage purifies water to a higher level. In some applications, only one or two stages are necessary. The level of treatment necessary depends on the water's intended use case, and what environment it will be discharged into.Mar 7, 2021
What is water treatment process?
Water treatment processesCoagulation/flocculation. During coagulation, liquid aluminium sulfate (alum) and/or polymer is added to untreated water (raw water). ... Sedimentation. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection. ... Sludge drying. ... Fluoridation. ... pH Correction.
What are the 4 steps of water treatment PDF?
Water treatment stepsCoagulation. Coagulation is often the first step in water treatment. ... Flocculation. Flocculation follows the coagulation step. ... Sedimentation. Sedimentation is one of the steps water treatment plants use to separate out solids from the water. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection.
What is water treatment plant steps?
The processes involved in removing the contaminants include physical processes such as settling and filtration, chemical processes such as disinfection and coagulation, and biological processes such as slow sand filtration.
Which is the first step in water purification quizlet?
In water treatment, the first step is filtration. The first filtration removes large pieces of sediment and debris. The next step is coagulation. In coagulation, a chemical is added to help the sediment and debris clump together.
What is the purpose of flocculation during the treatment of drinking water quizlet?
The purpose of coagulation and flocculation is to remove particulate impurities and color from the water being treated.
What is the most important step in water treatment?
Filtration. Filtration is one of the most crucial steps of the water treatment process. The flocs formed during flocculation are not removed entirely by sedimentation. Hence, to remove the finely sized particles and flocs, filtration is required.
What is water treatment?
The Water Treatment Process includes the treatment of water supplied to the household for drinking and other utility purposes and also the waste water to be disposed off into the water sources.
What is sedimentation with coagulation?
The sedimentation with coagulation is termed as clarification. It is required to increase the efficiency of sedimentation as stated above during the water treatment process. Plain sedimentation consumed too much time.
What are the two types of sedimentation tanks?
There are two types of sedimentation or settling tanks as described below: 1. Fill and Draw Type: The above mentioned tank is also known as Quiescent Tank. The water is filled in the fill and draw type first and then allowed to remain for a particular duration.
What happens to the weight of particles in a sedimentation tank?
The weights of the particles increase as they aggregate and then settle down. A sedimentation tank is so designed that the velocity of the flowing water is reduced. As the water is discharged into the sedimentation tank, the cross section area of the water flow is in the case and therefore, velocity reduces.
What are the two types of water sources?
There are two types of sources of water. One is the surface water source like river, reservoir, etc. the other one is ground water source like bore well. The water treatment process differs for these systems considerably.
Why is water softened?
Water softening is done to make the hard water soft. Surface water usually does not contain much hardness. However, the water taken from underground sources like bore well contains hardness due to the presence of ions.
What is the process of reducing turbidity in water?
Step 2 – Sedimentation Sedimentation is a physical treatment process used to reduce the turbidity of the water. Remember that turbid water looks cloudy, dirty, or muddy and is caused by sand, silt, and clay that are floating in the water.
What are the three chemicals used to clean water?
Three common chemicals used as ways to clean water and aid in sedimentation are aluminum sulphate, polyaluminum chloride (also known as or liquid alum) and ferric sulphate. Native plants are traditionally used in some countries in Africa and Latin America to help with sedimentation.
How does sedimentation work?
The sedimentation process can be quickened by adding special chemicals or native plants, also known as coagulants, to the water. Coagulants help the sand, silt and clay join together and form larger clumps, making it easier for them to settle to the bottom of the container.
What is water treatment?
The water treatment process to deliver safe and wholesome water to customers includes many steps. Coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection are the water treatment processes that make up a conventional surface water treatment plant. These water treatment processes ensure that the water consumers receive is safe ...
How does surface water treatment work?
In order to meet the requirements of the Surface Water Treatment Rule, a water system must both remove and inactivate the pathogens in the water. This process begins with coagulation, which destabilizes the particles in the water. Then, during flocculation, the destabilized particles bump into each other and form larger and larger flocs. These large flocs are given adequate time to settle out of solution via gravity during sedimentation. Any remaining particles and pathogens will be removed during the filtration treatment process. Finally, the water is disinfected to inactivate any remaining pathogens prior to entering the water system’s distribution system.
What is coagulation in water treatment?
History of Coagulation in Drinking Water Treatment. Coagulation has been an important process in high-rate filtration plants in the United States since the 1880s. Aluminum and iron salts have been used in the coagulation process since the beginning. These salts are still the most commonly used coagulants today.
What is turbidity in water?
This cloudiness is known as turbidity . Visual turbidity is unpleasant to consumers. Visual turbidity is also an indicator to operators and regulators that the water may still contain pathogens. The Surface Water Treatment Rule therefore requires that turbidity be removed to very low levels.
How does contact time work in water treatment?
In order for systems to be sure that they are properly disinfecting the filtered water, the Surface Water Treatment Rule requires systems to provide enough contact time. Contact time (CT) is a function of the known disinfection concentration and the amount of time that the disinfectant is in contact with the water. Contact time is expressed in terms of mg/L-min. The EPA has published tables that show how much CT credit water systems will receive. In order to use these tables you use the concentration of chlorine, time, water temperature and pH.
What is the process of coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, and filtration?
The water treatment process of coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, and filtration remove the pathogens. The disinfection water treatment process inactivates them. The small particles in water may consist of silt and clay, color bodies, precipitated iron or manganese oxides, and even bacteria and algae. Together, these particles make the water ...
What is the purpose of the Surface Water Treatment Rule?
The goal of the SWTR is to reduce illnesses related to pathogens in drinking water. These pathogens include coliform, Giardia, and Cryptosporidium .
Answer
There are A, 5. Screening, coagulation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection.
New questions in Biology
45 Latent fingerprints were collected at a crime scene. What MOST likely happened in the collection process? OB. OA. Silicone molds were used. AFIS wa … s used. O c. Fingerprint powders were used. OD Plastic prints were used. Reset Next
What happens after a large object is removed from water?
After any large objects are removed from the water, chlorination chemicals are added to control algae and other biological growth. Aeration, or the circulation of air through a liquid substance, also takes place in this step so that any dissolved gases can be dispelled.
What is the first step in grit removal?
Grit Removal. The first step in the treatment process is the removal of harsh grit particles (sand, gravel, cinder, etc.) and other large objects (cans, bottles, tree limbs, etc.). This step is necessary because it prevents damage to the pumps, which are used to transport the water from step to step in the treatment process.
Why is the sedimentation basin located close to the flocculation basin?
The sedimentation basin is often located within close proximity of the flocculation basin so that the particles do not have to travel far and will not have a chance to break apart. When they reach the sedimentation basin, the water’s velocity is slowed down so the floc particles can sink to the basin floor.
What is the Safe Drinking Water Act?
In the United States, for example, the Safe Drinking Water Act was created by the Environmental Protection Agency to provide standards for tap water and public water systems. Although drinking water treatment practices vary, most water treatment plants follow a six-step process to remove undesirable contaminants.
Where does drinking water come from?
Most drinking water comes from a surface water source, such as a lake or river, or a groundwater source, such as a well or spring. This water requires treatment before it can be safely consumed; the level to which the water is treated depends on the source of the water and also on federal regulations. In the United States, for example, the Safe ...
Do suspended solids settle in water?
Once a majority of the gases are removed from the water, suspended solids must be removed as well. In order to collect them, it is essential that they settle to the basin floor, but these particles are often so small that they cannot settle without assistance.
Why is water treatment important?
Water treatment is important because if water is not treated properly, it can cause you to get very sick. Water in rivers, lakes, and streams can be polluted with germs that must be removed before you drink or use it, so your city's water treatment center cleans and disinfects water before you use it.
What is the process of water coagulation?
When they stick together, the process is called flocculation, and those clumps are known as 'flocs' for short.
What is the next step in the floc process?
The next step is called sedimentation. When the floc sticks together, it usually settles at the bottom of the water. At this point, the floc is removed to begin the cleaning process. 4. After that, the water is moved through a filtration system.
How does filtration work?
It goes over rocks, sand, and other materials that filter the water, which means they catch and remove additional tiny particles from water. Filtration stops particles from floating around in the water. 5. Then the water goes through disinfection, which cleanses the water of germs.

Community Water Treatment
Water Fluoridation
- Community water fluoridation prevents tooth decay safely and effectively. Water fluoridation has been named one of 10 great public health achievements of the 20th century 1. For more information on the fluoridation process and to find details on your water system’s fluoridation, visit CDC’s Community Water Fluoridationpage. Top of Page
Consumer Confidence Reports
- Every community water supplier must provide an annual report, sometimes called a Consumer Confidence Report, or “CCR,” to its customers. The report provides information on your local drinking water quality, including the water’s source, contaminants found in the water, and how consumers can get involved in protecting drinking water. 1. View the CDC’s guide to Understandi…
Coagulation
Flocculation
- Following the coagulant chemical addition and the rapid mix processes, the raw water will continue on to a flocculation basin. The goal of the flocculation treatment process is to increase the size of the flocs in order to increase their ability to settle out.
Sedimentation
- The water continues on to the sedimentationbasin, or clarifier, after the flocs have been formed. The goal of this stage of the treatment process is to reduce the amount of solids in the water before the water is filtered in the next treatment step. The large flocs will settle out of suspension via gravity. Clarifiers can remove a very large percentage of the suspended materials in water. I…
Filtration
- The final water treatment process in removing particulates is filtration. The sedimentation process will have already removed a large percentage of the suspended solids. Sedimentation is unable to remove many small particles in water though. Filtration will remove these microorganisms and other suspended material that did not settle out previously.
Disinfection
- As discussed previously, the surface water treatment rule requires both the filtration and disinfection of surface water sources. The water must be disinfected now that it has been filtered.
Chlorination Operations
- Chlorination was one of the first drinking water disinfection methods. It is still the most commonly used disinfection method used today. The filtered water is injected with either liquid sodium hypochlorite, gaseous chlorine, or solid calcium hypochlorite. Chlorine is a strong oxidant. It is used to both disinfect and also to remove color, taste and odor compounds, iron and manganes…
Conclusion
- In order to meet the requirements of the Surface Water Treatment Rule, a water system must both remove and inactivate the pathogens in the water. This process begins with coagulation, which destabilizes the particles in the water. Then, during flocculation, the destabilized particles bump into each other and form larger and larger flocs. These large flocs are given adequate time to se…