Medication
You typically undergo radiation therapy for anal cancer for five or six weeks. Chemotherapy is typically administered during the first week and the fifth week. Your doctor tailors your treatment schedule based on characteristics of your cancer and your overall health.
Procedures
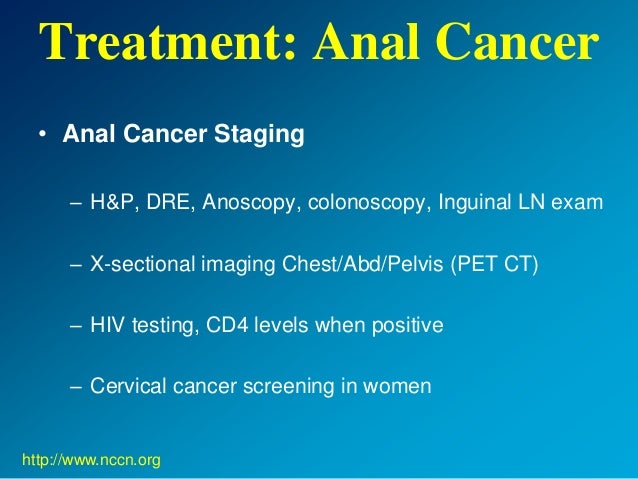
The following stages are used for anal cancer: Stage 0 Stage I Stage II Stage III Stage IV 1 Stage 0 2 Stage I 3 Stage II 4 Stage III 5 Stage IV
Therapy
Although anal cancer is primarily treated with chemotherapy and radiation protocols, there may be times when surgery is employed. Although uncommon, surgery can be used for early-stage anal cancer when the tumor is extremely small and localized. Your provider may refer to this type of cancer as superficially invasive.
Nutrition
The standard of care to treat anal cancer stages I-III is combined chemoradiation therapy, otherwise known as the ‘Nigro Protocol’. The standard of care to treat stage IV anal cancer is chemotherapy. Surgery is less commonly used for the primary treatment of anal cancer.
How long does it take to get rid of anal cancer?
What are the stages of anal cancer treatment?
Can surgery be used to treat anal cancer?
What is the standard of care for anal cancer?

How long is chemo for anal cancer?
The chemo is usually 5-FU with mitomycin. This combination of chemo is typically given during the first week and around the fifth week of treatment. The EBRT is given daily, Monday through Friday, for 5 to 7 weeks. If the cancer hasn't gone away completely after chemoradiation is done, more treatment might be needed.
Is anal cancer highly treatable?
When it is found early, anal cancer is highly treatable. The overall five-year survival rate following diagnosis of anal cancer is 64%.
How long does radiation therapy last for anal cancer?
You typically undergo radiation therapy for anal cancer for five or six weeks. Chemotherapy is typically administered during the first week and the fifth week. Your doctor tailors your treatment schedule based on characteristics of your cancer and your overall health.
How do doctors treat anal cancer?
Doctors usually treat anal cancer with a combination of chemotherapy and radiation. Together, these two treatments enhance each other and improve chances for a cure. Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy drugs are injected into a vein or taken as pills.
What is AP resection?
If your cancer hasn't responded to chemotherapy and radiation, your doctor may recommend a more extensive operation called abdominoperineal resection , which is sometimes referred to as an AP resection. During this procedure the surgeon removes the anal canal, ...
How does immunotherapy work?
Immunotherapy uses your immune system to fight cancer. Your body's disease-fighting immune system may not attack your cancer because the cancer cells produce proteins that make them undetectable by the immune system cells. Immunotherapy works by interfering with that process.
What is stage IV cancer?
By stage IV, the cancer has spread to distant areas of the body. The cancer staging system continues to evolve and is becoming more complex as doctors improve cancer diagnosis and treatment. Your doctor uses your cancer stage to select the treatments that are right for you.
What is the best way to kill cancer cells?
Radiation therapy. Radiation therapy uses high-powered beams, such as X-rays and protons, to kill cancer cells. During radiation therapy, you're positioned on a table and a large machine moves around you, directing radiation beams to specific areas of your body to target your cancer.
What type of test is used to determine the stage of cancer?
Tests may include: Computerized tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Positron emission tomography (PET) Your doctor uses the information from the procedures to assign your cancer a stage.
What are the services offered by the American Cancer Society?
These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help. The American Cancer Society also has programs and services – including rides to treatment, lodging, and more – to help you get through treatment.
What is important when choosing a cancer treatment plan?
In choosing your treatment plan, you and your cancer care team will also take into account your age, your overall health, and your personal preferences.
What happens after cancer is found?
A key goal of treatment is to save the muscles of the anal sphincter so you can control your bowels and stool so your overall quality of life is not affected. Your treatment options depend on many factors.
Why is it important to discuss all treatment options with your doctor?
It’s important to discuss all treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decision that best fits your needs. You may feel that you need to make a decision quickly, but it’s important to give yourself time to absorb the information you have learned. Ask your cancer care team questions.
What is the difference between a medical oncologist and a surgical oncologist?
A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with medicines such as chemotherapy and immunotherapy. A surgical oncologist: a doctor who uses surgery to treat cancer. A colorectal surgeon: a doctor who uses surgery to treat diseases of the colon, rectum, and anus. You might have many other specialists on your treatment team as well, ...
Why are clinical trials important?
Clinical trials are one way to get state-of-the art cancer treatment. In some cases they may be the only way to get access to newer treatments. They are also the best way for doctors to learn better methods to treat cancer. Still, they're not right for everyone.
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
How long does radiation treatment last for anal cancer?
For individuals with anal cancer stages I-III, radiation is typically 5 days a week for 5 to 6 weeks. Individuals with stage IV or recurrent cancer may receive radiation in locations where the cancer has spread.
How often is chemo given for anal cancer?
For these individuals, chemotherapy is typically administered twice, once at the beginning of radiation and then again at 5 weeks of radiation.
What is the protocol for anal cancer?
The standard protocols for treating anal cancer are listed in the NCCN guidelines and on the NHS website (UK). For stages I – III, radiation and chemotherapy are the standard protocol and are usually used in conjunction with one another (often called 'chemoradiation').
What happens if you have anal cancer after surgery?
If the tests after surgery show that anal cancer is still present, the patient will undergo further treatment , which may include another excision or chemotherapy and radiation.
How old is anal melanoma?
Anal melanoma is quite rare, and is mostly found in older adults, aged 60-80. Anal melanoma follows the treatment protocols for melanoma. As with other types of anal cancer, treatment will depend on the staging and position of the cancer, and your overall health and wellness.
How many people will have anal cancer in 2020?
Anal cancer is considered uncommon, with an incidence rate in the US of 1.8 in 100,000 people. In 2020, around 8,600 people were predicted to be diagnosed with anal cancer in the US and 1,600 people in the UK.
What is the treatment for stage IV cancer?
Your health status and ability to tolerate treatment are also taken into account when determining a course of action. Chemotherapy, radiation and surgery are usually prescribed in various combinations depending on your needs.
What is the treatment for recurrent anal cancer?
Treatment of recurrent anal cancer may include the following: Radiation therapy and chemotherapy, for recurrence after surgery. Surgery, for recurrence after radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy . A clinical trial of radiation therapy with chemotherapy and radiosensitizers. A clinical trial of chemotherapy options.
What is the treatment for cancer?
Substances made by the body or made in a laboratory are used to boost, direct, or restore the body's natural defenses against cancer. This type of cancer treatment is also called biotherapy or biologic therapy.
What is stage IV cancer?
In stage IV, the tumor is any size. Cancer may have spread to lymph nodes or nearby organs and has spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver or lungs .
How does chemo work?
Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping the cells from dividing. When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle, the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body ( systemic chemotherapy ).
What is radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing. There are two types of radiation therapy:
What is a treatment clinical trial?
A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer. When clinical trials show that a new treatment is better than the standard treatment, the new treatment may become the standard treatment.
What are the risk factors for anal cancer?
Risk factors for anal cancer include the following: Being infected with human papillomavirus (HPV). Having a condition or disease that causes a weakened immune system, such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) or an organ transplant. Having a personal history of vulvar, vaginal, or cervical cancers.
What to do if you have anal cancer?
If you have (or have had) anal cancer, you probably want to know if there are things you can do that might lower your risk of the cancer growing or coming back, such as exercising, eating a certain type of diet, or taking nutritional supplements.
Why do you see your doctor after anal cancer treatment?
After completing treatment for anal cancer, you should see your doctor regularly to look for any new symptoms or problems, because they could be caused by the cancer coming back or by a new disease or second cancer.
What is second cancer?
Cancer that comes back after treatment is called a recurrence. But some cancer survivors develop a new, unrelated cancer later. This is called a second cancer.
How long does cancer treatment last?
Almost any cancer treatment can have side effects. Some might only last for a few days or weeks to months, but others might last a long time . Some side effects might not even show up until years after you have finished treatment.
When should you follow up after chemo?
Close follow-up is very important in the first several months after chemoradiation treatment, especially if not all of the cancer is gone. Some tumors continue to shrink after chemoradiation, so the doctor will want to watch the cancer closely during this time to see if more treatment might still be needed.
Is anal cancer a non-Hodgkin lymphoma?
People diagnosed with anal cancer before age 50 also have an increased risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Anal cancer is linked to infection with human papilloma virus (HPV), and many of these cancers (cancers of the tongue, tonsil, cervix, vulva, and vagina) are also linked to HPV infection.
Can anal cancer be detected early?
Survivors of anal cancer should follow the American Cancer Society guidelines for the early detection of cancer, such as those for colorectal, breast, cervical, and prostate cancer. Screening tests can find some cancers early, when they are likely to be easier to treat.
How long do you live with anal cancer?
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time (usually 5 years) after they were diagnosed.
What is the relative survival rate of cancer?
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of cancer to people in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of anal cancer is 80%, it means that people who have that cancer are, on average, about 80% as likely as people who don’t have that cancer to live ...
Can cancer survival rates be predicted?
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they can’t predict what will happen in any particular person’s case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions.
How is anal cancer treated?
Anal cancers are most commonly treated with a combination of chemotherapy and radiation, which is discussed in further detail in the treatment section but can be expected to cause the tumors to completely regress in 80 to 90% of patients.
What is the best test for anal cancer?
Another test that is becoming more commonly used to stage anal cancers is an endoanal ultrasound.
What is the first step in determining how cancer should be treated?
Once a diagnosis of cancer is made from any site, one of the first steps done prior to determining how the cancer should be treated is to determine whether it is localized or has spread or metastasized either to nearby lymph nodes or to distant organs, a process known as staging a cancer.
What is the procedure to stage cancer?
Typically following a diagnosis, patients will have CAT scans of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis to stage their cancer. A CAT scan is a common x-ray procedure that in comparison to common x-rays of bones provides images of the internal organs and other structures such as blood ...
What is the stage of cancer?
The stage of a cancer is based on determining the T, N, and M for each tumor, which is then used to guide treatment and also provide an idea of the probability that the cancer can be cured or how effective the treatment is likely to be.
What is the staging system for cancer?
The American Joint Committee on Cancer has created a formal staging system for most cancers that is based on 3 criteria: T or tumor size and an assessment of invasion of nearby organs, N or whether or not the cancer has spread to local lymph nodes, and M , which denotes the absence or presence of metastases to distant organs. ...

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Alternative Medicine
Specialist to consult
Coping and Support
- Tests and procedures used to diagnose anal cancer include: 1. Examining your anal canal and rectum for abnormalities.During a digital rectal exam, your doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into your rectum. He or she feels for anything unusual, such as growths. 2. Visually inspecting your anal canal and rectum.Your doctor may use a short, lig...
Preparing For Your Appointment
- What treatment you receive for anal cancer depends on the stage of your cancer, your overall health and your own preferences.