
When asked how long it would take someone to clinically recover from the Ebola virus, Dr. Lahey
The Hague
The Hague is a city on the western coast of the Netherlands and the capital of the province of South Holland. It is also the seat of government of the Netherlands.
Full Answer
What is the treatment for Ebola?
Nov 05, 2019 · Recovery from Ebola Recovery from EVD depends on good supportive care and the patient’s immune response. Investigational treatments are also increasing overall survival. Those who do recover develop antibodies that can last 10 years, possibly longer. Survivors are thought to have some protective immunity to the type of Ebola that sickened them.
How long does it take to recover from Ebola?
May 10, 2022 · When asked how long it would take someone to clinically recover from the Ebola virus, Dr. Lahey stated that you could expect a few week recovery time. It generally takes one to two weeks for symptoms of the disease to appear, on average, and from that point death generally occurs within a couple of weeks.
How long does it take to test for Ebola?
Ebola causes fever, pain, diarrhea and bleeding. It has occurred in Central and West Africa but can be carried and spread by travelers from this region. The largest outbreaks occurred in 2014-2016 mostly in Liberia, Guinea and Sierra Leone. On average, 50% …
What is the incubation period for Ebola?
A single dose of mAb114 fully protects non-human primates five days after lethal Ebola virus infection, and results from a Phase 1 clinical trial of mAb114 indicated the investigational treatment is safe. ZMapp NIAID supported the early development and preclinical testing of ZMapp, a "cocktail" of three different monoclonal antibodies.
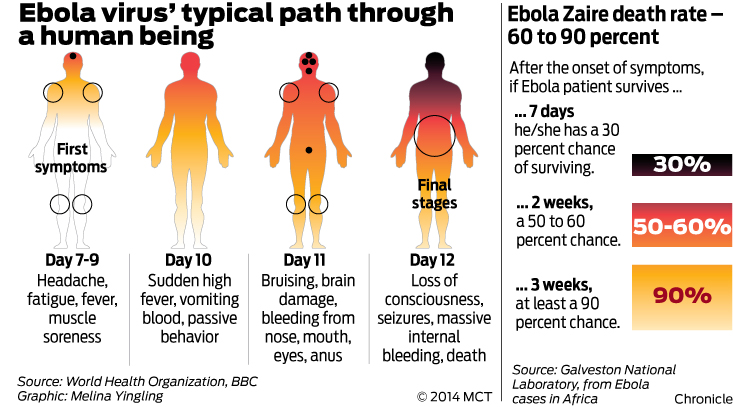
How long did it take to make a cure for Ebola?
How long does the Ebola illness last?
Is Ebola treatable or curable?
Is there a cure for Ebola 2021?
Is there vaccine for Ebola?
Is Ebola worse than Covid?
What is the most effective treatment for Ebola?
Why is there no treatment for Ebola?
Recovery from Ebola
Recovery from EVD depends on good supportive care and the patient’s immune response. Investigational treatments are also increasing overall survival.
Health Concerns for Survivors of Ebola
In most cases, people who have completely recovered from EVD do not become reinfected. However, many survivors suffer from health issues after recovery from Ebola.
Persistence of Ebola Virus
The virus can remain in areas of the body that are immunologically privileged sites after acute infection. These are sites where viruses and pathogens, like the Ebola virus, are shielded from the survivor’s immune system, even after being cleared elsewhere in the body.
How long does it take for Ebola to spread?
The Ebola virus is transmitted by direct contact with infected blood, bodily fluids and tissue of infected people or animals (alive or dead) and with an incubation period of as little as two days (or as many as 21), people remain infections as long as their blood and fluids contain the virus. With no known cure (several are in testing) ...
Is there a cure for a syphilis?
With no known cure (several are in testing) for the disease, the only treatments available are labeled as “ supportive intensive care ” and are administered to treat the symptoms and provide some small level of comfort.
How long does it take to recover from a symtom?
It generally takes one to two weeks for symptoms of the disease to appear, on average, and from that point death generally occurs within a couple of weeks. If you are lucky enough to survive, after this few week period you could be considered as recovered.
What is the first treatment for Ebola?
In October 2020, the FDA approved the first treatment for Ebola. The new medication, Inmazeb™, combines three antibodies (atoltivimab, maftivimab and odesivimab-ebgn). Patients who take Inmazeb have a higher chance of survival. Healthcare providers treat Ebola virus symptoms to improve the chance of survival.
What are the symptoms of Ebola?
Ebola symptoms include fever, pain and bleeding. Treatment improves the chance of survival. Overview. Symptoms and Causes. Diagnosis and Tests. Management and Treatment. Prevention. Outlook / Prognosis. Living With.
How does Ebola spread?
Ebola virus disease, or EVD, is a rare but deadly disease. It spreads from person to person through infected body fluids. Ebola symptoms include fever, pain and bleeding. Treatment improves the chance of survival.
Is Ebola contagious?
It is rare, very contagious (easily spread to others) and often deadly illness which spreads through contact of infected body fluids (from a sick person or from objects contaminated with body fluids, even door knobs). Ebola causes fever, pain, diarrhea and bleeding.
Where did the Ebola virus occur?
It has occurred in Central and West Africa but can be carried and spread by travelers from this region. The largest outbreaks occurred in 2014-2016 mostly in Liberia, Guinea and Sierra Leone. On average, 50% of people who get Ebola virus disease die.
How many people die from Ebola?
On average, 50% of people who get Ebola virus disease die. Medication and the treatment of symptoms improve the chance of survival. Controlling outbreaks helps keep the Ebola virus from spreading. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
What is the cause of Ebola?
Ebola is caused by a virus from the group of viral hemorrhagic fever (VHF) viruses (Marburg virus is another). Infection occurs by direct contact with infected body fluids - blood, diarrhea, saliva (“spit”), mucus (“snot”), urine (“pee”), vomit (“puke”), breast milk or semen from an infected person or animal (bat, monkey or ape).
Where is mAb114 from?
mAb114. mAb114 is a monoclonal antibody that was isolated from a survivor of the 1995 Ebola epidemic in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It was discovered by researchers at NIAID's Vaccine Research Center (VRC), in collaboration with the INRB in the DRC. VRC initially developed and manufactured the mAb114 antibody product, ...
What is ZMapp antibody?
NIAID supported the early development and preclinical testing of ZMapp, a "cocktail" of three different monoclonal antibodies. The antibodies bind to three different regions of the glycoprotein of the Ebola virus, inhibiting viral replication. During initial experiments, the antibodies were produced in tobacco plants specifically bioengineered ...
Who makes mAb114?
VRC initially developed and manufactured the mAb114 antibody product, which has now been licensed to Ridgeback Biotherapeutics for advanced development. mAb114 binds to an extremely conserved region on the Ebola virus (specifically the Zaire virus species), thus blocking its interactions with a receptor on human cells.
Where do antibodies bind to?
The antibodies bind to three different regions of the glycoprotein of the Ebola virus, inhibiting viral replication. During initial experiments, the antibodies were produced in tobacco plants specifically bioengineered to produce large quantities of the proteins.
What is BCX4430?
BCX4430 (also known as galidesivir) developed by BioCryst Pharmaceuticals with support from NIAID, is an investigational small molecule drug with broad spectrum antiviral activity, including against Ebola. BCX4430 has protected animals against infection with Ebola and Marburg viruses, and clinical study of BCX4430 is ongoing
Is there a cure for Ebola?
There's no cure for Ebola, though researchers are working on it. There are two drug treatments which have been approved for treating Ebola. Inmazeb is a mixture of three monoclonal antibodies (atoltivimab, maftivimab, and odesivimab-ebgn). Ansuvimab-zykl (Ebanga) is a monoclonal antibody given as an injection.
How long does it take for Ebola to show up?
Early on, Ebola can feel like the flu or other illnesses. Symptoms show up 2 to 21 days after infection and usually include: As the disease gets worse, it causes bleeding inside the body, as well as from the eyes, ears, and nose. Some people will vomit or cough up blood, have bloody diarrhea, and get a rash.
What are the symptoms of Ebola?
Doctors manage the symptoms of Ebola with: 1 Fluids and electrolytes 2 Oxygen 3 Blood pressure medication 4 Blood transfusions 5 Treatment for other infections
What is the drug used to treat Ebola?
Inmazeb is a mixture of three monoclonal antibodies (atoltivimab, maftivimab, and odesivimab-ebgn). Ansuvimab-zykl (Ebanga) is a monoclonal antibody given as an injection.
How to avoid getting Ebola?
The best way to avoid catching the disease is by not traveling to areas where the virus is found. If you are in areas where Ebola is present, avoid contact with bats, monkeys, chimpanzees, and gorillas since these animals spread Ebola to people. You may be able to get the vaccine from the World Health Organization.
How do you know if you have Ebola?
Early on, Ebola can feel like the flu or other illnesses. Symptoms show up 2 to 21 days after infection and usually include: 1 High fever 2 Headache 3 Joint and muscle aches 4 Sore throat 5 Weakness 6 Stomach pain 7 Lack of appetite
How many people contracted Ebola?
After listening to many experts discuss Ebola, after seeing on television the devastation of men, women, and children in Africa, and after listening to a few success stories about patients who survive this terrible disease, I believe there is evidence that some simple methods may be effective in slowing and/or stopping Ebola now.
What is a serum treatment for Ebola?
Dr. Kent Brantly is an American Ebola survivor who was treated in the U.S. and produces antibodies to the infection. These antibodies appear to be effective in reducing or completely blocking Ebola virus particles from reproducing by apparently blocking the virus from entering susceptible cells.
Can we stop Ebola?
In my opinion, this approach to Ebola treatment seems very possible to try; if it works, the ongoing crisis in Africa may be reduced or stopped. Its success would depend upon surviving patients willing to donate their blood, accurate blood typing, and the willingness of Ebola-infected patients to try this experimental therapy.
What to do if you have Ebola?
Avoid contact with other people’s blood and body fluids. Do not handle items that may have come in contact with an infected person’s blood or body fluids (like clothes, bedding, or needles). Avoid funeral or burial rituals that require handling the body of someone who has died from Ebola.
How long does it take for Ebola to show symptoms?
The incubation period for Ebola, from exposure to when signs or symptoms appear, can be anywhere from 2 to 21 days. The average is 8 to 10 days.
Where did Ebola originate?
Ebola is a rare and deadly disease that was first discovered near the Ebola River in what is now the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Since then, outbreaks have occurred sporadically in several African countries. Scientists believe that Ebola outbreaks start when a person is infected through contact with an infected animal, such as a fruit bat or primate (monkeys and apes). The disease can then spread from person to person through contact with infected blood or body fluids. Healthcare workers as well as family and friends in close contact with sick Ebola patients are at the highest risk of getting Ebola because they may come in contact with infected body fluids.
How does Ebola spread?
The disease can then spread from person to person through contact with infected blood or body fluids.
Does the CDC collect PII?
CDC does not collect Personally Identifiable Information (PII) when you use its digital media from your computer or mobile device unless you choose to provide that information to us.
Do third party sites share information?
Users of third-party sites often share information with the general public, user community, and/or the third-party operating the site. Consequently, you should review the privacy policies of third-party sites before using them and ensure that you understand how your information may be shared and used.
What is the age limit for a child to use a COPPA?
The Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) external icon governs information gathered online from or about children under the age of 13. Verifiable consent from a child’s parent or guardian is required before collecting, using, or disclosing personal information from a child under age 13.
