
Medication
- Fever (may be high when osteomyelitis occurs as the result of a blood infection)
- Pain and tenderness in the affected area
- Irritability in infants who can’t express pain
- Feeling ill
- Swelling of the affected area
- Redness in the affected area
- Warmth in the affected area
- Difficulty moving joints near the affected area
- Difficulty bearing weight or walking
Procedures
What Happens If Osteomyelitis Is Left Untreated?
- Osteomyelitis A patient will notice osteomyelitis first at the site of their wound or trauma site. ...
- Necrosis Necrosis is cell death triggered by infection, trauma, lack of blood supply, or a combination of several conditions. ...
- Sepsis
Self-care
To analyze characteristics and treatment of osteomyelitis (OM) in the treatment of grade IV pressure injury (PI) in patients with spinal cord injury/disorder (SCI/D) following the Basel Decubitus Concept. Because the variety of patients concerning SCI/D ...
Nutrition
How Long Does Osteomyelitis Last? Most people with osteomyelitis feel better within a few days of starting treatment. IV antibiotics often are switched to oral form in 5 to 10 days. People usually get antibiotics for at least a month, and sometimes longer depending on symptoms and blood test results.
What is the life expectancy of someone with osteomyelitis?
What happens if osteomyelitis is left untreated?
Is there a cure for osteomyelitis?
How long should osteomyelitis last?
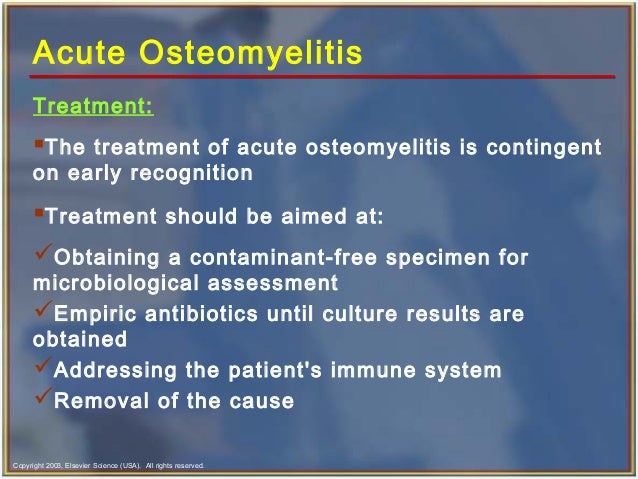
How long does it take for osteomyelitis to clear up?
You'll usually take antibiotics for 4 to 6 weeks. If you have a severe infection, the course may last up to 12 weeks. It's important to finish a course of antibiotics even if you start to feel better. If the infection is treated quickly (within 3 to 5 days of it starting), it often clears up completely.
How long do you need IV antibiotics for osteomyelitis?
Parenteral antibiotic therapy Formerly, experts usually recommended an intravenous (IV) therapy for 4 to 6 weeks followed by an oral course of additional weeks or months.
What is the best treatment for osteomyelitis?
Most people with osteomyelitis are treated with antibiotics, surgery, or both. Antibiotics help bring the infection under control and often make it possible to avoid surgery. People with osteomyelitis usually get antibiotics for several weeks through an IV, and then switch to a pill.
Does osteomyelitis require long term antibiotics?
Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis in children typically can be treated with a four-week course of antibiotics. In adults, the duration of antibiotic treatment for chronic osteomyelitis is typically several weeks longer. In both situations, however, empiric antibiotic coverage for S. aureus is indicated.
How long can you stay on IV antibiotics?
The optimal duration of intravenous antibiotic therapy is not clearly defined. Individuals usually receive intravenous antibiotics for 14 days, but treatment may range from 10 to 21 days. A shorter duration of antibiotic treatment risks inadequate clearance of infection which could lead to further lung damage.
How long does it take for antibiotics to work on a bone infection?
The infection may clear up faster if you start treatment within three to five days of first noticing symptoms. Treatments include: Antibiotics: Antibiotics kill infection-causing bacteria. You may need antibiotics for four to eight weeks, starting with intravenous (IV) antibiotics in the hospital for a week or two.
What is the strongest antibiotic for bone infection?
The classic antibiotic combination for bone infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus and P. aeruginosa is levofloxacin plus rifampicin. It is difficult to assess how long it will take for an infection to clear following the treatment of bone infection.
Can osteomyelitis be cured without surgery?
Non-surgical treatment of osteomyelitis requires a multidisciplinary team approach including primary care, infectious disease specialist care, nutritionist care and wound care. These wounds will require antibiotic therapy for a duration of six to eight weeks.
Can acute osteomyelitis be cured?
Although once considered incurable, osteomyelitis can now be successfully treated. Most people need surgery to remove areas of the bone that have died. After surgery, strong intravenous antibiotics are typically needed.
What are the chances of osteomyelitis returning?
Bone infection relapsed in 20.6% of the patients followed for more of one year, a slightly lower rate compared to that found in previous reports of adult osteomyelitis [6,7,8,9,10,11].
Does osteomyelitis require hospitalization?
The goal for treatment of osteomyelitis is to cure the infection and minimize any long-term complications. Treatment may include: Medications. Administration of intravenous (IV) antibiotics, which may require hospitalization or may be given on an outpatient schedule.
Can oral antibiotics cure osteomyelitis?
In a recent literature review by Spellberg et al. it was concluded that oral and parenteral antibiotic therapy have similar cure rates for the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis. Oral antibiotic therapy is associated with a lower risk to the patient due to avoiding the need of a central IV line.
Can you be on antibiotics for 6 weeks?
The mean duration of antibiotic treatment was 42 +/- 0.2 days and the mean clinical follow-up was 27 +/- 14 months. The treatment success rate was 91.5% (108/118). Six weeks of antimicrobial therapy appears to be effective for nearly all bone infections, regardless of the pathophysiology.
Are IV antibiotics better than oral?
Among physicians and patients alike, it is generally accepted that IV antibiotics are better than oral. They are stronger. They will work faster. They will save the day when oral antibiotics have failed.
Can you treat osteomyelitis with oral antibiotics?
The standard recommendation for treating chronic osteomyelitis is 6 weeks of parenteral antibiotic therapy. However, oral antibiotics are available that achieve adequate levels in bone, and there are now more published studies of oral than parenteral antibiotic therapy for patients with chronic osteomyelitis.
How long are you in the hospital for cellulitis?
For serious infections, treatment is usually started in hospital. You'll normally be given antibiotics directly into a vein through an injection or a drip. Many hospitals can then arrange for this treatment to continue at home or in an outpatient clinic. Treatment is usually for five days.
Who Is Affected by Osteomyelitis?
Osteomyelitis can affect both adults and children. The bacteria or fungus that can cause osteomyelitis, however, differs among age groups. In adult...
What Causes Osteomyelitis?
It can be caused by a variety of microbial agents (most common in staphylococcus aureus) and situations, including: 1. An open injury to the bone,...
What Are The Symptoms of Osteomyelitis?
The symptoms of osteomyelitis can include: 1. Pain and/or tenderness in the infected area. 2. Swelling, redness and warmth in the infected area. 3....
How long does osteomyelitis last?
Intravenous or oral antibiotic treatment for osteomyelitis may be very extensive, lasting for many weeks.
What are the long term complications of osteomyelitis?
Osteomyelitis requires long-term care to prevent further complications, including care to prevent the following: Fractures of the affected bone. Stunted growth in children (if the infection has involved the growth plate) Gangrene infection in the affected area.
What tests are done to check for osteomyelitis in children?
The provider treating your child will first do a thorough history and physical exam that may indicate signs of osteomyelitis like those listed above. An additional workup generally includes blood tests that look at white blood cells as well as markers for inflammation that are usually elevated during an infection.
What is the term for swelling of bone tissue?
Osteomyelitis is an inflammation or swelling of bone tissue that is usually the result of an infection. Bone infection may occur for many different reasons and can affect children or adults. Osteomyelitis may occur as a result of a bacterial bloodstream infection, sometimes called bacteremia, or sepsis, that spreads to the bone.
What is the term for inflammation of the bone?
Osteomyelitis is inflammation or swelling that occurs in the bone. It can result from an infection somewhere else in the body that has spread to the bone, or it can start in the bone — often as a result of an injury. Osteomyelitis is more common in younger children (five and under) but can happen at any age. Boys are usually more affected ...
How do you know if you have osteomyelitis?
The following are the most common symptoms of osteomyelitis; however, each individual may experience symptoms differently: Fever (may be high when osteomyelitis occurs as the result of a blood infection) Pain and tenderness in the affected area. Irritability in infants who can’t express pain. Feeling ill.
Can Osteomyelitis be a chronic disease?
This includes people with sickle cell disease or HIV or those receiving immunosuppressive medications like chemotherapy or steroids. Osteomyelitis can have a sudden onset, a slow and mild onset or may be a chronic problem, depending on the source of the infection. ViewMedica 8. Start Picture-in-Picture. Get Embed Code.
Why is it important to treat osteomyelitis?
The objective of treating osteomyelitis is to eliminate the infection and prevent the development of chronic infection. Chronic osteomyelitis can lead to permanent deformity, possible fracture, and chronic problems, so it is important to treat the disease as soon as possible.
What is osteomyelitis infection?
What is osteomyelitis? Osteomyelitis is a bacterial, or fungal, infection of the bone. Osteomyelitis affects about 2 out of every 10,000 people. If left untreated, the infection can become chronic and cause a loss of blood supply to the affected bone.
What is the disease that can cause bone tissue death?
Osteomyelitis. Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone that can affect both adults and children. If left untreated, it can lead to bone tissue death over time. Appointments 216.444.2606. Appointments & Locations. Contact Us. Overview. Symptoms and Causes. Diagnosis and Tests.
How do you know if you have osteomyelitis?
The symptoms of osteomyelitis can include: Pain and/or tenderness in the infected area. Swelling, redness and warmth in the infected area. Fever. Nausea, secondarily from being ill with infection. General discomfort, uneasiness, or ill feeling. Drainage of pus (thick yellow fluid) through the skin.
Is osteomyelitis more common in the tibia or humerus?
They include the femur and tibia in the legs and the humerus and radius in the arms. Osteomyelitis is not more common in a particular race or gender. However, some people are more at risk for developing the disease, including: People with diabetes. Patients receiving hemodialysis.
Can osteomyelitis affect children?
In adults, osteomyelitis often affects the vertebrae and the pelvis. In children, osteomyelitis usually affects the adjacent ends of long bones.
Can you have surgery for spinal abscess?
In the case of spinal abscesses, surgery is not performed unless there is compression of the spinal cord or nerve roots. Instead, patients with spinal osteomyelitis are given intravenous antibiotics.
How long does it take for osteomyelitis to develop?
Symptoms of Osteomyelitis. Acute osteomyelitis develops rapidly over a period of seven to 10 days. The symptoms for acute and chronic osteomyelitis are very similar and include: Osteomyelitis in the vertebrae makes itself known through severe back pain, especially at night.
Why is it important to treat osteomyelitis early?
In cases of acute osteomyelitis, early treatment prevents the condition from becoming a chronic problem that requires ongoing treatment . Besides the pain and inconvenience of repeated infections, getting osteomyelitis under control early provides the best chance for recovery.
What is the cause of osteomyelitis?
In most cases, a bacteria called Staphylococcus aureus, a type of staph bacteria, causes osteomyelitis. Certain chronic conditions like diabetes may increase your risk for osteomyelitis.
How to prevent osteomyelitis?
Preventing Osteomyelitis. The best way to prevent osteomyelitis is to keep things clean. If you or your child has a cut, especially a deep cut, wash it completely.
What is the disease of the bone?
Osteomyelitis. By Joanne Barker. Medically Reviewed by Jennifer Robinson, MD on May 11, 2019. Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone, a rare but serious condition. Bones can become infected in a number of ways: Infection in one part of the body may spread through the bloodstream into the bone, or an open fracture or surgery may expose ...
How many people get osteomyelitis?
Only 2 out of every 10,000 people get osteomyelitis. The condition affects children and adults, although in different ways. Certain conditions and behaviors that weaken the immune system increase a person's risk for osteomyelitis, including: Diabetes (most cases of osteomyelitis stem from diabetes) Sickle cell disease.
Can osteomyelitis be chronic?
In adults, osteomyelitis can be either acute or chronic. People with diabetes, HIV, or peripheral vascular disease are more prone to chronic osteomyelitis, which persists or recurs, despite treatment. Whether chronic or acute, osteomyelitis often affects an adult's pelvis or vertebrae of the spine.
How is osteomyelitis managed?
Osteomyelitis is best managed by a multidisciplinary team. It requires accurate diagnosis and optimization of host defenses, appropriate anti-infective therapy, and often bone débridement and reconstructive surgery.
How to treat osteomyelitis?
Treating osteomyelitis: antibiotics and surgery. Osteomyelitis is best managed by a multidisciplinary team. It requires accurate diagnosis and optimization of host defenses, appropriate anti-infective therapy, and often bone débridement and reconstructive surgery.
Can osteomyelitis be chronic?
It can affect all ages and involve any bone. Osteomyelitis may become chronic and cause persistent morbidity. Despite new imaging techniques, diagnosis can be difficult and often delayed. Because infection can recur years after apparent "cure," "remission" is a more appropriate term.
What causes osteomyelitis in children?
Osteomyelitis may result from hematogenous bacterial emboli from a distant source lodging in the bone, the contiguous spread of an adjoining soft-tissue infection, or direct bacterial inoculation secondary to trauma or surgery. Hematogenous osteomyelitis most commonly occurs in children, and it usually is caused by a single organism, ...
What is the most common cause of hematogenous osteomyelitis?
Hematogenous osteomyelitis most commonly occurs in children, and it usually is caused by a single organism, Staphylococcus aureus. Adults are most commonly affected by contiguous-spread osteomyelitis, and many infections occur in adults with vascular insufficiency.
How to treat osteomyelitis?
What are the treatments for osteomyelitis? There are several options your doctor may use to treat your bone infection. Antibiotics may be all that’s necessary to cure your bone infection. Your doctor may administer the antibiotics intravenously, or directly into your veins, if the infection is severe.
How long do you have to take antibiotics for a bone infection?
You may need to take the antibiotics for up to six weeks. Sometimes bone infections require surgery. If you have surgery, your surgeon will remove the infected bone and dead tissue and drain any abscesses, or pockets of pus.
What is bone infection?
What is a bone infection (osteomyelitis)? A bone infection, also called osteomyelitis, can result when bacteria or fungi invade a bone. In children, bone infections most commonly occur in the long bones of the arms and legs. In adults, they usually appear in the hips, spine, and feet. Bone infections can happen suddenly or develop ...
What to do if a wound does not heal?
If a wound/cut does not look like it is healing with home treatment, contact your doctor immediately to have it examined. Clean and dry amputation sites before placing your prosthesis. Also, use the proper footwear and protective equipment to avoid injuries when jumping, running, or participating in sports.
Is osteomyelitis a treatable condition?
Most cases of osteomyelitis are treatable. Chronic infections of the bone, however, may take longer to treat and heal, especially if they require surgery. Treatment should be aggressive because an amputation can become necessary sometimes. The outlook for this condition is good if the infection is treated early.
Can a staph infection spread to bones?
Many organisms, most commonly Staphylococcus aureus, travel through the bloodstream and can cause a bone infection. An infection may begin in one area of the body and spread to the bones via the blood stream. Organisms that invade a severe injury, deep cut, or wound can also cause infections in nearby bones. Bacteria can enter your system ...
