How many opioids are prescribed in the US each year?
Coinciding with the soaring use of heroin and fentanyl, 2012 and 2018 the national opioid prescription rate decreased by 36.7% to 51.4 prescriptions per 100 persons in the US after peaking in 2012 with over 255 million prescriptions, an average of 81.3 prescriptions per 100 persons
What percentage of deaths are due to opioid abuse?
81.2% of deaths involve synthetic opioids. Opioids are a factor in 81.7% of all overdose deaths. 23.4 out of every 100,000 residents die from an opioid overdose. That’s 60.3% above the national death rate. 2.83% of hospital births are cases of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome.
How much money has been given to fight the opioid crisis?
$9 billion in grants from HHS to states, tribes, and local communities to fight the opioids crisis in FY 2016-2019* 1.27 million Americans are now receiving medication-assisted treatment.
What is the rate of opioid dispensing in the US?
The overall national opioid dispensing rate declined from 2012 to 2020, and in 2020, the dispensing rate had fallen to the lowest in the 15 years, for which we have data at 43.3 prescriptions per 100 persons (total of more than 142 million opioid prescriptions).

How many people overdosed on opioids 2020?
Opioid overdose deaths: 68,630 Americans died from opioid overdoses in 2020, a rate of 21.4 deaths per 100,000 people. This is a rate 38 percent higher than 2019 when 49,860 Americans died of opioid overdoses (15.5 deaths per 100,000).
What population uses opioids the most?
The age group with the greatest past-year nonmedical use of opioids is young adults aged 18 to 25, yet the greatest use (i.e., exposure) of prescription opioids is among adults aged 26 and older.
What percent of opioid addicts are white?
Patients were included in the analysis if they entered the program between 2010-2013 and had a primary heroin use disorder which resulted in 2,797 participants. At the time of survey completion, the majority of participants included in the analysis were in their early 30's, white (79.5%), and male (56%).
Why is it so easy to become addicted to opioids?
Opioids are highly addictive, in large part because they activate powerful reward centers in your brain. Opioids trigger the release of endorphins, your brain's feel-good neurotransmitters. Endorphins muffle your perception of pain and boost feelings of pleasure, creating a temporary but powerful sense of well-being.
How many people died from opioids in 2018?
Opioids were responsible for 46,802 overdose deaths in 2018, nearly double the number of deaths attributable to non-opioid drugs. This is the first time in decades deaths from opioids has decreased though, a small victory compared to stemming the public health campaigns and new laws targeted towards avoiding addiction.
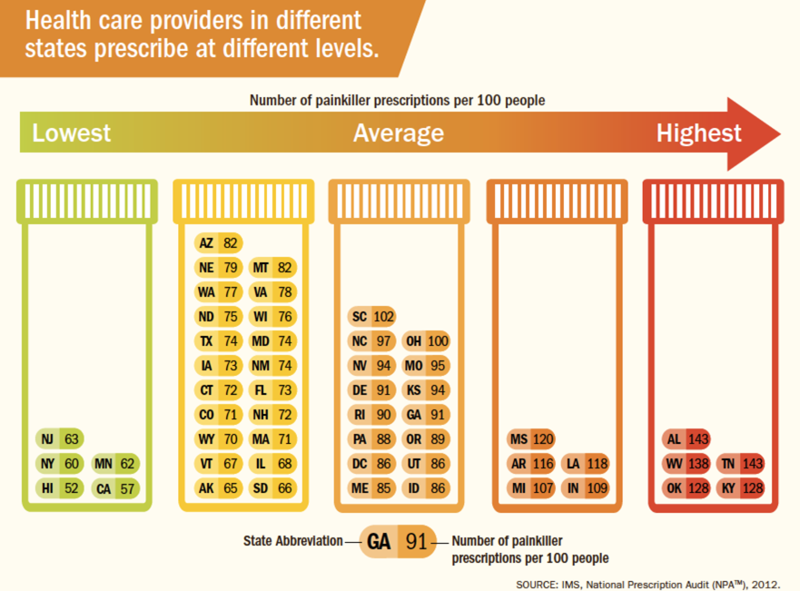
How many prescriptions per 100 people in 2012?
The availability of prescriptions painkillers peaked in 2012 at 81 prescriptions per 100 people.
Is heroin abuse increasing?
Heroin abuse has been steadily increasing, even as people report they are less likely to abuse or be dependent on other illicit drugs, such as cocaine and marijuana. The government has only tracked painkiller misuse since 2015, but data shows that nearly three times as many people abuse painkillers as heroin.
Is fentanyl stronger than morphine?
However, Fentanyl — a pain medication that is nearly 100 times stronger than morphine — stands out for an 800% increase in overdose deaths in just four years. Even tiny doses of Fentanyl can be deadly. Users often don’t know if their dose includes Fentanyl, and if so, how much.
What is opioid addiction treatment?
Opioid addiction treatment: Helps people who are addicted stop compulsive drug seeking and use. Varies depending the patient’s individual needs. Occurs in a variety of settings, takes many different forms, and can last for varying lengths of time. May save a life.
What are the consequences of using opioids?
Making mistakes at school or on the job because of using opioids. Hurting relationships with family and friends because of opioid use. Developing a tolerance and needing larger amounts of opioids to get high. Overdosing on drugs. Having strong cravings for opioids.
What is the purpose of a recovery plan for opioid addiction?
Medications for Opioid Addiction. A recovery plan that includes medication for opioid addiction increases the chance of success. Medications used in the treatment of opioid addiction support a person’s recovery by helping to normalize brain chemistry, relieving cravings, and in some cases preventing withdrawal symptoms.
How can treatment help with addiction?
Treatment for Addiction Can Help. Addiction is treatable and can be successfully managed. Treatment can help people struggling with opioid addiction get their lives back on track by allowing them to counteract addiction’s powerful effects on their brain and behavior. The overall goal of treatment is to return people to productive functioning in ...
How do you know if you are addicted to opioids?
Signs of Opioid Addiction. When using opioids has caused issues like job loss, money problems, or other hardships, a person’s continued use is a major warning sign of addiction. Other signs could also include: alert icon. Trying to stop or cut down on opioid use but not being able to. times circle icon.
Is opioid addiction a cure?
Manages the disease, is usually not a cure. Should be ongoing and should be adjusted based on how the patient responds. Needs to be reviewed often and modified to fit the patient’s changing needs. Evidence-based approaches to treating opioid addiction include medications and combining medications with behavioral therapy.
Is addiction a relapsing disease?
Talk with a doctor to find out what types of treatments are available in your area and what options are best for you and/or your loved one. Addiction is a chronic, relapsing disease; be sure to ask your doctor about the risk of relapse and overdose.
How many opioid deaths in 2019?
Opioids were involved in nearly 50,000 deaths in 2019, 12 which was over six times the number of opioid-involved overdose deaths in 1999. 1. The rate of drug overdose deaths involving opioids remains high, and CDC continues to track opioid overdose deaths. The graph below shows rates of overdose deaths associated with three categories of opioids, ...
How many people died from opioid overdoses in 2019?
Nearly 500,000 people died from overdoses involving any opioid, including prescription and illicit opioids, from 1999-2019. 1. This rise in opioid overdose deaths can be outlined in three distinct waves. The first wave began with increased prescribing of opioids in the 1990s, with overdose deaths involving prescription opioids ...
What are the waves of opioid overdose?
The findings show three distinct but interconnected waves that are driving America’s opioid overdose epidemic: an increase in deaths from prescription opioid overdoses since the 1990s, an increase in heroin deaths starting in 2010, and a more recent surge in deaths from IMF, including fentanyl analogs. 1,4. Data Sources.
What are the four categories of opioids?
CDC’s Injury Center looks at deaths and nonfatal overdoses for four categories of opioids: Natural opioids (including morphine and codeine) and semi-synthetic opioids (drugs like oxyco done, hydrocodone, hydromorphone, and oxymorphone) Methadone, a synthetic opioid. Synthe tic opioids other than methadone (drugs like tramadol and fentanyl)
When did the third wave of opioids start?
The third wave began in 2013, with significant increases in overdose deaths involving synthetic opioids, particularly those involving illicitly manufactured fentanyl. 4,5,6 The market for illicitly manufactured fentanyl continues to change, and it can be found in combination with heroin, counterfeit pills, and cocaine. 7.
Is methadone a synthetic opioid?
Methadone, a synthetic opioid. Synthetic opioids other than methadone (drugs like tramadol and fentanyl) Heroin, an illicit (illegally made) opioid synthesized from morphine that can be a white or brown powder, or a black sticky substance.
How many people overdosed on opioids in 2019?
In response to the opioid epidemic, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) officially declared a public health emergency in 2017. 49,860 people overdosed on opioids in 2019. 3.8% of American adults abuse opioids each year. At least 71.8% and as many as 80% of overdose deaths involve opioids.
How much does opioid abuse cost?
Up to 92% of opioid abusers use prescription opioids at least once in a year. Prescription opioid abuse costs $78.5 billion annually in the form of healthcare, legal programs, and lost productivity. Prescription opioids are a factor in 32% of opioid overdose deaths.
What are the two natural opioids?
Natural opioids include morphine and codeine. Semi-synthetic opioids include oxycodone, hydrocodone, hydromorphone, and oxymorphone. Methadone is a synthetic opioid that is usually categorized on its own in official data. Synthetic opioids other than methadone include tramadol and fentanyl.
How many Hispanic teens use opioids?
3.4% of Hispanic or Latino teenagers aged 12 to 17 misuse opioids in a year. Teenagers who legitimately use prescribed opioids are 33% more likely to misuse opioids after high school. 112,000 12- and 13-year-olds used opioids in 2019, a 12.5% decline from the previous year.
Which state has the highest opioid overdose rate?
Wyoming and Utah both have the highest rate of opioid overdose involving prescription opioids at 70%. Rhode Island has the lowest rate of overdose involving heroin at 9%. Washington D.C. and Vermont have the highest rates of overdose involving heroin at 66.5% and 53.5%, respectively.
How long does a patient have to participate in the opioid study?
Patients will be asked to participate in the study for two years.
What are the outcomes of methadone treatment?
outcomes associated with treatment using methadone, buprenorphine, or naltrexone, as well as counseling without medication, treatment program factors associated with positive outcomes, patient characteristics associated with positive outcomes, and. health-related quality of life for patients.
What is the treatment for OUD?
One common treatment option for OUD is medication-assisted treatment (MAT), a treatment combining the use of medications (methadone, buprenorphine, or naltrexone) with counseling and behavioral therapies.
How Many People Around the World Struggle With Opioid Addiction?
Opioid use disorder (OUD), or opioid addiction and abuse, is one of the most serious health crises not only in the United States, but around the world.
The Opioid Abuse Problem in the United States
The opioid abuse and overdose epidemic is considered to have begun in 1999, when prescribing practices around opioid painkillers changed, leading to higher levels of misuse and addiction. In the 20 years between 1999 and 2019, half a million people died from drug overdoses associated with prescription narcotics.
Treatment: The Struggle for Access & Better Data
Globally, health organizations like the CDC, WHO, NIDA, and others are working to adjust opioid prescribing practices and make addiction treatment more accessible.
Relapse Does Not Mean Treatment Has Failed
One study reports that the majority of people who undergo treatment for opioid addiction relapse within one year after completing rehabilitation. The study found that the most reported reason for relapsing back into substance abuse patterns was the desire to feel good.
